Hello reader, when it comes to fluid, there are five different types of fluid and there are six different types of fluid flow. In this paper, we will study all the types in very detail.
You can download whole document in PDF format at the end.
So let’s start
What is Fluid?
The fluid is a substance that can flow in any direction. Example: Water (Water can flow in any direction).
Now moving to types of fluid,
Types of Fluid:
There are five different types of Fluid:
- Ideal fluid
- Real fluid
- Newtonian fluid
- Non-Newtonian fluid
- Ideal Plastic Fluid

Ideal fluid:
Ideal fluids are the fluids that can not have viscosity and also can’t be compressed is known as Ideal fluid. But the reality is this type of fluid does not exist. This fluid is also called as Imaginary fluid.
Note: Each and every fluid contains some amount of viscosity.
Real fluid:
The real fluid is just opposite to Ideal fluid. Real fluid can be defined as the fluid which is having viscosity is known as Real fluid.
Real fluids exist in nature. Or you can say whatever fluid in nature can be real fluid.
Newtonian fluid:
Here one term is very important Newton’s law of viscosity. The fluid that follows this newton’s law of viscosity called Newtonian fluid.
Non-Newtonian fluid:
The non-Newtonian fluid is just opposite to Newtonian fluid. Non-Newtonian fluid can be defined as the fluid that can not follow newton’s law of viscosity called Non-Newtonian fluid.
Ideal Plastic Fluid:
The Ideal Plastic fluid can be defined as shear stress is proportional to the shear strain and the value of shear stress is more than the yield value is known or called Ideal Plastic Fluid.
Now moving to types of fluid flow,
Types of Fluid Flow:
There are six types of fluid flow and those are:
- Steady and Unsteady flow
- Uniform and non-uniform flow
- One, two, and three-dimensional flow
- Rotational or Ir-rotational flow
- Laminar or Turbulent flow and
- Compressible or Incompressible flow.

Steady and Unsteady flow:
The steady flow is defined as the flow in which the velocity, pressure, and density are constant at any point with respect to time.
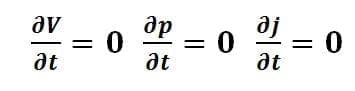
Whereas an unsteady flow is just oppostite to steady flow.
The unsteady flow is defined as the flow in which the velocity, pressure, and density are not constant and it is different with respect to time.
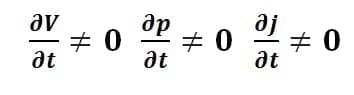
Uniform and non-uniform flow:
Uniform flow can be defined as the type of flow in which the velocity does not change with respect to space at any given time (I.e length of direction of the flow).

Nonuniform flow can be defined as the type of flow in which the velocity does change with respect to space at any given time (I.e length of direction of the flow).

One, two, and three-dimensional flow:
In one-dimensional fluid flow, the name itself indicates fluid is moving in only one dimension (Either X, Z, or Y).
u=f(x), v=0 and w=0
In two-dimensional fluid flow, the name itself indicates two the fluid is moving in two dimensions (Either XY, ZX, or YX).
u= f1(x,y,), v= f2(x,y,) and w= 0.
In three-dimensional fluid flow, the name indicates three the fluid is moving in three dimensions (Either XYZ, ZYX, or YZX).
u= f1(x,y,z), v= f2(x,y,z) and w= f3(x,y,z).
Rotational or Irrotational flow:
Rotational fluid flow is defined as in which the fluid particles move to streamline or along well-defined paths, which means the flow is straight and also rotates about its own axis is known as rational flow.
Irrational fluid flow is defined as in which the fluid particles move to streamline or along well-defined paths, but it does not rotate about its own axis is known as Irrational flow.
Laminar or Turbulent flow:
Laminar fluid flow is defined as in which the fluid particles move to streamline or along well-defined paths, which means the flow is straight and parallel is called Laminar Flow.
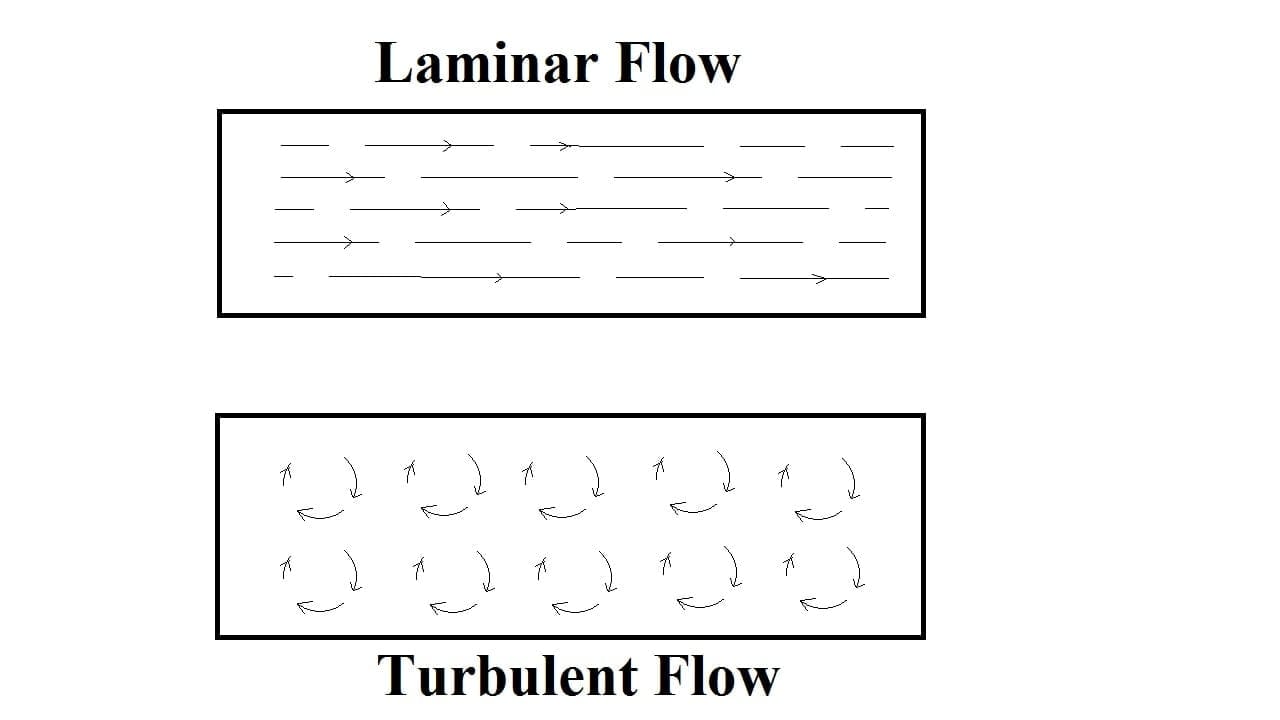
Turbulent fluid flow is defined as in which the fluid particles do not move streamline or along well-defined paths, It flows in a zig-zag way that means the flow is not straight and parallel, It is in a zig-zag way and it is called Turbulent Flow.
Compressible or Incompressible flow:
Compressible flow can be defined as the flow in which the density is not constant that means from point to point density is changing therefore it is known as compressible flow.
J ≠ constant
Incompressible flow can be defined as the flow in which the density is constant that means from point to point density is not changing therefore it is known as Incompressible flow.
J = constant
So Here we studied all the different types of fluid and fluid flow. Let me know which another topic you are looking for? till then do not forget to share on social media. Thank you and we will meet in another article.
Internal resources:
Impulse Turbine vs Reaction Turbine
Centrifugal vs Reciprocating pump
Reciprocating pump
Reference [External Links]:
- ScienceDirect Fluid flow
- Britannica turbulent flow





Discussion about this post