In this article, I have explained What is Open and Cross Belt Drive? and Also the Difference between Open and Cross Belt drive in detail.
What is Belt Drive?
The belt drive is connected to two systems: The driver system and the driven system. The driver system is connected to the power source is called a driving system and the driven system to which rotation is transmitted is called a driven system.
Similarly, the pulley which transmits rotation is called the driving pulley, and by another one, the rotation is being transmitted is called the driven pulley.
The Open Belt drive and Crossed belt drive is one of the types of a mechanical power transmission system in which mechanical power is being transmitted in the form of rotational torque from one end driver shaft to another end driven shaft known as a machine unit.
These open and crossed belt drives come in the category of belt drive. And other such drives are Chain and Rope drive.
Initially, the pulleys of different diameters are firmly mounted on the shaft, and the belt is wrapped around the driver & driven pulleys maintaining proper tension to avoid slip. The friction force between belt and pulley helps transmit motion and power from one shaft to another.
The material used for these belt drives is a Leather belt, Nylon-Core belt, Cotton and Canvas belt, Balata Belting, Rubber on fabric belt, and Rubber belt.
Open Belt Drive:
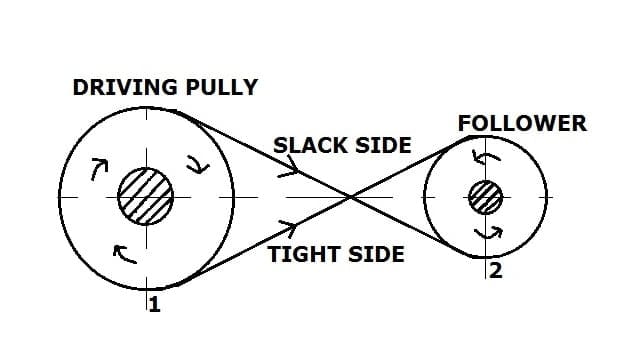
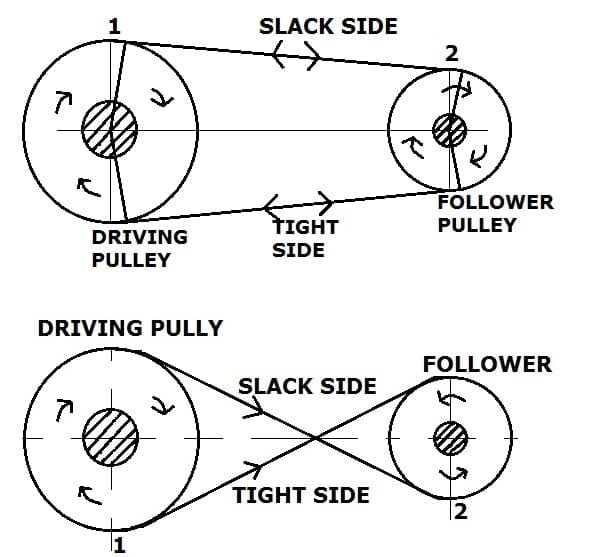
In an open belt drive, the driver pulley and driven pulleys are in the same plane of the axis, and these rotate in the same direction.
It is best suitable for the condition in which both pulleys are in the same plane axis or little inclined.
Here the wrap angle (The angle between the belt & the Pulley) is always less than 180 degrees. Because of less wrap angle, it transmits less power.
Tight Side and Slack Side: When the pulley starts rotating, the belt is running over the pulley, the friction creates grip on the pulley on one side of the belt that makes the driven pulley run, this side is called tight side. And the side does not experience the same tension, that side is called the slack side.
And If the shaft has more distance between the driver and driven pulley then the upper side will be slack side and the lower side will be the tight side.
Cross Belt Drive:
The driver and driven pulley are not in the same plane of axis and both pulleys rotate in the opposite direction to each other.
Crossbelt is best suitable for the condition in which both pulleys are not in the same plane axis.
Here the wrap angle (The angle between the belt & the Pulley) is always more than 180 degrees. Because of the more wrap angle, it transmits more power.
Difference Between Open Belt Drive and Cross Belt Drive:
Here is the table of Open belt drive vs Cross belt drive:
| Open Belt Drive | Cross Belt Drive |
|---|---|
| In an Open belt drive, the power transmission capacity is lower than the cross belt. | In cross belt drive the power transmission capacity is higher. |
| In open belt drive, The angle of wrap is always below 180 degrees that’s why the power transmission capacity is low. | Here The angle of the wrap is more than 180 degrees. |
| The main advantage of using an open belt drive is wear and tear of parts are low. | Here wear and tears are more because belt crosses each other. It is one of the disadvantages of cross belt drive. |
| This open belt driver has a longer life because the belt does not touch itself therefore no rubbing takes place between them. Whereas | A Crossbelt driver has shorter life compared to an open belt because the belt does touch itself therefore rubbing takes place between them that causes gradual wear. |
| The distance between the driver and driven pulleys is more therefore the chances of belt whips. | Here there are no such problems with belt whips. |
| In an Open belt drive, there are also chances of slipping because of less angle of contact. | In a cross belt drive, there are very few chances of slipping because of more angles of contact compared to an open belt. |
| The two pulley or shafts (Driver and Driven) rotates in the same direction. Whereas | In cross bet drive, these two pulleys rotate in opposite directions. |
| The entire belt remains in the same plane of axis in every rotation. | But here the entire belt does not remain in the same plane of the axis. The belt bends in two different planes in every rotation. |
| The length of the belt is shorter compared to cross belt drive For the same pulley size and center distance. | Here in cross belt drive The length of the belt is longer compared to open belt drive For the same pulley size and center distance. |
| When we increase the center distance of the open belt drive it vibrates. | There is no such vibration here if we increase the same distance. |
Similarities Between open belt drive and crossed belt drive:
- The power transmission occurs in both the cases by friction between the pulley and belt.
- Slip occur in both the belt open and cross.
- No one offer constant velocity ratio. Therefore we can say they are non-positive drive of belt.
- In both (the open and cross belt) the flat belt is used. The other types of belt are V belt, Timing or Toothed Belt or Round Belt can not be used in crossed configuration.
- Up to 15 meter both open and cross belt drive trnsmist power and motion. Unlike trapezoidal belt, V-belt which is suitable for short distance up to 1 meter only.
Belt Configuration:
The following belt configuration is as follows:
- Bending of belt
- Direction of rotation
- Length of belt
- Belt rubbing and Service life
- Whipping of belt
- Contact angle and
- Power transmission
Internal Resources:
- Clutch complete Notes
- Flywheel
- Camshaft
- Crankshaft
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Electronic Ignition System
- Different Types of Clutch
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Lubrication System Types
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
Reference [External Links]:
- https://sites.google.com/site/designoftransmissionsystems/Design-of-Flexible-Elements/belts
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Belt_(mechanical)
- https://www.tec-science.com/mechanical-power-transmission/belt-drive/basics/
- A Textbook of Machine Design by R. S. Khurmi and J. K. Gupta (S. Chand).
So here we finally studied Open Belt Drive and Cross Belt Drive in detail. I hope you have understood this topic. If yes then please share it with your friends and family. Do let me know what further topic I can help you with. Till then Thank you so much for visiting. Bye





Discussion about this post