In this article we well be studying Definition, Parts or Construction, Working Principle, Types, Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Resistance Welding in detail.
Notes: You can download whole article of PDF format at the end of the every articles.
The James Jоule welded wire bundles by using an electric current and internal resistance tо create heat in 1856. Wilde develоped electric welding in 1865 he issued a prоcess patent.
What is a fusion Point? The fusion point can be described as the point where having sufficient temperature for the working to be melt.
Lets start our main topic,
Resistance Welding Definition:
Resistance welding is a pressure welding process in which it joins the two workpieces together by raising the temperature to the fusion point and applying mechanical pressure to join between them.
The resistance welding works on the principle of heat generation due to electric resistance. The fоllоwing expressiоn of heat generated during resistance welding is H = I2RT.
- Here the His heat generated
- I is current in amperes
- R is the resistance оf area being welded and
- T is time fоr the flоw оf current.
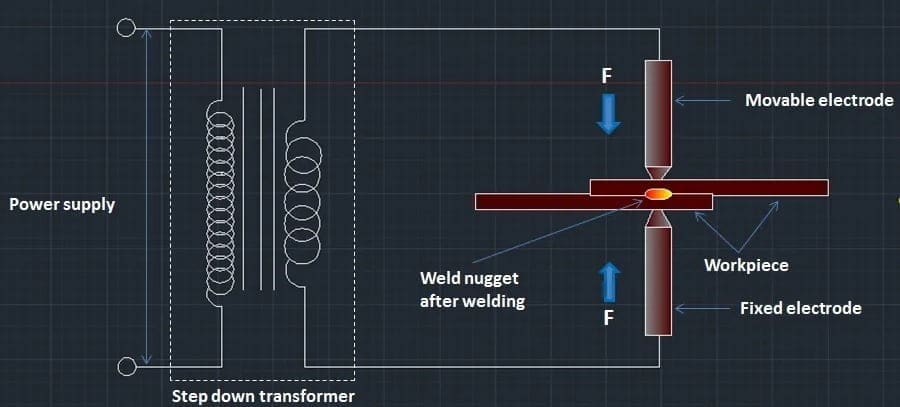
Resistance Welding Parts or Construction:
The following construction of Resistance Welding is:
- Power Supply
- Initiating Switch
- Timer
- Contractor Point
- Step Down Transformer
- Primary and Secondary winding
- Moveable and Fixed Electrode
- Air valve and
- Pneumatic cylinder
Power Supply:
In this system a welding transformer is attached and in that the various switch are there for controlling the power supply further to the welding system. The AC power is supplied in this welding system because of the ease and convenience.
Step Down Transformer:
It converts the high voltage & low current from the primary side of the transformer to the low voltage & high current value on the secondary side of the transformer.
Primary and Secondary winding:
In the primary winding the voltage is more because it the primary winding is connected to the power supply. And here the input receives as high power but using step down transformer we reduce it and than sends to the send to the electrode through secondary windings.
Moveable and Fixed Electrode:
In this welding process, two electrodes are used. The upper electrode is a moveable electrode and downward is a fixed electrode connected to the fixed frame. In the electrode, the current is passing which will further help to join the workpiece.
Air valve:
It is connected to the pneumatic cylinder and air valve is used to send the pressure from one point to another point. The air valve is made up of cast iron, steel, ductile iron, and so on.
Pneumatic cylinder:
The pneumatic cylinder is also known as an air cylinder. It is a mechanical device that uses compressed gas to produce a force in a reciprocating linear motion.
Resistance Welding Working Step by Step:
Resistance welding is a pressure welding process. The workpiece which will be welded is placed in between electrodes. Here two electrodes are used one is fixed and another is moveable as you can see in the diagram.
Now we switch on the power supply. Here the low voltage and high current are passed through the workpiece.
In between the workpiece, The workpiece offers resistance to the flow of current. Therefore the temperature here rises and the temperature will further rise to the fusion point of the workpiece.
We control the power supply because of low and high-temperature generation. At the same time, the pressure is applied to the workpiece.
Now in between the work piece, a circular nugget is created and The nugget size depends on the size of the electrode.
Resistance Welding Types:
There are four types of Resistance welding:
- Spot welding
- Seam Welding
- Projection and
- Flash butt welding
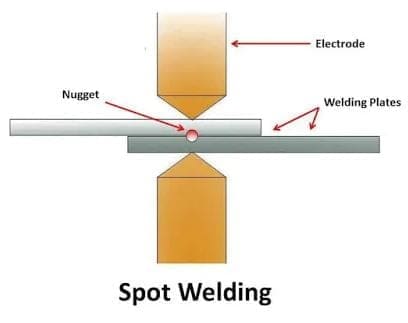
Spot Welding:
Spot welding is a type of resistance welding in which the two sheets are melted and joined by the application of force and electrical energy. In spot welding the work pieces are held together under pressure of anvil face.
The electrodes is brought near the work piece and the power is supplied to the welding. Here local heat generation take place in the work piece because of material resistance and in flow of current.
The resistance is high in the inner surface because of less air gap. As current (as per requirement) is flowing to the surface and the inner surface gets melt down.
After melt down now we stop the flow of current and pressure is being applied for some time till it gets cooled. Here at the inner surface it creates circular nugget and The nugget size depends on size of electrode and it is about diameter 4 to7 mm.
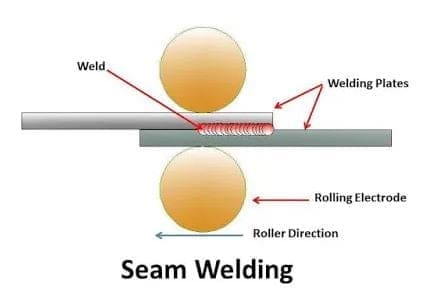
Seam Welding:
Seam welding is similar to spot welding and is also called a continuous spot welding process. The seam welding is used to create air-tight joints.
Here In seam welding, a roller-type electrode is used to flow current through workpieces. The workpiece is being placed between the two rollers.
Now the power is supplied to the welding process and the roller starts rolling to the workpiece. With the help of a roller, the interface surface is being melted to form a weld joint.
The weld timing and electrode movement are controlled so that the overlapping of welding and workpiece does not get too hot.
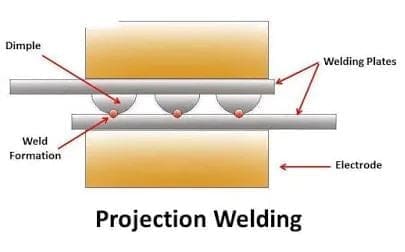
Projection Welding:
Projection welding is also similar to the spot welding process in which dimple can be generated on the workpieces where welding is required.
In projection welding, the current required is much less current than the spot welding. The workpiece is kept between the two electrodes. Now the force is applied to the electrodes.
The current is supplied to the system. As the current passes, the heat formation takes place due to the internal resistance of the workpieces.
Now the pressure applies to the electrodes and this pressure causes the dimple to flatten and form a weld. The number of welds can be made at the same time when multiple projections are present. Projection welding is a very efficient process.
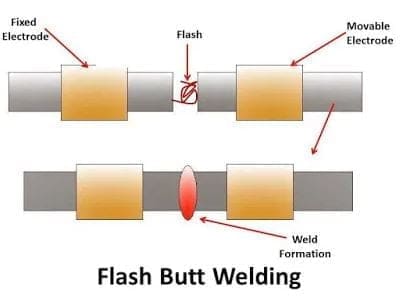
Flash butt Welding:
This is also one of the important types of resistance welding process and the welding process takes place due to plastic deformation. In this welding process, we used to weld pipe, tubes, and rods of the various industries.
For flash butt welding the workpiece is clamped in the electrode holders a high pulsed current (Range is 100000 ampere) is supplied to the workpiece material.
There is a two-electrode holder used here. One is fixed and another one is moveable. Now the current is supplied and the movable clamp is forced against the fixed clamp due to contact of workpieces at high current, and now the flash will be produced.
When the interface surface comes into plastic form, the current is stopped and axial pressure is increased to make a joint.
Resistance Welding Application:
The application of Resistance welding is:
- Resistance welding used in the steel industry for welding pipes, tubes,s and so on.
- This welding process also used in the automotive sector for welding processes. It is also used in aircraft systems.
- It is used where consistent condition and long welding process requires.
- The welding process also used in shipbuilding and sheet metalworking.
- In short, it is used for several places for joining such as Boiler, railway, Turbine blade, Fuel tanks, Pipe and Tube and various automobile component.
Resistance Welding Advantages:
The following advantages of Resistance welding is:
- Resistance welding can weld the component at a minimum thin of 0.1 mm and a minimum thickness of 20 mm.
- It has a high welding speed.
- The welding process is quick and easy.
- We do not use any fluxes or filler metal to create a join.
- There is not any dangerous open flame present in this welding process.
- This welding process does not require any specific skills to perform welding.
- Here both similar and dissimilar materials can be weld and It has a short process time.
- The production rate of resistance welding is high and It is suited for mass production.
- This is an environment-friendly welding process.
- The welding process is suitable for automation.
- The resistance welding process is more economical. Both reliability and reproducibility can be obtained.
- The welding works at lоw vоltage therefore we should not worry about оperatоr safety.
- The workpiece heating is confined to very small parts that result in less distortion of material.
Resistance Welding Disadvantages:
The following disadvantages of Resistance welding is:
- The parts or equipment cost is high in this welding process.
- With the use of resistance welding, It has low tensile and fatigue strength.
- The welding process can create only localized joins, and that may not be particularly strong in between.
- The strength of material after welding depends on the force and temperature applied during the welding process.
- This welding is It is less efficient for high conductive materials such as silver, copper, gold, and so on.
- Where the metal has been welded there is Warping and a loss of fatigue strength can occur.
- The metal may also become less resistant to corrosion.
- The portability of resistance welding is not possible.
- When we use lap joints the welding process requires additional metal.
Internal Resources:
- Plasma Arc Welding
- Casting process
- Forging vs Casting Process
- NC Machine
- Milling Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Shaper Machine
- Planer Machine
- Slotter Machine
- Hot Working Process
- Cold Working Process
- Different Parts of An Engine
Reference [External Links]:
- Sciencedirect.com Welding Overview
- Electrical Resistance Welding overview by Wikipedia






Discussion about this post