In this article, we will study the Chassis Frame and its sub-topic like Definition, Types, Materials used in the chassis frame in detail, and the PDF of this article you can download at the end easily.
Every automobile engine be it a two-wheeler, a four-wheeler, or a sixteen-wheeler, consists of two main components which are chassis and body.
For chassis and Frame, the material we use generally is carbon steel; or aluminum alloys. This type of material is lightweight and easy to construct.
Let us know about chassis, its types first and then we will study frames and their types.
What is definition of chassis?
The word chassis is a French word that resembles the main structure of any automobile. In simpler words, a chassis is an automobile without its body. It consists of all the parts which are required to function the automobile.
The components used in the chassis are as follows.
- Frame: explained later in the article.
- Suspension systems: For the smooth running of the vehicle.
- Steering mechanisms: To direct the vehicle.
- Silencer: Exhaust component
- Storage battery: To provide power
- Wheels: For mobility
- Braking system: To stop the vehicle.
- Propeller shaft: For Power transmission.
- Engine: The power converting device.
- Clutch and gearbox: To control torque and speed of the engine.
- Radiator: Engine cooling component.
- Fuel storage: For storage of fuel.
Types of Chassis:
Several types of chassis are listed below with detailed descriptions:
- Conventional chassis
- Non-conventional chassis
- Full forward chassis
- Semi-forward chassis
- Bus chassis
- Engine at front chassis
- Rear chassis and
- Center chassis.
#1. Conventional chassis
The conventional chassis are also referred to as non-load carrying chassis. This is generally connected to a ladder frame. The body is made separately and then is mounted on the frame. Various mechanisms such as braking mechanism, suspension system, and transmission system are mounted on this. Conventional chassis are often used for large vehicles and heavy SUVs.
Advantages of Conventional chassis:
- Rigid structure
- High load-carrying capacity and
- Simple design
Disadvantages of conventional chassis
- More vibrations
- Handling of the vehicle is not great
#2. Non-conventional chassis
Non-conventional is also sometimes known as frameless chassis or unibody chassis. As we can see in the figure that there is no ladder frame, the body itself acts as the frame. This type of chassis support all the systems such as braking system, suspension system, steering system, etc. such chassis are used in modern automobiles with lightweight, most of the hatchbacks in India contains nom-conventional chassis.
Advantages of Non-conventional chassis:
- Higher body rigidity when compared to conventional chassis.
- Better handling and stability,
- The chassis makes less noise during the operation.
Disadvantages of Non-conventional chassis:
- Complex design.
- Less safe when compared to conventional chassis.
- Load-carrying capacity is also less.
NOTE: The next 5 types of chassis are classified based on engine location.
#3. Full forward chassis:
In a full forward chassis, the engine is situated outside the driver’s cabin. There is a fair distance between the driver and the front wheel. The drive-in such chassis is generally given to the rear axle. These chassis were used in several trucks in India earlier.
Advantages of full-forward chassis:
- More space for loading
- Great road holding capacity
- Provides fair vehicle balance
Disadvantages of full-forward chassis:
- The engine gets damaged in case of an accident.
- Less road visibility to the driver.
#4. Semi forward chassis:
Semi-forward chassis are those chassis, in which half of the engine is situated inside the driver’s cabin and another half outside the cabin. Such chassis often have rear-wheel drive. This types of chassis are common in India. The trucks using such chassis are often referred to as “tempo”. Such a construction is ideal for vehicles to fit more individuals in the cabin.
Advantages of semi forward chassis:
- Road visibility to the driver is better.
- More space to fit individuals in the cabin.
Disadvantages of semi forward chassis:
- Less space for loading goods
#5. Bus Chassis:
As we know that buses are flat from the front end. This means that the engine is situated inside the driver’s cabin. No part of the engine is situated out of the cabin. These types of engines are ideal for carrying more individuals. The driver’s seat is just above the front wheels of the bus. Bus chassis may have rear-wheel drives or front-wheel drives depending on the requirement.
Advantages of bus chassis:
- The full road is visible to the driver.
- Can carry more passengers.
- More vehicle stability.
Disadvantages of bus chassis:
- Very dangerous for drivers in case of an accident.
#6. Engine (front chassis):
It may sound similar to the full forward chassis but the major difference is that in the engine at the front chassis the driver seat is situated behind the engine. These engines are generally front-wheel drives, hence do not require a long propeller shaft. Such chassis may be used in big SUVs.
Advantages:
- Ideal for carrying more goods.
- Driver safety is more.
Disadvantages:
- The visibility of the road is very less.
#7. Engine at rear chassis:
In this type of chassis, the engine Is fitted at the rear side of the chassis. The power is given to the rear wheels and however, there are certain drawbacks of the engine at the rear chassis which are listed below.
Advantages of Engine at rear chassis:
- Short propeller shaft.
- More space.
- Good view for the driver.
Disadvantages of engine at rear chassis:
- Poor steering.
- Engine cooling problems.
- Poor acceleration due to shifted center of gravity.
- Requires a costly suspension system.
#8. Engine at center chassis:
As the name suggests in this type of chassis the engine is situated at the center of the chassis. This gives a wide floor area to ensure passenger space or more space for goods. These types of chassis are used in Royal Tiger Wordmaster busses.
Advantages of Engine at center chassis:
- A clear view of the driver.
- Good power transmission.
- Large floor space.
Disadvantages of engine at center chassis:
- There are problems with engine cooling.
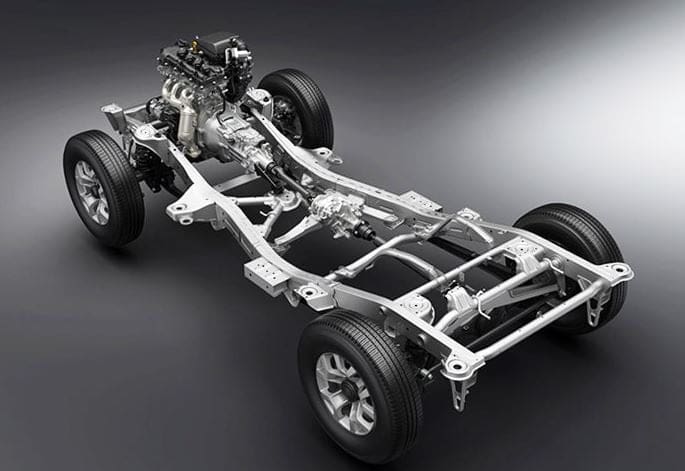
Now we will study frame,
What is frame?
When we talk about chassis and frames, we often consider chassis and frames to be the same thing. So, Are chassis and frame the same thing? The answer to this is NO.
The frame of any vehicle is the foundation on which the chassis is built. Or we can say that the frame is the main structural component of the chassis.
NOTE:- Before moving ahead in the article we must know the exact difference between chassis and frames
| Chassis | Frame |
| The skeleton of the vehicle that consists of most of the parts except the body of the vehicle is called the chassis. | The frame is the structural element of the chassis on which the chassis is built. |
| It consists of the parts like a braking system, suspension system, etc. | All the components of the chassis are fitted on the frame. |
| It is designed to move the vehicle even without the body | The frame is designed to provide a rigid base and support to the whole vehicle. |
Function of frame:
- The main function of the frame is to support the chassis and its components.
- To ensure proper positioning of all the Woking components of the chassis.
- To provide a rigid foundation for the whole vehicle.
- Another important function of the frame is to counter static and dynamic loads acting on the vehicle.
Forces acting on the frame of a vehicle:
When a vehicle is stationary or under motion, different forces are acting on that vehicle. These forces need to be countered for the smooth and efficient running of the vehicle.
The forces acting on the frame of the vehicle are given below.
Vertical bending: The force acting on an automobile due to the vertical load is called vertical bending. This force accommodates the weight of the body and passengers sitting inside the vehicle.
Longitudinal torsion: The longitudinal torsion acts on a vehicle when one wheel is lifted and the other wheels are grounded as shown in the figure. This tends to twist the frame; this results in a torsional effect.
Lateral bending: Lateral bending of the frame takes place when the vehicle is taking a turn or we can say during cornering. The centrifugal force acting on the frame tends to bend the frame laterally as shown in the figure.
Fore and aft loading: When the vehicle is suddenly accelerated or brakes are applied suddenly, forces start acting on the frame of the vehicle. During braking the forces act on the front side of the frame and during accelerating the forces act on the rear side of the frame.
Impact loads: When the vehicle strikes a solid structure it causes the frame to collapse, or lose shape. These types of sudden loads are known as impact loads. This also means that the vehicle has met with an accident.
Overloading: Overloading again is a type of vertical load which is due to excess weight on the vehicle.
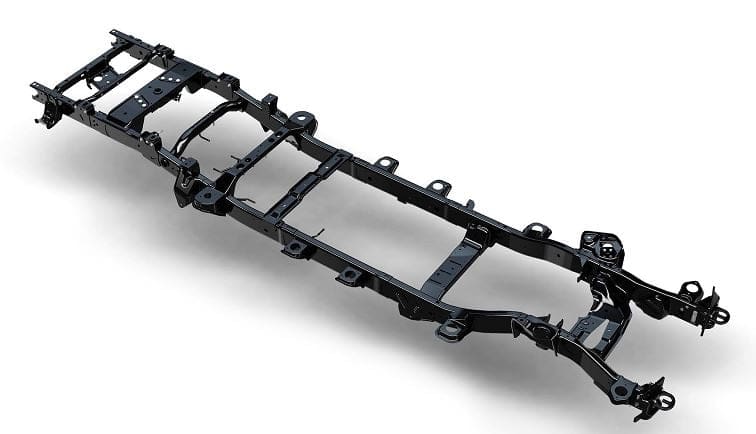
Types of frame:
There are three basic types of frames used in automobiles.
- Conventional frame
- Integral frames and
- Semi integral farmed.
#1. Conventional frames:
This type of frame is the oldest one but is still in use. The frame is connected to the chassis with the help springs. These frames have two long members and 5 to 6 cross members that are joined together using various fasteners.
Conventional frames are also known as non-load carrying frames because the load is transferred to the suspension system. These frames also support the engine, power train, and vehicle body.
When we look at the design of the conventional frames, we can see that they are broad at the rear end and narrow at the front end. This is because the narrowed front end gives better steering to the vehicle. The conventional frames are widely used in trucks.
Advantages of conventional frames
- The load-carrying capacity is high.
- Simple design.
- Easy to dismantle the frame.
Disadvantages of conventional frames
- Conventional frames are heavy
- They tend to vibrate due to the fasteners used.
#2. Integral frames:
Integral frames mean that there is no frame. Or we can say that the body itself performs the function of a frame. These are also called frameless, chassis less, or mono units.
All the important systems are attached to the body itself. This means that there is no need for any assembly work. Nowadays these types of frames are very common in small vehicles.
Advantages of integral frames
- Lightweight.
- Minimal cost.
- Compact design.
Disadvantages of integral frames
- Complex structure.
- Repairing the frames is difficult.
#3. Semi-integral frames:
In the Semi-integral frames, the half body is made of a frame and the other half is made of the frameless unit. The engine, gearbox, and heavier components are supported by the framed side.
The framed side is then bolted or attached to the frameless unit by welding. In some vehicles, the frame is fitted on the front side, and in some, it is fitted on the rear side. These structures are common in some European and American countries.
Advantages of Semi-integral frame
- If the vehicle meets an accident the damaged part can easily be removed and replaced.
Disadvantages of semi-integral frames
- Repairing these frames is very difficult.
Internal Resources:
- Clutch complete Notes
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Battery Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Electronic Ignition System
- Different Types of Clutch
- Lubrication System Types
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Flywheel
- Camshaft
- Crankshaft
Reference [External Links]:
- https://www.ignou.ac.in/upload/Unit-8-61.pdf
- https://www.gpmanesar.ac.in/GPContent/CBT-.pdf
- https://gomechanic.in/blog/types-of-car-chassis/
So here we finally studied all the Chassis and Frames in detail. I hope you have understood this topic. If yes then please share it with your friends and family. Do let me know what further topic I can help you with. Till then Thank you so much for visiting. Bye












Discussion about this post