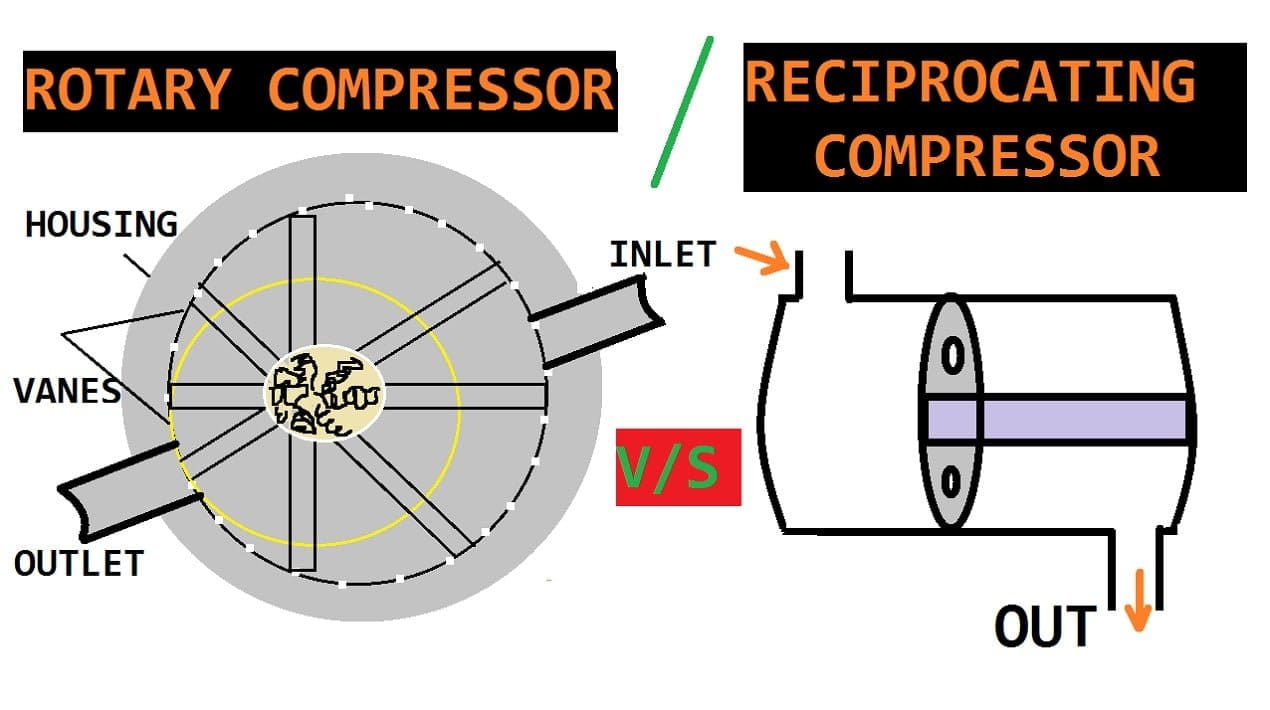
The main difference between Rotary and Reciprocating Compressor is that the flow rate of air is high in the rotary compressor and It is low in the reciprocating compressor.
In this article we will study Difference Between Rotary and Reciprocating Compressor.
Difference Between Rotary and Reciprocating Compressor:
| Sl. No | Rotary Compressor | Reciprocating Compressor |
| 1. | The flow rate of air is high in the rotary compressor. | The flow rate of air is low in a reciprocating compressor. |
| 2. | Because of perfect balancing, the speed of the compressor is great. | Because of the unbalanced force, the speed of compressor is low. |
| 3. | It has fewer moving parts. | It has a good number of moving parts. |
| 4. | Lubrication and maintenance requirement is less. | Lubrication and maintenance requirement is more. |
| 5. | It can be directly coupled with the prime mover. But | The reciprocating compressor can not be due to slow or low speed. But it requires a reduction in speed. |
| 6. | A rotary compressor is used where a large quantity of air at lower pressure is required. | A reciprocating compressor is used where a small quantity of air at higher pressure is required. |
| 7. | Here the air is continuous deliverance. | Here it is intermittent. |
| 8. | In the rotary compressor, the compression takes place due to the rotary motion of the blade. | Compression takes place with the help of piston and cylinder arrangement and also the reciprocating motion of the piston. |
| 9. | The pressure ratio and deliver pressure is low. | Here it’s high (the pressure ratio). |
| 10. | The working fluid is air or other gases. | The working fluid here is pressurized steam. |
| 11. | It works on 1 step or process of the Rankine cycle. | It works on a complete Brayton cycle. |
| 12. | The installation space requirement is less in a rotary compressor. | The installation space requirement is more in a reciprocating compressor. |
| 13. | It is suitable for the large discharge of air at low pressure. | It is Suitable for the small discharge of air at high pressure. |
| 14. | No balancing problem. | Here the balancing problem is more. |
| 15. | The maximum delivery pressure in a rotary compressor maximum is 10 bar only. | But here it is the 1000 bar. |
| 16. | A maximum free air discharge rate is as high as 3000 m3 per minute. | A maximum free air discharge rate is as low as 300 m3 per minute. |
| 17. | The operational speed is high. | The operational speed is low. |
So here we studied a total of seventeen points on Rotary vs Reciprocating Compressor.
I have also written articles on Venturi meter and Orifice meter you can check that too.
If you have any doubt let me know in the comment box. And if you like the article do not forget to share it on social media.




Discussion about this post