An Automobile can be defined as a vehicle that is self-propelled and is primarily used for the transportation of passengers and goods. Automobiles are commonly propelled using an internal combustion engine which is powered by a volatile fuel. The fuels used are generally Petrol, Diesel, CNG, Electricity, etc.
Nowadays, technological development has led to the use of electric power and hydrogen for powering vehicles.
An automobile is a complex technical system comprising many sub-systems with specific functions. Thousands of component parts have evolved with time creating a breakthrough in the existing technology.
The major subsystems include body, chassis, engine, drivetrain, control systems, and emission control systems.
Passenger cars take up a large part of automobiles used, with around 1.4 billion cars in operation worldwide and nearly 70 million new units built each year worldwide. The design of the vehicle depends to a large extent on its intended use.
History of Automobile:
Automobiles date back to 1672 with the invention of the steam-powered vehicle, which led to the creation of the first steam-powered automobile, built by Nicolas Cugnot in 1769.
Samuel Brown first tested the industrially applied internal combustion engine in 1826. German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz-Motorwagen in 1886. He developed a gasoline-powered vehicle and made several copies.
The 1901 Mercedes designed by Wilhelm Maybach and Gottlieb Daimler for Daimler Motoren Gesellschaft, is the first complete modern car in all essentials.
The thirty-five horsepower engine weighed only fourteen pounds per horsepower, and it achieved a top speed of fifty-three miles per hour. It was followed by the Ford Model T, created by the ford motor company in 1908, the first to be mass-produced on a moving assembly line.
William Durant founded General Motors in 1908. This led to cars becoming widely available in the market by the early 20th century. Ford, General Motors, and Chrysler emerged as the leading companies by 1920.
During the aftermath of the world war, production in Europe and Asia soared to meet the growing demands. With the rise of Japan as the leading automaker by 1980, the industry became a shared global enterprise.
Notable European and Asian producers include companies like BMW, Volkswagen, Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda.
Types or Classification of automobiles:
Automobiles can be classified into types based on various criteria. The following are the classification of automobiles:
#1. Based on the purpose of the vehicle:
Automobiles are classified on the purpose of the vehicle depending on whether the vehicle is used to carry passengers or used for transportation of goods or USD for any special purpose.
- Passenger vehicle – Car, bus, taxi, etc.
- Commercial vehicle – Trucks, tempos, containers, etc.
- Special purpose vehicle- Ambulance, fire brigade, police vehicle, etc.
#2. Based on the load-carrying capacity:
This classification is done on the basis of the load-carrying capacity of the vehicle. This also implies classification based on the motor and body of the vehicle.
- Light motor vehicle (LMV) – Car, Jeep, Minivan, etc.
- Medium motor vehicle (MMV) – Tempo, bus, mini truck, etc.
- Heavy motor vehicle (HMV) – Truck, trailer, container, tractor, multi-axle bus, etc.
#3. Based on the number of wheels:
The number of wheels used in a vehicle is also classified.
- Two-wheeler – Scooter, Motorcycle, etc.
- Three-wheeler – Autorickshaw.
- Four Wheeler – Car, jeep, mini van, tractor, etc.
- Six-wheeler – Bus, mini truck, etc.
- More than six wheels – Truck, trailer, container, multi-axle bus, etc.
#4. Based on the fuel used in the vehicle:
The fuel used is a very important component in terms of the classification of vehicles. Fuel plays a major role in the performance and efficiency standards of the vehicle.
Petrol – The system which uses petrol is called the Spark ignition system. The octane number of petrol decides the anti-knock, performance, and efficiency factor. Generally, the octane numbers available are 87, 89, and 91-93. Mostly used in passenger vehicles and two-wheelers.
Diesel – The system is called a Compression ignition system. The cetane number of diesel decides the compression and fuel needed for ignition. Generally, the cetane numbers range from 45 to 55. Mostly used in commercial and heavy vehicles.
CNG – Compressed natural gas in another form of fuel used as an alternative to petrol. The advantage is that it produces less toxic emissions from the vehicle and the disadvantage is that it reduces the performance of the vehicle as compared to that of petrol. These are mostly used in public transportation vehicles and passenger cars.
Electric – Electric vehicle is relatively a new technology used as an alternative to combustible fuels. These vehicles use electricity as fuel from the high-capacity battery.
Hydrogen – The hydrogen fuel cell is an upcoming invention in the automobile industry which is currently in full swing research. It is expected to provide a safer and more economical route for the automobile industry.
#5. Based on the transmission system of the vehicle:
Automobiles can be classified into three types based on the transmission system. They are the following:
Manual transmission system – This system uses a frictional clutch attached to the driving shaft. The linkage between the fictional clutch and flywheel is used to clutch and declutch the transmission.
Automatic Transmission system – A torque converter is used to transmit rotational energy in this system. The gear changes are controlled by the computer systems in the automobile which uses planetary gears, clutches, and brakes.
Semi-automatic transmission system – It can be referred to as a hybrid of automatic and manual transmission systems. The input is manual and the output is automated in this system, the only difference being the absence of a manual clutch.
Continuously variable transmission (CVT) – In CVT transmission, the push belt transfers torque from one pulley to another. This is used to smoothly change the gears.
#6. Based on the power source of the vehicle:
The power supply of an automobile is an important factor and the classification of power supply used in automobiles is the following:
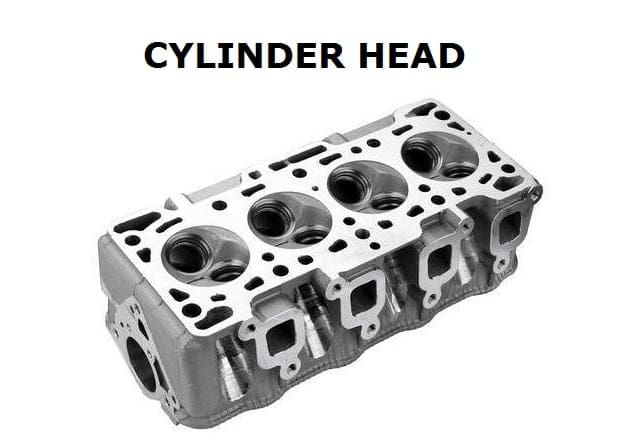
Internal combustion engine (ICE) – As the name suggests, IC engines use combustible fuel for power generation in the engine. It consists of parts such as an intake manifold, intake valve, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, flywheel, exhaust manifold, exhaust valve, and spark plug (only in petrol engines).
Electric battery (EV) – These vehicles use one or more electric motors for propulsion instead of an IC engine. The electricity is supplied by the high voltage batteries present in these vehicles. These vehicles are currently on a high rise in the market as a solution to the rising pollution, global warming, depleting natural resources, etc.
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicle (FCEV) – Hydrogen fuel cell is the next-gen technology that uses hydrogen as fuel. HFEV is considered a permanent replacement for combustible fuels as hydrogen resources are available in abundance. The reaction is hydrogen with oxygen is used to produce power which is used to run the motor. The exhaust of the system is in the form of water vapor.
#7. Based on the suspension system of the vehicle:
The suspension system decides the load distribution and comfort level of the vehicle. Vehicles are categorized on the basis of suspension systems as follows:
Independent Suspension system – In this type of system, only the wheel under load adjusts its position and there is zero to little effect on the opposite wheel. It is generally used for the front axle. Examples are Mac person strut, wishbone, etc.
Non-independent or rigid suspension system – In this type of system, when one wheel is in contact with any bump or uneven road the other one will also change its position and may tilt or move upwards or downwards. This is mostly used in heavy vehicles.
Air suspension system – Airbags fed with air are used as shock absorbers in this type of system. Compressed air under the pressure of around 5.6-7 kg/sq.m is used with the help of the air compressor in the suspension system.
Pneumatic air suspension system- This system is an electrically controlled air suspension system. It consists of an electronic control unit (ECU) that feeds and releases the air pressure inside the airbags according to the bumps or uneven surfaces. It also consists of a motor that runs the control unit and air compressor.
#8. Based on the wheel drive of the vehicle:
Wheel drive of a vehicle implies the axle of the vehicle which is used for the driveshaft. The driver shaft transmits the power of the vehicle from the engine to the wheels. These are classified as follows:
Front-wheel drive (FWD) – As the name suggests, the propeller shaft is connected to the front axle and it’s used as the driver shaft of the vehicle. The front wheels rotate and move the vehicle. Front-wheel drive has better traction and efficiency than rear-wheel drive as the vehicle is more weighted at the front.
Rear-wheel drive (RWD) – In rear-wheel drive, the propeller shaft is connected to the rear axle and the rear wheels of the vehicle rotate. These types of vehicles have better stability and cornering control as the front wheels are used for the sole purpose of steering and it has less effect on the front wheels.
All-wheel drive (AWD) – In all-wheel drive, the propeller shaft is attached to both the axles of the vehicle. All the wheels in the vehicle rotate with the power distributed equally. These types of vehicles utilize the maximum power of the engine.
#9. Based on the drive end of the vehicle:
Vehicles are also classified based on the position of the steering system. It consists of two types:
Right-hand drive – The vehicles which have the steering system on the right side of the car are right-hand drive vehicles. These vehicles have steering on the right and move on the left side of the road.
Left-hand drive – The vehicles which have the steering system on the left side of the car are left-hand drive vehicles. These vehicles have steering on the left and move on the right side of the road.
#10. Based on the engine location of the vehicle:
The location of the engine in a vehicle is different in various vehicles. These are categorized as follows:
Front engine – In this system, the engine is located at the front end of the vehicle over or ahead of the front axle. These vehicles are weighted at the front end.
Mid-engine – In this system, the engine is located near the rear end of the vehicle but forward of the rear axle. These vehicles have weight evenly distributed.
Rear engine – In this system, the engine is located beyond the rear axle. These are less common as compared to other systems.
Internal Resources:
- Brake System
- Chassis Frame
- Electronic Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Rack and Pinion Steering
- Lubrication System Types
- Open Belt Drive vs Cross Belt drive
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Propeller Shaft
- Clutch complete Notes
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
Reference [External Links]:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Outline_of_automobiles
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/automobile
So here we have studied a depth automobile classification system. Let me know have you understood or not? using the comment box. And if you like the article do not forget to share it with your friends and family. And let me know what other topics you are looking for?







Discussion about this post