The automobile industry has developed step by step all these decades. A car is not essential but an important part of one’s transportation purposes.
A user needs to have basic knowledge about the car working analysis parts. Every car is designed differently and each component has different types and styles.
However, It is designed by the designer according to its utility.
The major components of an automobile consist of a chassis, engine, transmission system, body, steering system, and braking system. It also consists of many other components as well.
A detailed overview of these is as follows:
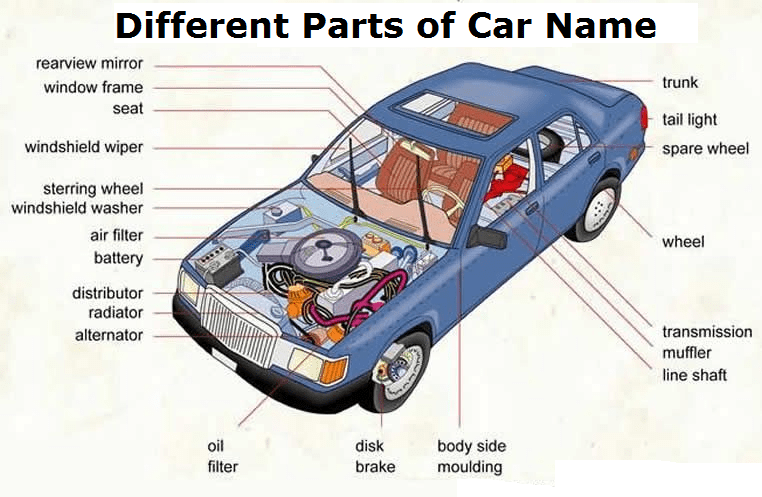
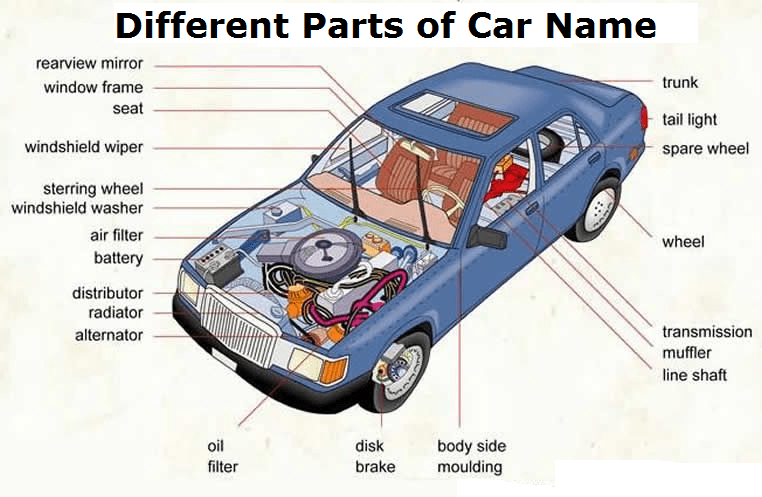
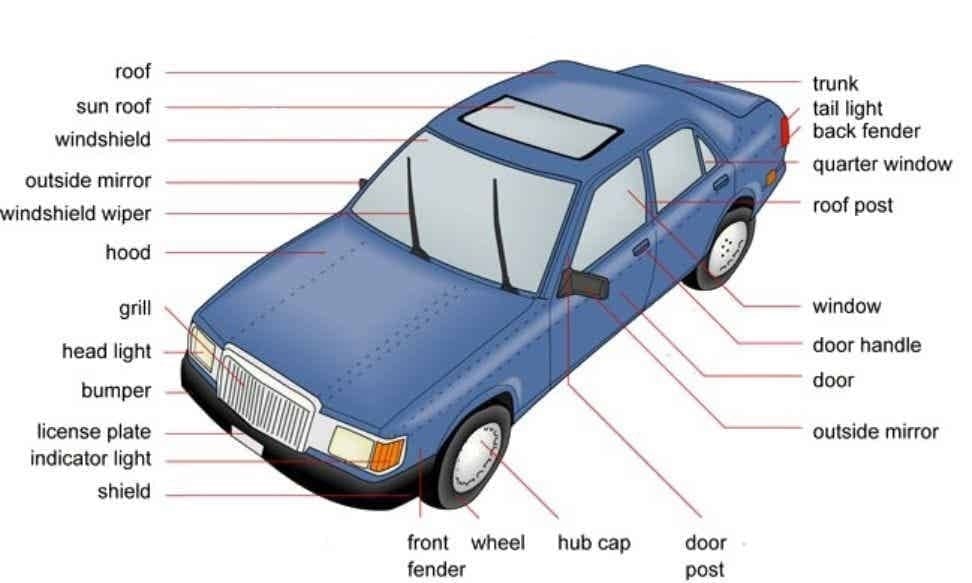
Different Parts of a Car Name:
- Chassis
- Engine
- Transmission System
- Body
- Steering System
- Braking System
- Electrical
- Battery
- Alternator
- Alternator Pulley
- Serpentine Belt
- Cooling System
- Radiator
- Lubrication System
- Ignition System
- Power train
- Clutch
- Propeller shaft
- Differential
- Axles
- Gear Shift
- Timing Belt
- Suspension System
- Shock Absorber
- Exhaust System
- O2 Sensor
- Catalytic Converter
- Resonator
- Mufflers
- Exhaust Manifold
- Electronic Control Unit
- Air Filter
- Airbags
- Seat Belt
- Headlights
- Tail Lights
- Indicator Lights
- Windshield
- Windshield Wipers
- Proximity sensors
- Car Hood
- Trunk
- Wheel / Tyre
- Fuel Tank
- Fuel Gauge
- Speedometer
- Temperature Gauge
- Odometer
- RPM Gauge
- Cruise control
Car Parts Image:
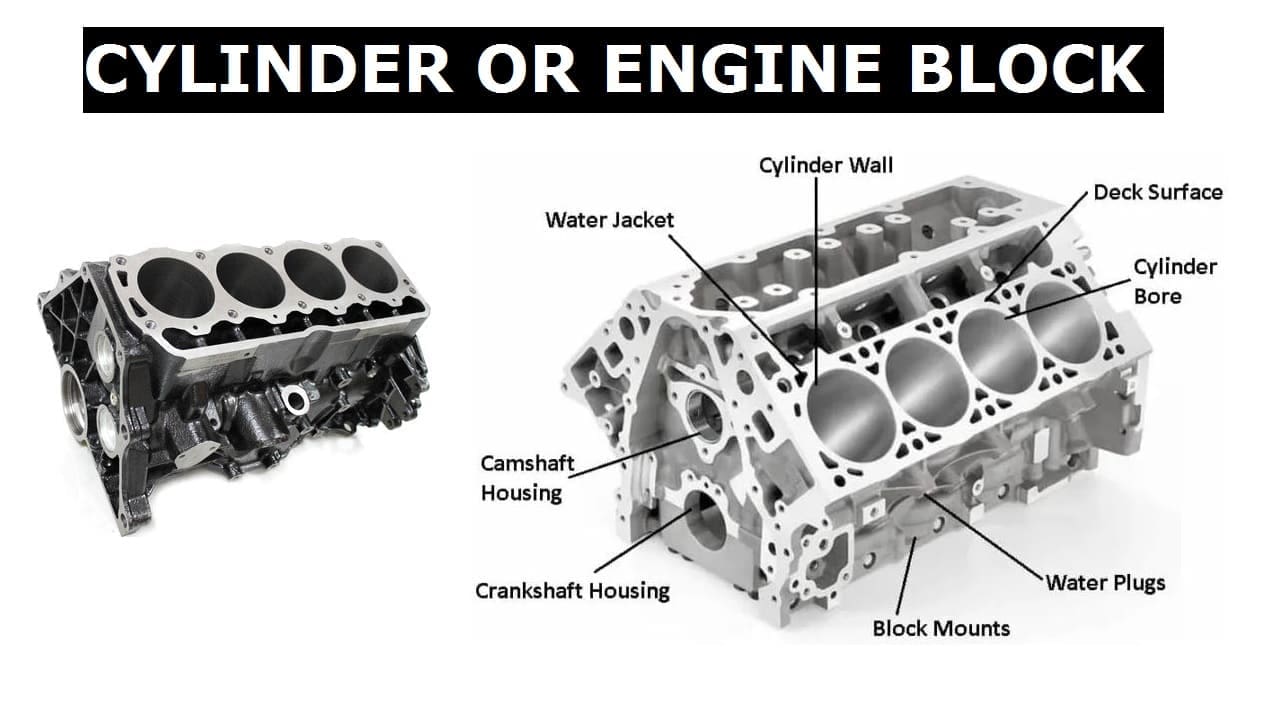
Chassis:
The Chassis is the frame or structure of the vehicle on which all the parts of the vehicle are mounted. It is the basic structure of the vehicle without the body. The chassis provides rigidity to the vehicle structure.
The chassis of an automobile consists of the frame, suspension system, axles, and wheel as the main components.
The frame can be in the form of a conventional chassis or unit construction may be adopted.
In the case of a conventional chassis frame, the frame forms the main skeleton of the vehicle. It supports the engine, power transmission, and body of the vehicle.
The frame is supported on axles through springs. It carries the weight of the vehicle and passengers and withstands engine, transmission, accelerating, and braking torques.
In the case of unit construction type, there is no frame and the structure of the body of the automobile is first formed, then different components such as the engine, transmission system, and other parts are placed at suitable places in the body of the vehicle.
The other parts of the chassis include the suspension system, axles, and wheel.
The suspension system absorbs the vibrations caused due to the up and down movement of wheels. This function is performed using the springs and shock absorbers connecting the frame and the axle.
The springs can either be leaf springs, coil springs, or torsion bars. Rubber or air are also considered to form the material of springs.
‘Live’ and ‘Dead’ axle are terms used when power from the engine is transmitted and when no power is supplied to it respectively.
The axle also resists the stresses due to braking and driving torque, in addition to providing support to the weight of the vehicle.
Engine:
The engine of car is the source of power for an automobile. It is a very crucial part of an automobile because in the absence of an engine, the automobile may not move at all, and its basic function of transporting passengers or goods would not be possible.
The power produced by the engine determines the working of the automobile.
In the same manner, the efficiency of the engine plays a major role in the efficiency of an automobile.
The engine mostly is an internal combustion engine. This can be a spark-ignition engine consuming petrol as fuel or it could be a compression ignition engine using diesel as fuel. The engines used are multi-cylinder engines.
A single-cylinder engine is capable of providing the desired power but may become very heavy and therefore may be unsuitable. In the case of a multi-cylinder engine, with each cylinder handling a smaller amount of power, it keeps the engine light in weight.
In an IC engine, the total heat produced by the burning of fuel is not converted into work. This is because a part of it causes overall heating of the engine which is undesirable. This heat needs to be dissipated properly. Coolant in the form of air or water is used to take away the heat.
An engine can be air-cooled or water-cooled. Technology has led to some chemicals being developed which have cooling properties, and these remain unaffected for a longer period.
These chemicals are used as coolants, these do not require frequent maintenance.
Apart from their long life, these are more efficient as well.
Similarly, lubrication is another aspect of an engine requiring periodic attention from the user. The moving parts in an engine require regular lubrication to reduce unwanted friction.
The properties of lubricants are now highly developed. There is a standard rating for it and for every purpose a specific lubricant is available.
Apart from internal combustion engines, an electric motor is also used as a power source in some vehicles. These are known as electric vehicles and they use electricity instead of fuel to run the motor and power the automobile.
Transmission System:
In a car the transmission system transmits the power developed by the engine to the wheels. The power available as output from the engine is in the form of rotation of the crankshaft and flywheel.
This movement is transferred to the wheels to cause rotary motion and makes possible the movement of the vehicle.
The transmission system consists of various parts such as a clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, differential, and axle. The wheels are at the ends of the axle.
The motion is transmitted through these parts and every part of the transmission system performs its function.
The clutch is a part of the transmission system next to the crankshaft. Its function is to enable the rotary motion of one shaft transmitted to the second shaft.
The gearbox is the component of the transmission system connected to the clutch. It consists of a gear train, and it provides different gear ratios. These ratios determine the speed of the output shaft from the gearbox.
The term gearbox ratio can be explained using the cycle gearbox for example. The 1st gear has a smaller rotation gear and a bigger rotating gear. It also has a higher amount of torque.
As a result, one full rotation of the smaller head is not enough for the bigger to rotate. If the smaller gear needs five full rotations to complete a full rotation of the bigger gear, the ratio is 1:5.
The gear ratio increases with the increase in gear and as a result, the vehicle moves freely in the 4th and 5th gears.
The differential is the component of the transmission system linked to the propeller shaft. The motion of the propeller shaft is fed to the differential which turns it through 90 degrees. This is essential as the axle is at 90 degrees i.e. perpendicular to the propeller shaft.
The axle is the component of the transmission system which is attached to the differential and receives the power from the engine.
Body:
The body part of car use of a separate frame to which the body structure is attached is obsolete except for some applications for heavy-duty commercial vehicles.
Most heavy-duty vehicles now use ‘sub-frames’ of simple construction to which the engine and gearbox are attached.
The sub-frame gets support from the mainframe and is fixed on it through some suitable rubber connections which isolate the engine vibrations.
All the assembly units of the vehicles are attached to the body which also acts as the frame, this is due to development in spot welding and sheet pressing techniques.
This makes the vehicle compact, and lightweight and the cost is also reduced.
Steering System:
A steering system is used to turn the wheels of the vehicle and change the direction of the vehicle of the car. Steering systems have evolved from the recirculating ball to rack and pinion to power steering system now.
While the recirculating ball had a circular gear to change the direction, the rack and pinion used two sets of gears perpendicular to each other to enact an easy and smooth change of direction of the wheels.
Power steering systems use highly pressurized fluid in the tube of rack and pinion for pressurized movement of the gears which reduces the effort required by the driver by using either electric or hydraulic assistance.
It consists of a motor that is run on the battery, to supply the high-pressure fluid into the tube.
The fluid used is a lubricant known as a power steering fluid. It requires timely maintenance to keep the components away from premature wear.
Braking System:
The braking system is an essential aspect of an automobile since the speed of the wheels needs to be controlled or completely stopped at some point.
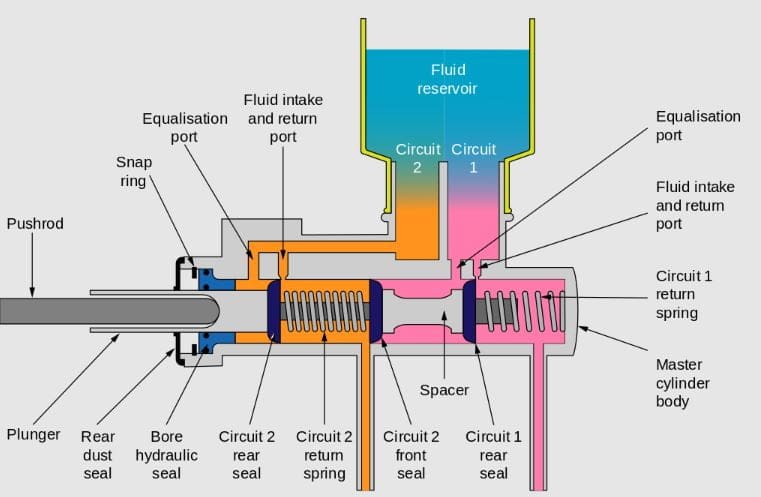
Almost every modern car has a hydraulic braking system. Major components include the brake pedal, master cylinder, caliper, brake drum, braking pipe, brake shoes, and linkages.
The application of the master cylinder is to supply high-pressure braking fluid through the braking pipes to the drums for efficient braking.
Conventional braking systems consisted of the traditional brake pad fitted on a brake caliper and the drum for resistance.
Developments invented the use of disc brakes instead of the conventional drum for better braking force and reduced heating of the brake pads.
Brake discs are usually made up of grey cast iron, but in some instances are produced from composites such as reinforced carbon or ceramic matrix composites.
Another invention led to the development of an anti-lock braking system (ABS) since sudden braking force led to uneven locking of the wheels causing immense load on the passengers.
An anti-lock braking system causes the wheels to not lock and steadily slows the vehicle down when the brakes are applied.
Electronic brake distribution is another new technology, which distributes the brake force equally on all the wheels.
This technology uses a central electronic control unit (ECU) which calculates the brake force and distributes it evenly among the wheels for less wear and tear of the wheels and also for better grip of the wheels on the road surface.
Electrical System:
It is the electrical system that is responsible for the supply of energy to operate and power the motor and all the accessories. This system works continuously in a unison with major components such as the battery, alternator, starting motor, heater, and ignition coil.
Battery:
The car battery is also an essential component of car function as it provides the electricity needed for all the electrical components to work.
It is a rechargeable battery to start the electric starting motor or ignition system which in turn starts the engine.
The battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy to power the car. It powers the starter, headlights, stereo system, and other electrical accessories.
It keeps the electric current steady in the circuit by stabilizing the voltage.
Alternator:
An alternator is a device responsible for charging the battery of the car while the car is being driven.
It also provides energy to most of the electrical components in the car such as headlights, power steering systems, power windows, windshield wipers, radio, and dashboard instruments.
The alternator generates direct current (DC) and supplies it to the components.
The working principle is based on converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. It consists of a pulley that is attached to the alternator.
The pulley is driven by a Serpentine belt, which is powered by the mechanical force generated by the crankshaft pulley. Further explanation of the belt and other tensions are explained below.
Alternator Pulley:
It can be described as a coil consisting of magnets and is driven by the engine’s driving belt system. The magnets when driven spin and generate alternating current (AC) around the coil.
This current is supplied into the alternator’s rectifier and converted into DC power.
Alternative pulleys are commonly available in two types namely, stamped steel and cast aluminum.
The alternator pulley is an important component as far as electrical systems are concerned but does not affect the functioning of the engine.
A worn-out overrunning pulley can cause the belt to slip and create a short chirp noise.
Serpentine Belt:
The serpentine belt is a long rubber belt that connects and drives multiple devices – the alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, water pump, and radiator fan. It is also known as the fan belt or drive belt.
Earlier, vehicles used to have multiple belts for purposes but modern vehicles consist of a single belt to power all devices.
It is very important in modern cars due to its connection to several systems and causes such as A/C, dead battery, engine overheating, loss of power steering, and damage to engine accessories.
It is different from the timing belt and has multiple V-shaped grooves running vertically along the belt.
Cooling System:
Internal combustion engines operate at very high temperatures and need to be operated at an efficient temperature for better performance and life of car engine parts.
The temperature increase is due to the combustion of fuel with air inside the cylinder. The cooling system is designed such that the engine neither overheats nor overcooks.
The cooling system comprises parts such as a radiator, cooling fan, coolant, and a thermostat that monitors the temperature of the coolant.
Radiator:
The radiator is an important part of the car engine’s cooling system and helps to drain out the excess heat from the engine. The liquid coolant passes through the hoses and engine to absorb the excess heat and moves back into the radiator.
The hoses are like a piping system located over the engine for heat transfer. The passing of coolant over the engine releases the excess heat in the form of vapor and the hot coolant mixes again in the radiator.
The hot air is released into the atmosphere with the help of the coolant fan, a group of thin metal fins.
The radiator is cooled with the help of cool air passed in through the car’s front grille and in idle conditions, the fan blows air to help reduce the coolant temperature.
A water pump located close to the cylinder head is used to pump the coolant water to parts of the engine. Moreover, a core plug is used to avoid leakage of the coolant.
Lubrication System:
Moving parts develop wear eventually as they move along each other. An engine has several moving parts and it is essential to prevent wear due to the metal-to-metal contact.
A lubricant is circulated between these moving parts so that the parts move over each other with minimal friction. This helps in reducing the power loss due to friction.
Oil passages and galleries pave the way for the flow of lubricants to moving parts of the engine. The lubricants also act as a coolant themselves.
These are highly viscous fuels that are suited to work at high temperatures and pressure. It is also a sealing medium inside the engine and helps to prevent leakages.
Ignition System:
The ignition system is responsible for self-starting the vehicle using the either combustion of an air-fuel mixture or a high voltage spark.
The system which uses a high voltage spark is called the Spark Ignition system (SI) and combustion of the air-fuel mixture is used in the Compression Ignition system (CI).
The SI system uses a separate spark plug for ignition purposes and the CI system requires only the compression of the mixture to high pressure.
Powertrain:
The powertrain in a car is everything involved for the car to work from well to wheel (fuel tank to propulsion).
In other words, it is the propulsion system of the car. It creates and delivers the power to the wheels on the ground for the car to move.
The powertrain consists of the clutch, transmission system, propeller shaft, differential, and axles.
Clutch:
A clutch is also an important parts of car which is inside the transmission system used to isolate the transmission from the engine crankshaft. Since the car engine is constantly running, the crankshaft never stops rotating.
This can hinder the gear-changing process due to friction. As a result, a clutch is used as a connector between the transmission and the engine.
It is used to disconnect the transfer of power from the engine to the transmission and facilitate the change of gears.
Even though clutches are present in both manual and automatic transmission, the way of application is entirely different.
In a manual transmission, the clutch is detached using the force developed by the clutch pedal on the splint sleeves.
Whereas in an automatic transmission, a torque converter is used to avail automatic change of gears, and clutches are detached due to the hydraulic pressure developed inside.
Propeller shaft:
The transmission system creates the power according to the torque provided. The power is transferred to the wheels using the propeller shaft. It is also called a driveshaft.
Made up of high-quality steel, these have universal joints at both ends.
The concept of Rear Wheel Drive (RWD), Front Wheel Drive (FWD), and All Wheel Drive (AWD) are based on the propeller shaft and differential.
RWD has a propeller shaft connected to the rear axle, FWD has a propeller shaft to the front axle and AWD has a propeller shaft to both axles.
Differential:
The power transmitted from the transmission is transferred in the form of rotational force via the propeller shaft.
The differential splits the power transmitted from the propeller shaft to the axle. A differential feeds equal power to both wheels at a smooth surface.
It is also responsible for providing the required amount of power to a particular side when one side is under more load.
Moreover, a differential is also related to RWD, FWD, and AWD. These have a differential at the rear axle, front axle, and both axles respectively.
Axles:
It is nothing but shafts that are used to mount the wheels and are of two types namely, Front Axle and Rear Axle.
The front axle is located at the front end and it’s connected to the front suspension. Front axles are associated with the steering system and are responsible to pivot when making turns.
Rear Axle consists of a simple suspension structure and is not related to steering. The axle which has a differential connection is called the driving axle and is differentiated as FWD, RWD, and AWD as mentioned above.
The driving axle is a split axle consisting of two halves connected by the differential in the middle. Each half is known as a half shaft and connects to the wheels through a constant velocity (CV) joint.
Gear Shift:
In a car the gear shift is generally a shifter or stick, technically known as the transmission lever.
It is a metal lever used as an input device of the transmission system. In simpler words, a Gear Shift is used to engage and disengage the gears for the movement of the vehicle.
While in manual transmission, the term gear shift is used referring to the shift lever for change of gears according to torque using the clutch pedal; automatic transmission (torque converters and clutch-less manuals) has a similar lever known as a gear selector which has only forward, reverse and neutral positions.
Timing Belt:
As the name suggests, the timing belt is used to keep the crankshaft and camshaft in sync. It is located inside the engine and its function is to ensure that the engine intake and exhaust valves open and close simultaneously in time with the pistons.
This consists of a horizontal teeth setup assembled to turn the camshaft in time with the crankshaft.
It is a very important component of an engine, as it ensures the valves close in time to avoid contact with the position and also avoids the mixing of particles in the intake and exhaust valves.
Modern cars use timing chains instead of a belt for better durability.
Suspension System:
The main function of the suspension system in a car is to minimize the effect of irregularities of the road surfaces on the vehicle. The suspension system is responsible for this function.
It absorbs the vibrations caused due to the vertical motion of the wheels with the help of the springs, connecting linkages, and a shock absorber which compromises the suspension system.
Suspension systems of a car are generally of two types namely, Rigid systems and Independent systems.
Rigid systems are usually employed on both axles of heavy vehicles and only on the rear axles of light vehicles. An Independent system, on the other hand, is employed on the front axle of light vehicles. A rigid system comprises road springs connected to rigid beam axles and these springs change positions together. As a result, if one rear wheel undergoes an irregularity the other wheel is also affected.
An Independent system does not have a rigid axle. As a result, if one wheel undergoes irregularity the other wheel maintains its position. This is why an independent system is preferred on the front axle of light vehicles, for better stability and comfort on any surface condition.
Shock Absorber:
The suspension system on the vehicles undergoes wear when impacted frequently due to uneven road surfaces. The spring in the suspension system needs to be brought into its original position after deformation for efficient functioning.
The role of a shock absorber is to minimize the effect of the impact on the vehicle and adjust the spring into its original position after deformation with the help of a hydraulic pump consisting of highly viscous oil.
This uses hydraulic pressure created by the pump to load and reload the springs when required. Along with smoothing the bumps on road, it also ensures the wheel remains attached to the axle.
Exhaust System:
A system that uses controlled processes to guide the reacted gases away from the combustion chamber is called Exhaust System.
The exhaust system is responsible for reducing noise, carrying away exhaust gases, and improving engine performance and fuel consumption.
This system consists of several parts that work in unison. Different components of the exhaust system are the O2 sensor, catalytic converter, exhaust manifold, resonator, and muffler.
O2 Sensor:
Known as the Oxygen Sensor, it is responsible to calculate the oxygen content in the exhaust. It is positioned just in front of the catalytic converter, connected to the exhaust valve.
The oxygen content is sensed and informed to the car’s electronic control unit (ECU). The excess oxygen found in the exhaust is recycled into the engine and improves the engine’s air-fuel ratio.
This detection helps the engine to supply enough oxygen to the catalytic converter and use the excess oxygen for engine efficiency.
Catalytic Converter:
The catalytic converter is used to convert the toxic gases in the exhaust into CO2 and Nitrogen, which are less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction (reduction-oxidation).
Catalytic Converters are of two types namely, Two-way and Three-way.
The two-way system is used in diesel engines and the three-way system is used in petrol engines. Converters in diesel engines target particles known as soluble organic fractions. It converts hydrocarbons to carbon dioxide and water.
A Three-way system performs the same function as that of a two-way one but with the addition of a reduction catalyst. It reduces nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and oxygen gases.
Resonator:
IC engines produce loud noise due to the combination process. To control the engine noise, a resonator is used.
It is employed specifically to tackle the engine rpm and is positioned just after the catalytic converter and in front of the muffler.
Resonator is a chamber that is used to modulate and change the sound in such a way that it is further muted by the muffler. Resonators are used to make the job easier for mufflers.
Mufflers:
Resonators help decrease the sound and Mufflers decrease the volume. These work as dampers to the sound released due to the powerful exhaust strokes.
Mufflers are made up of steel and coated with aluminum to protect them from the heat and chemicals released during the process.
Exhaust Manifold:
Located at the end of the muffler is the exhaust manifold. It releases the exhaust air from the vehicle into the air. These are attached to the rear of the vehicle with the help of a bracket.
Electronic Control Unit:
The abbreviation of the Electronic control module is ECU. As the name suggests, an ECU is a device that controls and connects various electronic configurations or modules in a vehicle.
The working of an ECU is based on numbers and parameters installed in its memory. The sensors around the vehicle feed the ECU with data and it works by making changes according to the input data.
For example, the crash sensors detect the velocity of the crash and feed the data to the ECU. The ECU compares the data in its memory to launch the airbags. If it detects the velocity to be greater than the safety standards set, it employs the airbags.
A vehicle may have multiple ECUs each having different tasks to perform. Some of the modules are the Engine Control Module which works on fuel injection and ignition timing, the Brake Control Module used for the functioning of ABS, Transmission Control Module used for smooth gear shifts on an automatic transmission.
Almost every modern vehicle has an ECU in it, without which some cars may not even start.
Air Filter:
The engine requires to mix up with fuel for the combustion process. So, it is necessary to clean the air before it is passed on to the cylinders to prevent dust, dirt, grit, and other debris from entering the cylinders.
If these contaminants enter the engine cylinders, they can lead to damage to the interior parts.
Air filter ensures that only clean air enters the cylinders and hence improves engine performance and efficiency. This also plays a role in extended engine life.
Airbags:
An airbag is a bag designed to inflate quickly and provide cushioning to the occupants of the vehicle upon impact.
It protects the passengers from hitting interior parts of the vehicle or from throwing the passenger out of the seat due to impact.
These absorb the force developed due to the impact and provide a softening effect on the passenger’s upper body.
Since it needs to be deployed quickly, the bags are filled with a chemical called sodium azide.
When the sensor detects sudden deceleration or collision, it sends the data to the ECU and thereby sends an electric signal to an ignitor. The ignitor produces heat causing the sodium azide to decompose into sodium metal and nitrogen gas.
Airbags are usually provided in front of the passenger, I.e on the dashboard for front passengers.
Some cars have side airbags and knee airbags as well. These are located in the door panel on both sides for impact protection on the sides and the lower end of the dashboard for protecting the knee respectively.
Seat Belt:
A seat belt is a safety device, a belt that is designed to secure an occupant of the vehicle against unwanted movements that may be caused during a collision.
It helps to keep the occupants positioned safely and prevents the passenger from being thrown away from the vehicle on impact.
It is very essential as far as the occupants at the front are concerned, as there is a chance of contact with the windshield upon impact.
Seat Belt also increases the effectiveness of the airbags, if employed, and are considered Primary Restraint Systems (PRS). It consists of parts such as webbing, retractors, buckles, and pillar loops.
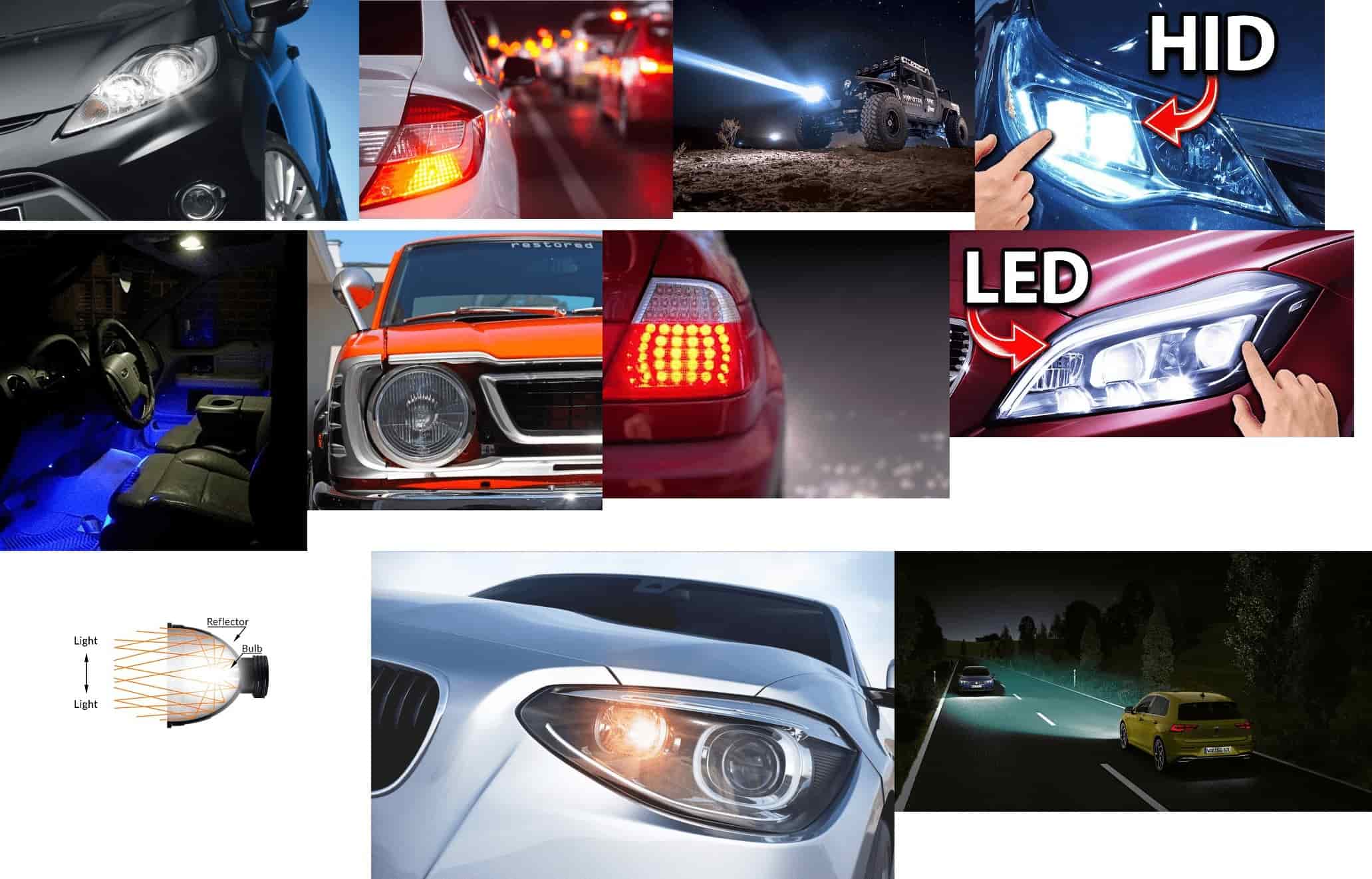
Headlights:
The Headlight in a vehicle is a device used to produce a beam of light illuminating the road ahead. These mostly consist of a headlamp, mirrors, and housing to cover the lamps.
Headlights have evolved over the years and modern vehicles have various types of headlights. Halogen, LED, HID, Laser, Projector, and Matrix are the types of headlights in modern cars. Halogen is yellowish whereas LED is white.
Headlights provide clear illumination of the road ahead and facilitate a fatigue-free drive for the driver. It also helps to decrease the number of accidents.
Tail Lights:
Tail lights are located at the rear of the car. It is mounted above the bumper and is red.
Tail lights are used to make the cars behind aware of your presence on the road to avail safe travel in the dark. The Tail light set also includes a white light besides, which is the reverse light.
The reverse light is used to indicate when the vehicle is moving in the reverse direction and it is started when the gearshift is moved on to reverse.
Indicator Lights:
Indicator lights are direction indicator lamps or turn signals, also known as blinkers. These are blinking lamps mounted along with the headlights and tail lights.
Activated by the driver using the forks present at the back of the steering wheel, these are also present on the sides or side mirrors of some vehicles.
It is used to indicate a change of direction of the vehicle to other vehicles on the road, before making the turn.
Windshield:
The screen or glass shield at the front end of the vehicle is called a windshield or windscreen. It is used to protect the occupants inside and visibility to the driver.
These are laminated safety glasses, a special type of treated glass that consists of two curved sheets of glass with a layer of plastic laminated between them for adhesion and attached to the window frame.
It’s responsible for protecting the vehicle’s occupants from wind and debris such as dust, dirt, and insects. It also helps with the aerodynamic drag of the vehicle.
Some modern cars also have a UV-coated windshield to protect them from the ultraviolet rays of the sun.
Windshield Wipers:
A windshield wiper is a cleaning device used to clear the windshield from rainwater, washing fluid, snow, or debris for a clear and visible windscreen.
Also called car wipers, it is a legal safety requirement for every car to have a wiper. It consists of a metal arm that is powered by an electric motor.
One end of the arm pivots and the other end has a long rubber blade attached to it. The blade swings back and forth over the glass and pushes the contaminants from the glass surface.
It is activated by the driver using the forks attached to the steering wheel, opposite the indicator fork. Modern cars have speed-adjustable Wipers with several velocities which can be adjusted using the fork.
Proximity sensors:
Most modern cars have sensors that detect and alarm the driver if the vehicle gets too close to an object or a vehicle. These are mostly mounted on rear bumpers for reverse assistance.
Although few cars have these mounted on the front bumper for forwarding clearance assistance. These sensors are generally of two types namely, Ultrasonic and Electromagnetic.
Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency straight sound waves to detect objects. The sound pulses are reflected off the nearby object and received by the receiver. The distance from the vehicle to the object is calculated and the alarm sound increases with decreasing distance.
Electromagnetic sensors use electromagnetic frequencies instead of ultrasonic waves. These are mounted inside the bumper as opposed to Ultrasonic and often come with a camera installed together.
Car Hood:
A car hood also known as a bonnet is a metal cover that is hinged and rested on the front of the vehicle. It is used to cover the engine of the car in front-engine vehicles.
It is hinged to provide easy access to the engine for repair and maintenance. A latch located inside is used to put up a lock and hold down the bonnet. These are generally made up of steel and in rare cases, aluminum is used.
Modern cars have been producing stronger bonnets and front grilles, which can distribute the force equally upon impact and decrease the effect on the occupants.
As a result, different designs and styles have originated with time. To open the trunk, a trunk open button is present inside the driver’s cabin.
Trunk:
A car trunk refers to the space at the rear end of the vehicle used as a primary storage area. It is also known as boot. It is held on by a latch or modern cars even have a hydraulic system attached to the latch.
Some cars also have an automated boot open and lose a button. Generally, sedans and SUVs have a greater amount of boot space as compared to hatchbacks.
Also, the boot open and close button is present inside the driver’s cabin or some cars have to be manually opened like a door using the key.
Wheel / Tyre:
Every axle has two ends that are attached to wheels or rims. These wheels are rotated by the driving axle when power is produced in the powertrain.
The wheels are wrapped around by round-shaped layers of synthetic rubber. This is called a tire and it’s black.
Since rubber is white in nature, a dye or a chemical compound called carbon black is used to convert it into black color.
The black color is preferred as it carries away heat and tires do not melt due to the friction generating heat. This increases the durability and stability of the tire.
Moreover, the tires have treads along the rotating axis to reduce the heat and have a better grip on the road.
The rims or the wheels have evolved over the wear in terms of shape and appearance.
It has come a long way from cycle-like rims attached to the central axle by spokes to diamond-cut alloy wheels which have a crystal-like appearance.
These are generally made up of aluminum and magnesium.
Fuel Tank:
A fuel tank is a part of the engine system which is used to store flammable fluids and release them into an engine. It is generally located under the middle section of the car.
The tank is refilled using a small fuel tank cap located on the outside of the body of the car. The fuel cap prevents the entry of contaminants into the fuel tank.
The contaminants can cause the clothing of the fuel filter, fuel lines, fuel investors, and the fuel pump.
The fuel filter is used inside to further filter the fuel to avoid any small particles of dust and the fuel pump is used to pump the fuel into the injectors through the fuel lines.
Fuel lines and fuel caps are made up of steel, aluminum, and brass.
Fuel Gauge:
A fuel gauge is a measurement device used to indicate the fuel level present inside the fuel tank of the vehicle. It has a scaling unit present inside the fuel tank to detect the amount of fuel and sends the data to the gauge or indicator.
Speedometer:
A speedometer is a speed indication device used in vehicles to indicate speed. It is usually combined with a device called an odometer that records the distance traveled.
A speedometer works on the principle of interruption of the magnetic field of the coil, which detects and sends data to the car’s ECU.
The ECU uses the data to compute the speed of the vehicle and the distance covered and the revolution speed of the engine (RPM).
The speed is then displayed on the speedometer. Modern cars generally have two types of speedometer namely, analog dial and digital display.
Temperature Gauge:
Engines work under high-temperature ranges and need to be cooled constantly for safety purposes. A gauge is designed to measure the temperature of the engine’s coolant.
It has a sensor, located in the thermostat housing to sense the temperature of the coolant and send an electric signal to the car’s ECU.
The data has a specific coolant temperature, giving an accurate reading of the coolant temperature and hence the gauge is accurate.
The normal working temperature of the coolant may vary from car to car depending upon the engine type and size.
Modern cars have an engine light and overheating light on the dashboard to indicate issues with the coolant temperature.
Some cars don’t start if such an incident happens due to the safety clauses set by the manufacturer.
Odometer:
A car trip meter, also known as an odometer is a device used for measuring the distance traveled by the vehicle.
The odometer is an important aspect as far as maintenance is concerned because the odometer helps the users to record the distance covered by the vehicle after the last maintenance and replace important parts before the limit set by the manufacturer for optimum utility.
The odometer could be mechanical or digital based on your vehicle and it is located just below the speedometer.
Moreover, the odometer has the trip option (Trip A and B) available by pressing the button near the speedometer. This function helps the user to reset and calculate the distance covered after the reset.
RPM Gauge:
A tachometer or rev counter is an indication device that measures and indicates the rotation speed of the crankshaft. The device displays the speed with revolutions per minute (RPM) unit.
The numbers indicated on the tachometer are usually multiplied by 1000 revolutions which are displayed near the speedometer and temperature gauge.
Cruise control:
A cruise control feature may be an advanced form of technology used in cars but the number of cars with cruise control systems has increased dramatically in recent years.
It is a feature that helps reduce fatigue the drivers while driving over a long distance. The system automates the acceleration process and maintains the car at the same speed.
This reduces the constant need to press and release the accelerator pedal. The system uses a cable or wireless system which is connected to the ECU of the vehicle.
It maintains the throttle in a certain position to keep the pre-set speed.
The cruise control system is switched ON/OFF using a fork attached adjacent to the steering wheel. It can also be switched OFF if the driver presses the brake or accelerator.
Internal Resources:
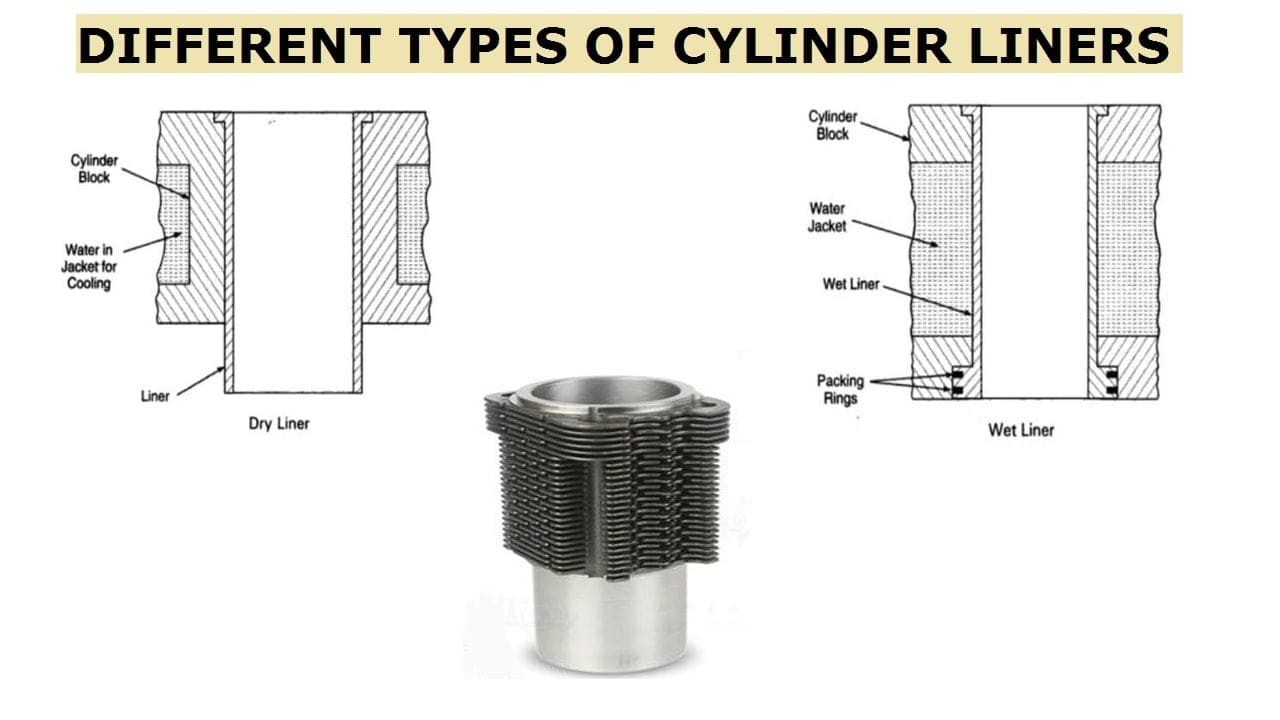
- Cylinder Liner
- Automobile Classification
- Flywheel Camshaft Crankshaft
- Clutch complete Notes
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Battery Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Electronic Ignition System





Discussion about this post