In this article, we will study Definition, Parts, Working, Types, Operation, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application of Shaper Machine.
At the end of every article, you can easily download a PDF version of this article.
So let’s start with the introduction of Shaper Machine,
Shaper Machine Introduction:
A shaper Machine is a reciprocating type of machine that is used for producing horizontal, vertical flat surfaces. The workpiece is fixed on the table and the Ram holds the single point cutting tool. During forwarding stroke, (the single point tools attached to the ram and workpiece is fixed on a table).
Shaper Machine Definition:
Shaper Machine is a production machine in which the single point cutting tools are attached and the workpiece is fixed and while moving forward the tool cuts the workpiece and in return, there is no cut on the workpiece and used for producing flat and angular surfaces.
Now coming to Shaper Parts,
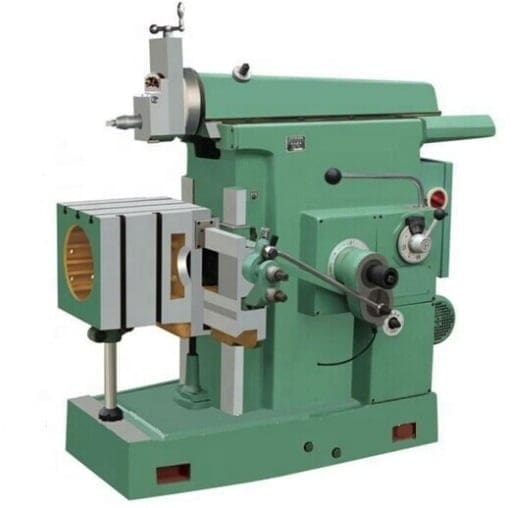
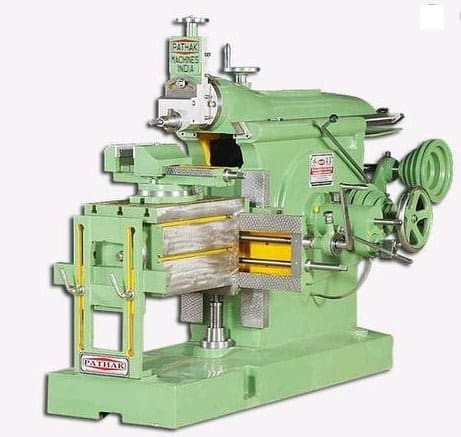
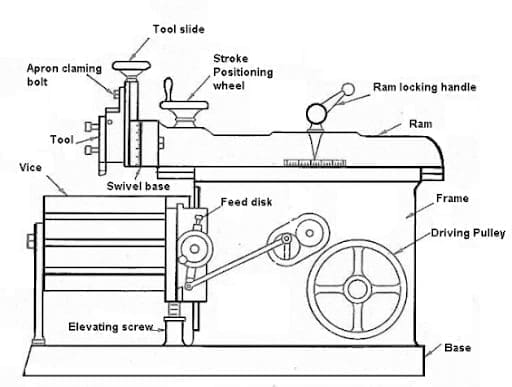
Shaper Machine Parts:
Let’s understand one by one,
Base:
The base is the most important part of the shaper because it holds all the loads of the machine. It is made up of cast iron. It absorbs vibration and other forces that occur while performing shaping operations.
Column:
The column is mounted on the base. It is also made up of cast iron. Column supports the ram that is moving forward and backward for operation. It also acts for covering the drive mechanism.
Table:
It is mounted on the saddle. It is also one of the important parts of the machine.
The table can be moved crosswise by rotating the crossfeed rod and also for vertical by rotating the elevating screw. It is a box-like casting with an accurately machined side and top surfaces.
These surfaces having T-Slots for clamping the work. In heavier type shaper machines, the table clamped with table support to make it more rigid.
Cross rail:
It is also mounted on the column on which the saddle is mounted.
The vertical movement and Horizontal movement is given to the table by raising or lowering the cross rail using the elevating screw and by moving the saddle using the cross feed screw.
Ram:
The Ram reciprocates and it carries the tool head in which single point cutting tool is attached.
The tool head is in the clapper box, which causes cutting action only in a forward stroke of the ram. The feed or depth of cut of the tool is given by down feed screw.
Shaper Machine Working:
In short, The shaper works on the principle of the Quick return motion mechanism.
Let’s understand in depth,
As you can see the above diagram of Shaper machine, The tool is hold by Ram and workpiece is fixed over table.
When we switch on the power the ram reciprocates with respect to the table that means the cutting tool cuts workpiece material in the forward direction and when moving return there is no cut.
The cutting process take place at low speed of ram and return stroke take place at high speed.
With the use of hand transverse wheel we can do up and down of the table.
Shaper Machine Working Video:
Now come to operation,
Shaper Machine Operation:
Generally, There are Four types of Operation performed on Shaper that are:
- Vertical Cutting Operation
- Horizontal Cutting Operation
- Inclined Cutting and
- Angular or Irregular Cutting Operation
Shaper Machine Types:
There are nine different types of Shaper Machine:
- Standard Shaper
- Vertical Shaper
- Horizontal Shaper
- Geared Shaper
- Universal Shaper
- Crank Shaper
- Draw cut Shaper
- Hydraulic Shaper and
- Contour Shaper Machine
We will study these machine in detail, Let’s start:
Standard Shaper:
Standard shaper is commonly use types of machine in the industry. During forward the cutting process occur and backward there is no cutting.
Vertical Shaper:
The movement of the tool in the vertical axis. The workpiece is kept on a table that can have a cross, longitudinal, and rotational movement.
Vertical Shaper is widely used for cutting slots, key holes, grooves etc.
Horizontal Shaper:
The ram holding the tool in a horizontal axis and the ram is reciprocating.
This type machine is also used for the production of flat surfaces, key-ways, external grooves, and more.
Geared Shaper:
Very less industry using this type of machine nowadays. In a Geared shaper, rack and pinion arrangement is utilized to make the ram reciprocate for cutting operation.
The speed and direction of the traverse depend on the number of gears and its arrangement in the gear train.
Universal Shaper:
The major advantages of Universal shaper is that, you can feed the table in all directions. Either horizontally, vertically or an inclined plane.
In this type of machine, you can also swivel the table about its own axis. This universal features enables to perform various types of operations on this machine.
Crank Shaper:
It is also very common types of shaper. The tool (Single Point) is reciprocating in motion equal to the length of the stroke and the work is clamped in position on an adjustable table.
Draw cut shaper:
In this machine, the workpiece metal is removed during the return stroke of the Ram.
Hydraulic Shaper:
In this type of machine, the reciprocating motion of the ram is provided by the hydraulic mechanism. This Hydraulic shaper uses the oil under high pressure and the end of the piston rod is connected to the ram.
The high-pressure oil first acts on one side of the piston and then on the other causing the piston to reciprocating and the motion is transmitted to the ram.
The main advantages of this machine the cutting speed and force of the ram drive are constant. From start to finish of the cut it does not makes noise and operates smoothly.
Shaper Machine Specification:
The following specification of shaper is:
- Weight of the Machine.
- Floor space required.
- Maximum stroke of Ram
- Drive types (Hydraulic, Gear and Crank type)
- Input Power
- Cutting to Return Stroke ratio
- Angular Movement of the table and
- Feed
Advantages of Shaper Machine:
Following Advantages of Shaper are:
- The tool (Single Point cutting tool) cost is low.
- The workpiece can be held easily in this machine.
- It produces flat or angular surfaces.
- Setup of Shaper is very easy and tool changing is also easy.
Disadvantages of Shaper Machine:
The following disadvantages of Shaper Machine:
- The cutting speed is not much high.
- Only one cutting tool can be fixed. There is no option for more than one cutting tool.
Application of Shaper Machine:
The following application of Shaper Machine are:
- A shaper Machine is used to make Internal splines.
- It generates straight and flat surfaces either horizontal, vertical or angular planes.
- It also makes gear teeth.
- Make keyways in pulleys or gears.
- It also Producing contour of concave/convex or a combination of these.
Understand Shaper Machine by Video:
Important FAQs of Shaper:
A shaper is a machine tool in the manufacturing industry that is used for removing material from a workpiece to produce a flat surface on the workpiece.
It works on a Quick return motion mechanism principle.
The following operation is performed:
Machining Horizontal, vertical, Inclined, Irregular surfaces and Cutting slots, keyways, grooves.








Discussion about this post