Today, I will tell you about the cold working process and its working in detail. In the last article, I discussed Hot Working Process in detail.
In the beginning, you will learn about the definition, methods, and detailed working. Afterward, we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of the Cold working Process.
You can download PDF at the end.
So, let’s get started with the definition first.
What Is Cold Working?
Cold working is the process of metal forming in which the deformation of metal occurs below its recrystallization temperature. In most cases, We perform cold working of metal at room temperature.
You might be thinking, But, what is recrystallization temperature?
It is the minimum temperature at which plastically deformed metals form new grains or crystals within the specified time. Recrystallization temperature in most the metal is found between one-third to one-half of its melting point.
Methods of Cold Working Process:
There are five different methods of the Cold Working Process:
- Cold Rolling
- Cold Extrusion
- Cold Drawing
- Bending and
- Shearing Process
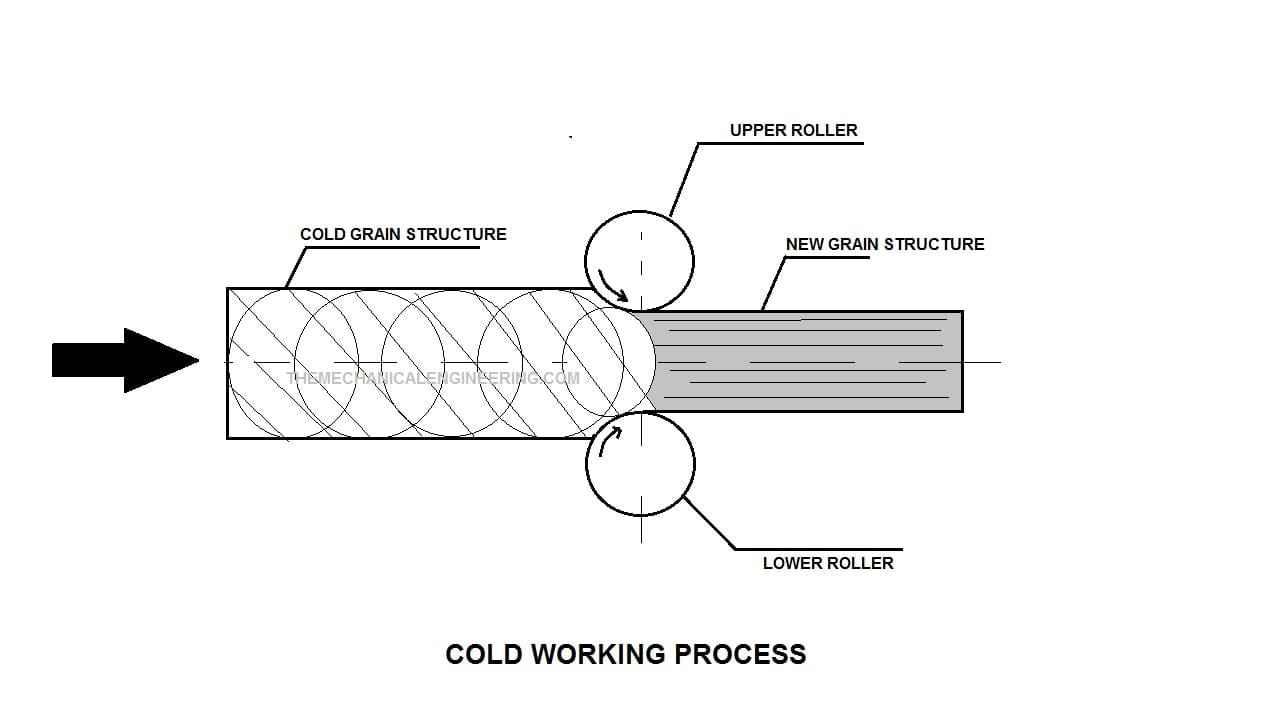
#1. Cold Rolling:
Cold Rolling is the method of metal forming generally, this process is done by passing the metal stock through the pair of one or more rollers to achieve uniform thickness or decrease in thickness, with the increase in length.
This cold rolling process is carried below the recrystallization temperature of the metal or, in most cases at room temperature, it is called cold rolling.
Usually, cold rolling is used after the hot rolling of metal to give the metal a clean and smooth finish. It also increases tensile strength and stiffness.
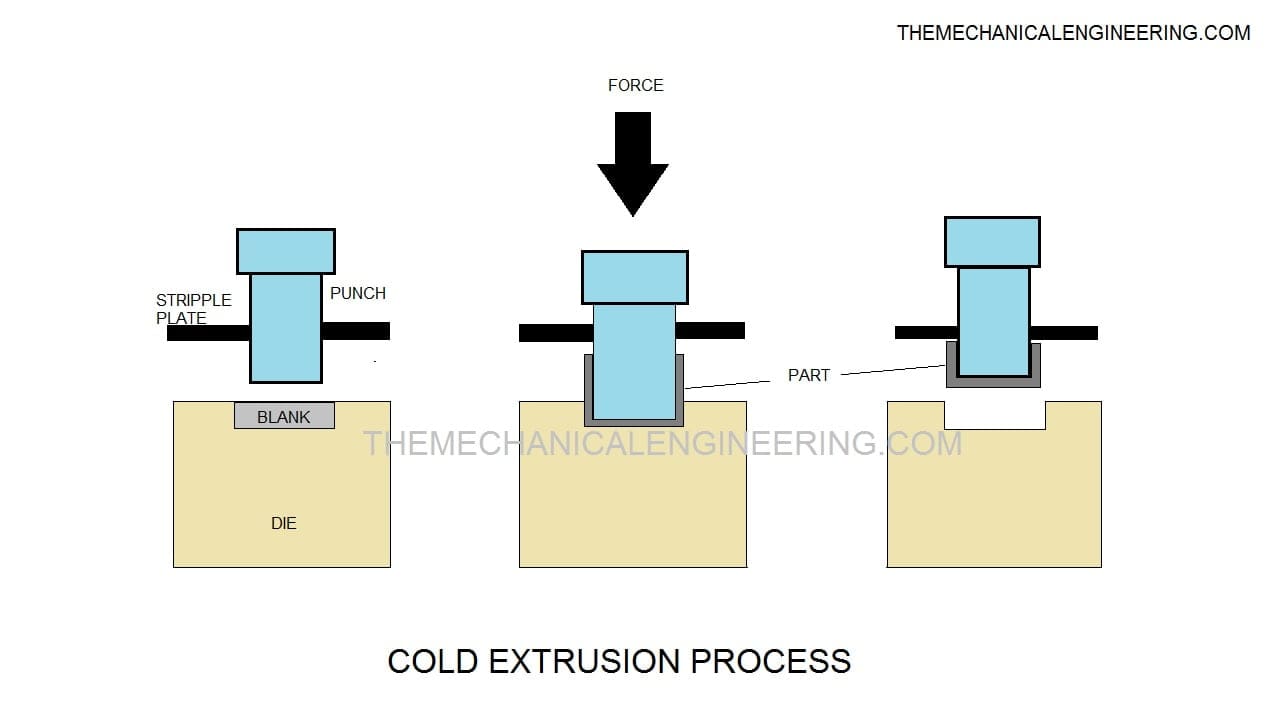
#2. Cold Extrusion:
Cold Extrusion is also done by passing the metal stock or piece through the dies by applying a compressive force to change the shape of the metal piece.
And this method is carried out below the recrystallization temperature of the metal or at room temperature.
Generally, cold extrusion requires a huge amount of force as compared with the hot extrusion process. Usually, cold extrusion increases the strength of metal and provides a smooth finish. The materials produced by this method are fire extinguisher cases, shock absorber cylinders, etc.
#3. Cold Drawing:
Cold Drawing is also a forming method used to reduce cross-section and increase the length of metal stock. This process uses tensile forces to stretch the workpiece. In this process, the workpiece with a large cross-section area is forced to pass through a die with a small cross-section.
This deforms the metal piece by reducing the cross-section area and increasing the length of the metal piece. And, this process is carried out below the recrystallization temperature which is room temperature.
Cold drawing provides a material with a bright and polished finish, enhanced mechanical properties, and uniform dimensional tolerance. The material produced steel bars & wires.
#4. Bending:
In this process, the metal can be deformed by applying stress beyond the yield strength but below the ultimate tensile strength. There is no effect on the surface area of the metal.
In simple words bending means the deformation of metal over an axis. It is usually used to produce U-shaped and V-shaped materials.
#5. Shearing Process:
Shearing is the metal forming method also known as die-cutting. In this method, the metal sheet or flat metallic plates generally having a thickness of less than 6 mm are applied with the presser to induce a variety of stress so that the metal can be cut.
So, that the desired size or shape of metal can be achieved. Shearing includes several processes like punching, blanking, notching, nibbling, shaving, etc.
In the shearing process, we have two blades one is the upper blade and the other is the lower blade between these two blades the strip is placed, when the upper blade is moving down sheer force act on the metal strip bending the strip and further cracks start to nucleate and nucleation of cracks further lead to cut the metal strip.
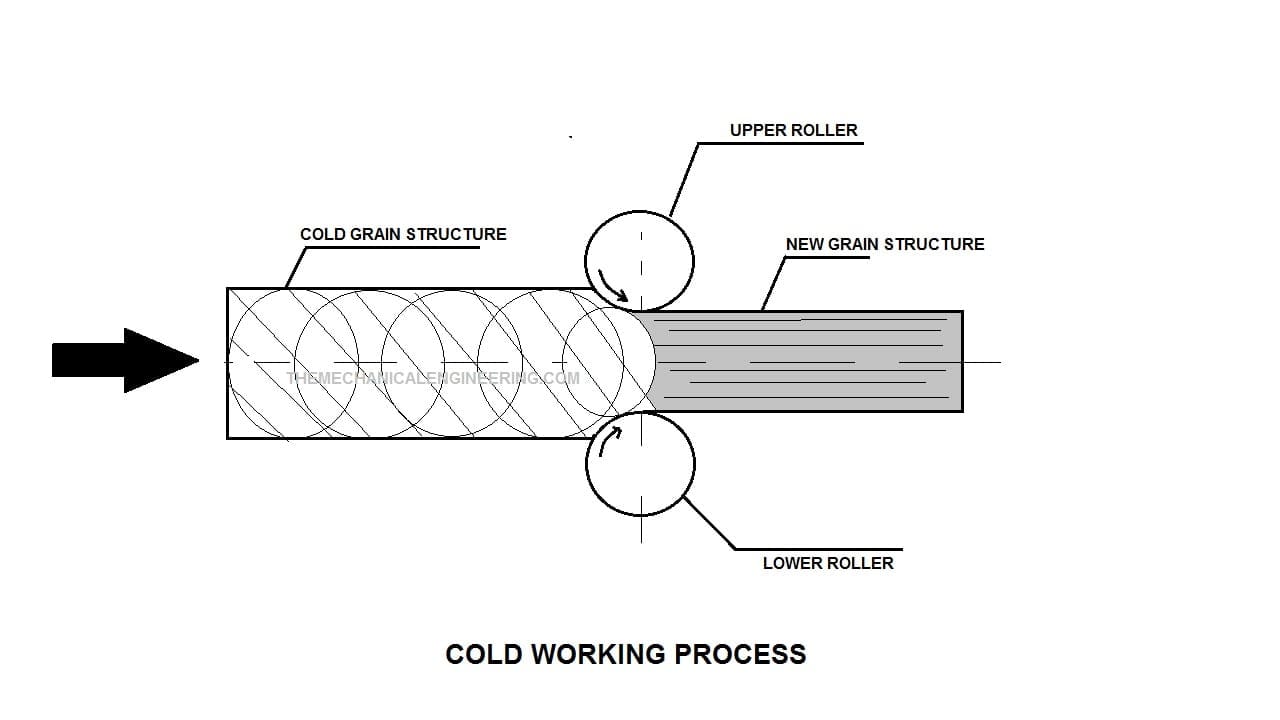
Cold Working Process:
Cold Working is the process done below the recrystallization temperature or at room temperature.
Under this process, the metal stock is placed behind the pair of two rollers.
Before passing the metal stock from the roller the metal is at room temperature or slightly above the room temperature but below the recrystallization temperature.
This method generally requires a high compression force as metal stock is passed at room temperature.
Due to high compression force the grain structure of the metal changes and forms a new shape. Cold working is done for the brittle metal.
Cold Working Video:
Cold Working Advantages:
The advantages of the cold working process include:
- The cold working procedure produces a smooth surface finish.
- This produces an accurate dimension of the parts.
- It increases the strength and hardness of the metal but reduces the ductility.
- As this procedure is performed without heat so no oxide is formed on the surface resulting in a smooth surface.
- This process is mostly used for bulk production.
- The defect in this process can be easily detected and can be removed.
- Since tensile strength, yield point, and ductility is improved so, this reduces the rust resistance.
- Prevents the loss of metal due to corrosion.
- Heating of metal is not required.
- As it does not require heating results in saving costs.
- Strain hardening occurs.
Cold Working Disadvantages:
The disadvantages of the cold working process include:
- It requires a clean and smooth surface.
- Brittle metals cannot be cold-worked properly.
- It requires a higher amount of force to begin and end the work.
- It requires more powerful equipment.
- Due to higher yield strength and low ductility, the maximum amount of deformation that can be given is limited by the capability of the press and hammer.
Application Of Cold Working Process
The cold working process is used to manufacture different products in industries like large flat sheets, metal tubes, screw heads, riveted joints, and much more. cold working is used by different industries like aviation, iron and steel, automobile, etc. Cold working is majorly used for ductile metals.
As this process gives smooth finishing and strength it is also used after the hot working of metals. By the application of the different methods of cold working like sheering, cold rolling, and cold extrusion multiple products are produced.
Internal Resources:
- Forging vs Casting
- Hot Working Process
- Laser Beam Machining
- Lathe Machine
- Milling Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Planer Machine
- Slotter Machine
Conclusion:
Cold-working is one of the important methods of metal forming that help manufacturing industries produce a different variety of products.
There are different methods of cold working like cold rolling, cold extrusion, cold drawing, sheering, and bending but the most commonly used method is sheering and cold drawing.
I hope, this article has helped you to get a clearer view of the Cold working of metal and its advantages & disadvantages.







Discussion about this post