An air suspension system is a suspension system in which an air spring or airbag is used instead of a metal spring (coil or leaf) to support the vehicle on the axles with an organization of the airbags.
In this article, we are going to study What is Air Suspension System? How does it work? and Construction or main parts, Types, Functions, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications in detail.
Note: At the end, I have attached the PDF format of this article you can download it.
The air suspension system works on the principle of using compressed air to vary the height of the suspension system of the vehicle. In simple words, air suspension is a suspension where the properties of air are used for cushioning effect.
The bumps on the road compress airbags and they bounce up and down allowing the wheels to move. The airbags are nothing but a rubber bladder that holds air, usually made from textile-reinforced rubber or a composite of rubber and polyurethane.
The materials are used to provide structural integrity, air-tight construction, and resistance to corrosion. These bladders are referred to as bellows.
Bellows are nothing but a column of air confined within a rubber and fabric container that looks like an automobile tire stacked one over the other.
The other types used are piston type and elongated bellow type. The airbags act like springs when compressed. The compressed air is supplied using an air compressor motor. A height sensor is used to sense the change in height of the suspension when the vehicle is loaded. The compressed air is used to inflate the airbags and raise the chassis from the axle.
An on-board air receiver tank that stores the compressed air is used for supply without any delay. The basic utility of the air suspension system is to keep the height of the vehicle constant when the load on the vehicle varies and to provide stability to the vehicle by absorbing road shocks.
The installation and layout of the air suspension system vary from vehicle to vehicle but the working principle remains the same.
Unlike a hydropneumatic suspension, air suspension does not use pressurized liquid, but pressurized air. These systems have been in use for around forty years and have proven to provide the smoothest and shock-free ride.
It is mainly used on different heavy-duty trucks, trailers, and buses today. Modern electronically controlled systems in automobiles and light trucks feature self-leveling along with raising and lowering functions.
History of Air Suspension System:
Sir William brush is known as the father of suspension systems in automobiles. Air suspension system dates back to the early 1900s.
Archibald Sharp, a British engineer patented a method for making a seal allowing pneumatic or hydraulic apparatus described as a rolling mitten seal, in January 1901. He also applied for the use of the device to provide air suspension on bicycles.
In 1909, a company named Air Springs Ltd started producing the A.S.L. motorcycle. The motorcycle had pneumatic suspension at front and rear, a rear suspension being usual at that time in any form of motorcycle.
On 22 January 1901, William W. Humphreys patented the idea ‘Pneumatic Spring for Vehicles’ which consisted of a right and left air spring longitudinally channeled nearly the length of the vehicle.
During world war II, the U.S. started using air suspension for heavy aircraft in order to save weight. Air suspension systems were also used in heavy trucks and aircraft to provide self-leveling suspension. This made it possible for the axle height to be independent of the vehicle load.
The Citroën DS started using four-wheel hydropneumatic suspension in 1955. Air suspension experimented on EMD’s Aerotrain in 1956. General Motors developed air suspensions for trucks and airplanes using the world war II experience.
It introduced air suspension on the new 1957 Cadillac Eldorado Brougham. Several other cars such as the Rambler ambassadors, American motors “cross country” station wagon, Eldorado Seville, Borgward P 100, Mercedes-Benz W112 started using self-leveling air suspension systems by the early 1960s.
It was followed by Rolls-Royce in 1965 and Ford motor company in 1984. In 1986, the first electronically controlled system was launched by Toyota, a semi-active full air suspension system (spring active, variable attenuation force). In 2013, Tesla model A started offering height-adjustable air suspensions.
Air Suspension System Definition:
An air suspension system can be defined as a type of suspension system which uses properties of air inside a column made up of reinforced rubber for the cushioning purposes of the vehicle.
The column is also called a bellows which can withstand the highly pressurized air. The bellows inflate and template when the air is filled and released respectively.
The bellows are used to absorb the shocks on the suspension instead of the traditional metallic springs.
Air suspension systems use height control valves to measure the amount of air required in the bellows according to the vehicle load conditions.
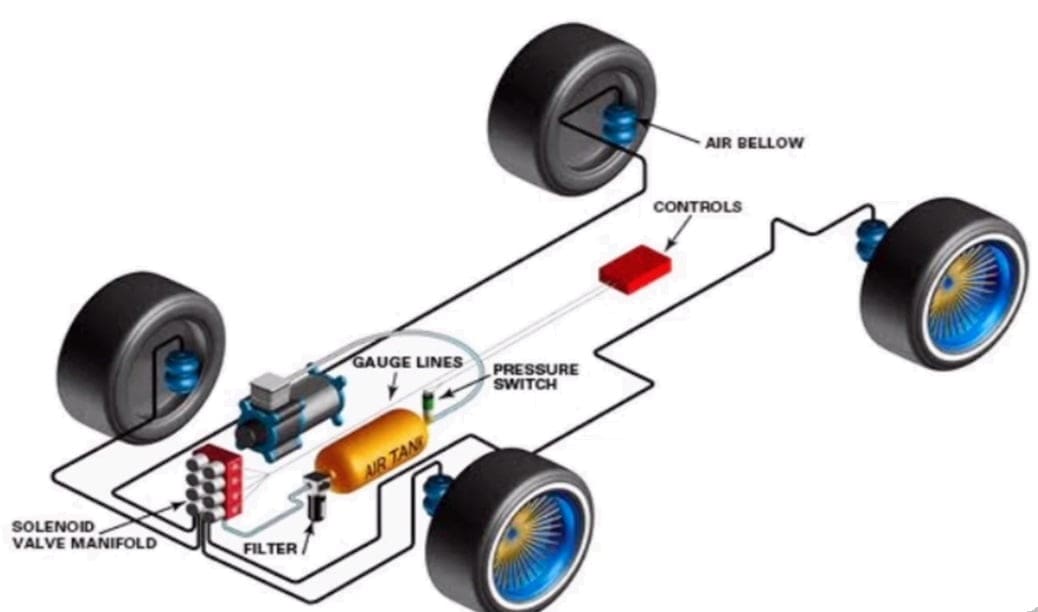
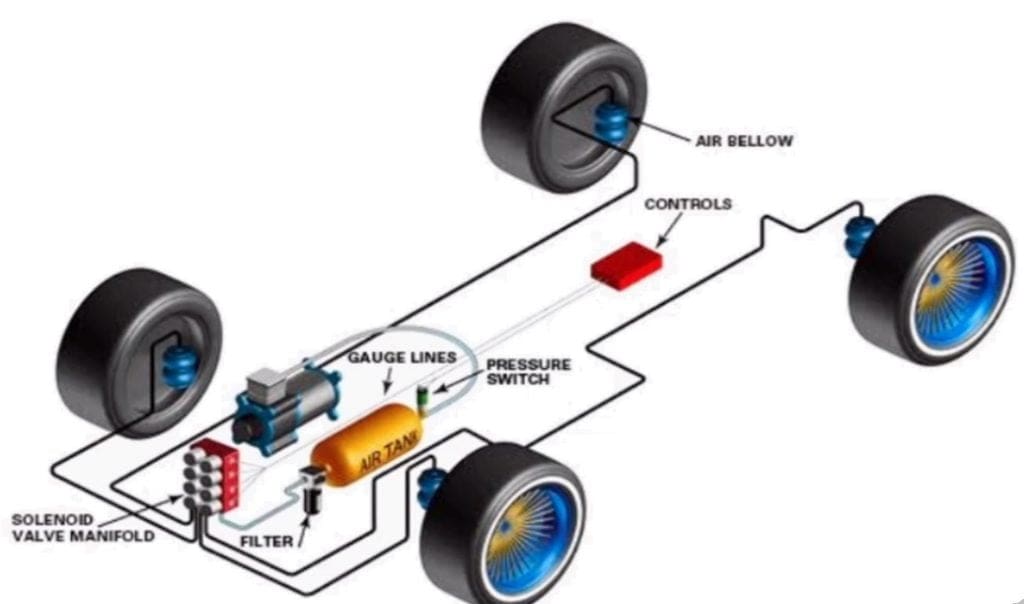
Construction or Main Parts of an Air suspension system:
The Air suspension system consists of three basic components namely the air compressor, air accumulator, supply line, airbag, the height control valve, and solenoid (in electrical systems).
#1. Air compressor:
The Air compressor is the primary component of the air supply system in the suspension. It works by drawing the atmospheric air into the pump and compressing it to a pressure of about 240 MPa through a filter.
It is generally mounted on the vehicle’s frame or in the trunk. The drier in the compressor uses a substance known as a desiccant to absorb the moisture from the air before the air is sent into the system.
A desiccant is an absorbent substance, a substance that can hold another substance within itself. This is done to avoid the moisture in the air and prevent the moisture from getting into the system as it can wreak havoc inside a closed system with the reactions.
The compressor can be activated either manually or automatically and can be controlled by the driver itself or automatically in an electronic system or a combination of both.
#2. Air accumulator:
Some advanced compressors need a storage medium to store the high-pressure air produced. These storing mediums are called air accumulators.
Air accumulators provide an even transition between the pressures. A safety relief valve is also attached to the accumulator to release the excess air.
#3. Supply line:
Supply lines are used to carry the compressed air to the airbags. It is similar to the common high-pressure airlines and is routed along with the frame of the vehicle.
These are mostly made up of rubber or polyurethane composition but they can also be replaced by custom steel lines which offer a cleaner look and more rugged construction.
#4. Airbag:
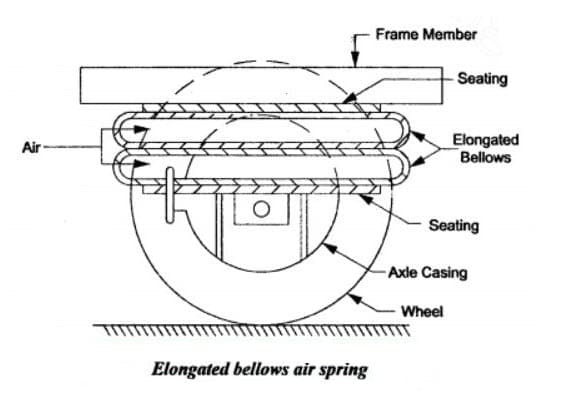
Airbags are simple rubber that holds the air. It is also referred to as air bellows. The other types of airbags include piston type and elongated bellow type.
Airbags use the compressive abilities of air and rubber to absorb vibrations and raise or lower the vehicle. The compressed air is pushed into the airbags to inflate it and increase the height of the suspension. These are located in the middle of the frame of the vehicle and the vehicle axles.
Airbags allow to lift and level up a sagging vehicle when it is towing or carrying uneven loads. It is adjustable according to the load which allows compensating for the inconsistent load and is typically made up of polyurethane or textile reinforced rubber.
The modern airbags are manufactured using the same method as that of tires by using high-strength cords which are encapsulated in rubber.
#5. Height control valve:
The height control valve is a type of sensor which detects the change in the height of the axle with respect to the frame. Mostly these are mechanical valves but electronic height control mechanisms are available in modern vehicles. Height control can also be referred to as HCV.
It is attached to the frame of the vehicle and an L-shaped linkage connects the HCV to the axle. When the axle moves up and down with respect to the frame, the linkage travels the valve or electronic mechanism.
In mechanical valves, HCV is located between the air supply line from the accumulator to the airbags. HCV also has an exhaust port which is used to release the air when the airbags deflate. HCV controls the height of the vehicle.
#6. Solenoid:
The solenoid is present only in electronic air suspension systems. When the control linkage moves up or down, an electronic sensor sends information to an electronic control unit (ECU) which is the central control system. These controls open or close the solenoid valves as required to inflate or deflate the airbags.
How does Air suspension system works or Working?
The air accumulator supplies air to the valves (HCV) which are attached to the frame of the vehicle. The valves are connected to the airbags via the supply lines.
At the point when the load is added to the vehicle, the HCV linkage deflects and travels the valve in accordance with the load on the vehicle to keep the suspension at a constant height.
The valving of the HCV supplies air to the airbags according to the deflection on the linkage. The supplied air inflates the airbags and brings the suspension back to its original position.
This ensures a correct ride stature and the HCV linkage moves to an unbiased position. The valves also return to their original state and secure the airbags to keep up the best possible ride height.
When the weight is expelled from the vehicle or the suspension system, the load on the axle moves away and returns to its original position.
The air is released from the airbags through the exhaust port and the linkage climbs to its neutral position. After this, the exhaust port is shut and the remaining air inside the airbags is locked again, keeping up the correct ride height.
What are different Types or Classification of Air suspension system?
There are mainly three types of air suspension systems based on the design of the air springs:
- Bellow type air suspension system
- Piston type air suspension system
- Elongated bellows type air suspension system
Types based on the working:
- Full air suspension system
- Semi air suspension system
Types of air bellows:
- Double convoluted bellows
- Sleeve bellows
- Rolling lobe bellows
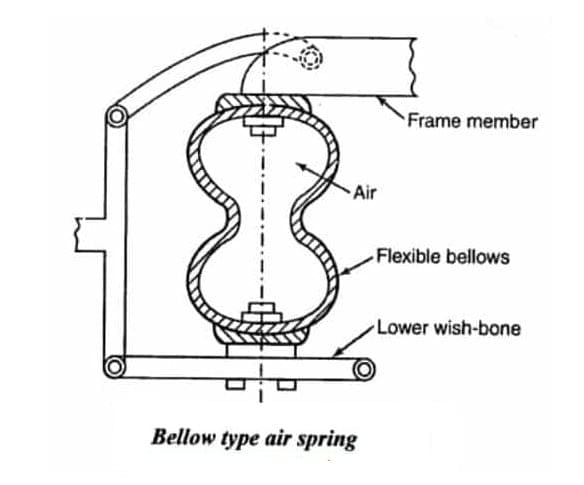
#1. Bellow type Air Suspension System:
This type of system consists of rubber bellows or rubber bladders. It consists of a circular rubber having two convolutions for the proper transition when compressed air is filled or released.
In simpler words, the traditional coil spring suspension system is replaced by convolutional bellows. It is a column of air confined within a rubber and fabric container that looks like an automobile tire stacked one over the other.
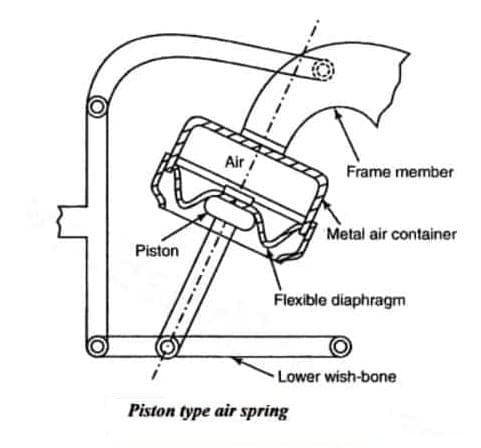
#2. Piston type air suspension system:
This type of system has a metal-air container in the form of an inverted drum. The drum is used in place of a spring. It also has a sliding piston connected to the lower wishbone. A diaphragm is used to provide a seal and its outer circumference is tightly connected to the lip of the drum.
#3. Elongated bellows-type air suspension system
An elongated bellows-type air suspension system is used when the air suspension is employed to the rear axle of the vehicle. These are just like the bellow type spring but approximately rectangular in shape having two semi-circular ends. These elbow-shaped structures are linked between the rear axle and the frame of the vehicle.
#4. Full air suspension system:
The full air suspension system implies a fully automatic or adjustable suspension system. This system includes replacing the conventional suspension system on both axles with a full air suspension system.
These filter out the minor unevenness on the road surfaces and thereby increase ride comfort. The components in this system include the compressor, accumulator, airbags, height sensor, supply lines, and the electronic control unit (ECU).
#5. Semi air suspension system:
The semi-air suspension system implies supporting the existing conventional suspension system with the use of air springs. This system is often used on vehicles that regularly carry heavy loads.
In this system, the air spring is fitted between the chassis and the rear axle to raise the ride height of the vehicle when under load and to generate a constant ride height regardless of the load. This system, therefore, helps increase the level of comfort and stability of the vehicle.
#6. Double convoluted:
The double convoluted spring looks like two oval-shaped structures horizontally placed one over the other. The bellows are attached to the bead plate by a permanent crimp in the plate.
These have more load carrying capacity, shorter stroke, and a more progressive spring rate which is suited for use on most front suspension systems where the spring sits considerably inboard of the load point. Convoluted springs provide good vibration isolation and linear or angular actuation.
#7. Sleeve bellows:
It springs with a smaller diameter, a longer stroke, and a more linear spring rate. The bellows are attached to the bead plate by an external clamp. These are best suited for rear suspension systems where the travel requirement is more. It provides good vibration isolation but only linear actuation.
#8. Rolling lobe bellows:
The rolling lobe bellows have a piston at one end of the bellows, in place of a bread plate. It is generally not recommended for vibration isolation and is mostly found in vehicle suspensions.
What are Characteristics of an Air suspension system?
The air springs are soft initially when the vehicle is not loaded, but the stiffness increases with load due to increasing air pressure inside the air spring. So, the ride quality is the same when the vehicle is in loaded and unloaded conditions.
The ride height of the vehicle or suspension is kept constant by varying the air pressure when variations occur in the loading conditions.
The ability to adapt the stability to different situations and vary load capability. These systems control many things from ride height to bag pressure, offering a smooth, controlled drive.
The air springs absorb the road shocks and uneven surfaces thus increasing the stability of the vehicle.
These systems are designed to maximize safe load-carrying capacity, stability, and overall ride quality.
Advantages of air suspension system:
- Air suspension causes less wear and tear on the suspension system and vehicle components, due to reduced harshness and vibration. Air suspension compensates for potholes, uneven surfaces and speed bumps in the road allowing the vehicle a smooth ride over the road surface.
- Greater cornering speeds and levels of control when turning corners can be achieved with air suspension, as the vehicle is better suited to the conditions of the road.
- Air suspension provides consistency across all wheels, and there is a lower risk of body roll when turning corners, less risk of breakages and less load shifting and damage caused due to reduced vibrations through the suspension.
- Air suspension makes for a more comfortable ride on poor quality roads and can improve control when off-roading due to the adjustable property. This reduces both the passenger and driver fatigue.
- The spring rate varies less between the loaded and unloaded conditions, as compared with that of conventional steel spring. This reduces the dynamic loading.
- The stiffness in the air springs increase when the deflection in the HCV linkage increases.
- Since the vehicle altitude is constant, changes in headlamp alignment due to varying height is avoided.
- As the vehicle can be adjusted according to the road type due to the air springs, it can provide a better fuel economy. For example, a suspension that is better suited to a particular road surface with better control can achieve higher corner speeds and lead to time-saving on routes with many turns.
Disadvantages of air suspension system:
- High initial cost is one of the major disadvantages of air suspension systems. This is because air suspension systems use components and technology which is costlier than a traditional spring suspension system.
- Cost of maintenance is also another major disadvantage of air suspension systems. These systems are reliable but require time to time maintenance. The maintenance becomes necessary because the vehicle can lose stability and control.
- These are also prone to mechanical issues. Any malfunctions from rust or moisture damage from the inside, or a fitting failure of the supply lines inside the system can cause mechanical issues in the system. Leaks in the airbags are also common and can cause a compressor burnout.
- If the linkage does not operate properly, the ride height of the vehicle could be disoriented.
- Air suspension systems are more complex systems and they require larger areas to operate.
Difference between the air suspension system and conventional suspension system:
| Air suspension system | Conventional suspension system |
| In the air suspension system, airbags or bellows are used. | In conventional suspension systems, metallic springs (coil or leaf) are used. |
| Pressurized air is used for the cushioning effects. | The elastic properties of spring are used for the absorbing effect. |
| Increased ride quality and comfort with noise level reduction. | Riding comfort and quality is less as compared to air suspension |
| Springing rate is less between loaded and unloaded conditions | The springing rate is more as compared to air suspension |
| The stiffness of the system increases with an increase in deflection of the linkage | The stiffness of the system decreases with an increase in deflection of the linkage. |
| Reduces fatigue to drivers and passengers. | More fatigue to drivers and passengers as compared to air suspension. |
| Consists of a Compressor, accumulator, height control valve, air springs, or air bellows. | Consists of a leaf spring or coil spring, shock absorber, shackle joint, bracket. |
| The ride height of the vehicle is constant. | The ride height of the vehicle varies with load. |
What are Functions of the Air suspension system?
- To increase the stiffness of the system when the load on the system is increased.
- To cause less wear and tear on the components and reduce the harshness and vibration.
- To absorb the road shocks and to provide a smooth ride on uneven road surfaces.
- To reduce the tendency of short wheelbase vehicles to bounce over rougher roads and terrain when the vehicle is empty.
- To improve the ride height of the vehicle according to the load weight and speed of the vehicle.
- To provide stability and control on the vehicle at high corner speeds.
- To focus the headlamp alignment in a constant direction.
- To provide better fuel economy by absorbing minute bumps on uneven surfaces and not decreasing the vehicle speed.
Applications or Uses of air suspension system:
- Air suspension systems are generally used in luxurious categories of vehicles including automakers such as BMW, Mercedes-benz, Audi, etc.
- These are also used in heavy-load carrying trucks and buses for stability and control.
- Railways also use air suspension systems for its coaches to provide better cushioning and ride height.
- It is also used in sports card and off-road vehicles due to the adjustable ride height.
Internal Resources:
- Brake System
- Chassis Frame
- Electronic Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Rack and Pinion Steering
- Lubrication System Types
- Flywheel, Camshaft, Crankshaft
- Clutch complete Notes
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Open Belt Drive vs Cross Belt drive
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Propeller Shaft
Reference [External Links]:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Air_suspension
- https://rdso.indianrailways.gov.in/works/uploads/File/Pamphlet%20on%20Air%20Suspension%20system%20fitted%20on%20Hybrid%20Coaches.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2214785321027358
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tSKGPIxKkWQ
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gEe-Wa6GZ6Y
So here we have studied in depth about the Air suspension system. Let me know your thoughts have been understood or not using the comment box. And if you like the article do not forget to share it with your friends and family. And let me know what other topics you are looking for?


![Different Types of Measuring Tools and their Uses [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Types of Measuring Tools](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Types-of-Measuring-Tools-300x171.jpg)
![Steel: Properties, Different Types and Applications [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Steel](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Steel-300x168.jpg)



Discussion about this post