In this Twist Drill article, we will study Definition, Nomenclature, Type, Advantages, Disadvanta0ges, Application, and Material in detail.
So let’s start with the definition first,
Twist Drill Definition:
A twist drill is basically a cylindrical piece of steel with special grooves. One end of the cylinder is pointed and the other end is so shaped that it can be attached to the drilling machine. The grooves are usually called flutes. The flutes formed by twisting a flat piece of steel into a cylindrical shape and such types of cylindrical shape drills are called twist drills.
Now let us discuss the various parts or Nomenclature of the twist-drill bits:
Twist Drill Nomenclature:
The following Nomenclature of Twist Drill are:
- Body
- Shank
- Dead Center
- Point
- Lips
- Body clearance
- Chisel edge
- Chisel edge corner
- Face
- Flank
- Flutes
- Heel
- Neck
- Tang
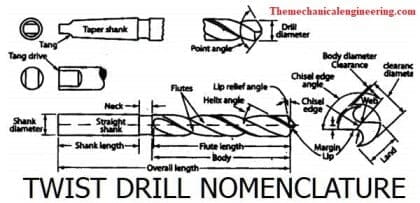
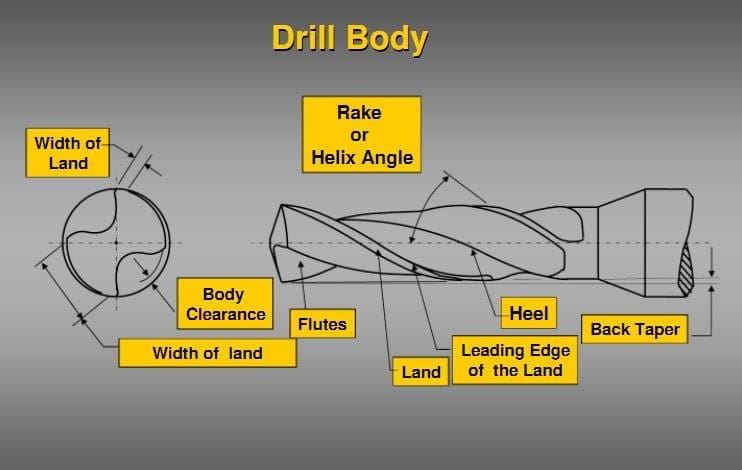
Body: The portion between the shank and the drill bit tip is called ‘Body. The body is mostly fluted and relieved.
Shank: The part of the drill bit that holds into the holding is called the ‘shank’.
Dead Centre: The sharp edge at the extreme tip end of the drill is formed by the intersection of the cone-shaped surfaces of the point. The dead center is always at the exact center of the axis of the drill.
Point: The entire cone-shaped surface at the cutting end of the tool.
Lips: The main cutting edges of the drill are formed by the intersection of the flank and the flute surfaces. For a good cutting, it should be straight, symmetrical with the axis of the shaft and equal in length.
Body clearance: To provide diameter clearance the body surface diameter is reduced.
Chisel edge: The chisel edge is the point. Here two cutting lips meet at extreme tip.
Chisel edge Angle: The chisel edge angle is the angle between the chisel edge and cutting lip measured plane normal to the axis.
Face: The flute surface portion adjacent to the lip, when it is cut from the work the chip impinges.
Flank: Drill surface which extends behind the lip to flute.
Flutes: The Twist Drill body has grooves and it is known as flutes.
Heel: The Heel is the intersection of the flute surface and the body clearance.
Neck: Neck is the portion of the body with reduced diameter between body and shank.
Tang: The tang is flattened end of the taper shank.
Now moving to different types of Twist Drill,
Various Type of Twist Drill:
The various types of Twist Drill are follows:
- Taper-shank Drills
- Cobalt Highspeed Steel
- Straight shank drills, taper length
- Straight shank drills, jobber’s length
- Heavy-duty drills
- Cotter pin drills
- Straight fluted drill
- Half-round drills
- Multi-cut drill
- Deep Hole Drill
- Shell-type core drill and
- Carbide Drills
Now we will discuss some of them in brief so let’s start,
Taper-shank Drill:
Taper shank drill is the general-purpose drill and has a morse taper shank. The taper-shank size varies with the drill body diameter.
Cobalt High-Speed Steel:
Cobalt high-speed steel is used in the case of heavy-duty work.
Straight-Shank Drill, taper length:
These drills have a straight shank for the same diameter as the bodies and the same overall length and the flute length as Per taper shank drills.
Carbide Drills:
Carbide Drills are used for drilling small holes. Solid carbide drills are used because they are very Rigid. It has high resistance to vibration and it produces clean and true holes in the work piece.
Twist Drill Advantages:
The following advantages of twist drill is:
- Twist Drill tool efficiency is higher.
- It saves time also because of higher speed and feed can drill the workpiece fast.
- It takes less power for performing an operation while other tools take high power for performing the operation.
- Through the flute, the unwanted material cuts from the workpiece easily come out.
Now moving to disadvantages,
Twist Drill Disadvantages:
The following disadvantages is:
- If the tool has a smaller diameter there are chances of breaking.
- The finish is not as good as compare to other tools like Single Point Cutting Tool and Multi-Point.
- If the tool works continuously for a long duration, it may break because of heating. So there is coolant required as it may be water or other.
Twist Drill Application:
A twist drill is a tool that is used in the drilling machine for operations like making holes in the workpiece. The hole in the workpiece depends on the diameter of the twist drill tool.
Twist Drill Material:
Many of the twist drills are made up of High- speed steel with or without a carbon steel shank joined to the body. Some Twist drills are made up of cobalt alloys and others have inserts of cement carbide.
So finally here we studied Twist Drill in detail. I have also written several articles on Manufacturing Technology Like Lathe, Milling, Shaper, Planer and Slotter Machine you can check that too.
Now if you have any query please let us know in the comment box. Till then do not forget to share with your friends. We will meet in other article.






Discussion about this post