In this article, we are going to study What is Rack and Pinion Steering system is and its subtopic like Definition, History, Construction or Main Parts, Working, Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages in detail.
Note: The PDF of this article you can easily download at the end.
History of Rack and Pinion Steering System:
In the 1930s, German automotive manufacturer BMW invented the rack and pinion steering system, thereby using it in their cars. It was brought up as an alternative to the existing recirculating-ball steering system which was more complex and expensive to build.
American automakers were slow to adopt the technology and started using rack and pinion systems in the Ford Mustang II in the 1970s. An upgrade on the rack and pinion system was patented by Australian engineer Arthur E. Bishop in 1973.
The existing system tended to be over-sensitive when used at high speeds, which affected the stability of the wheels.
In Bishop’s system, the rack had varied tooth spacing along its length. The teeth at the ends were closely spaced and teeth at the center were more widely spaced.
Due to this, the steering wheel causes relatively little movement at the beginning of a turn and more movement as the steering wheel is further moved.
What is Rack and Pinion Steering?
Rack and pinion steering is a type of steering mechanism used in automobiles. It is the most common type of steering used in cars and small-sized trucks.
The rack and pinion Steering system is based on the conversion of the rotating motion of the steering wheel into a linear motion onto the wheels and consists of two gears namely, rack and pinion which assist in turning the vehicle relative to the driver’s needs.
The pinion at the end of the steering column meshes with the rack, which is a circular shape that moves either to the left side or right side according to the steering movement.
The rack and pinion steering system is the most widely used system in the automotive industry because of its driver-friendly and effective mechanism.
The rack and pinion are enclosed in a metal tube and each end of the rack is connected to a rod called a tie rod. It is preferred in the modern market because it provides a gear reduction which makes it easier to turn the wheels.
It has an advantage over the recirculating ball steering system in terms of weight, steering ratio, and effort required to rotate the steering.
Rack and pinion is a simple steering system that involves fewer parts as compared to recirculating ball steering. The friction involved is also less due to less number of parts involved.
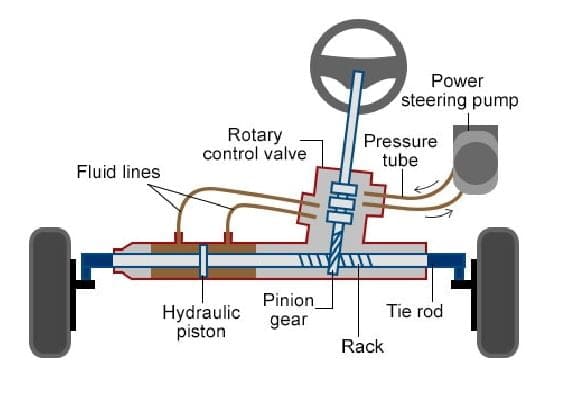
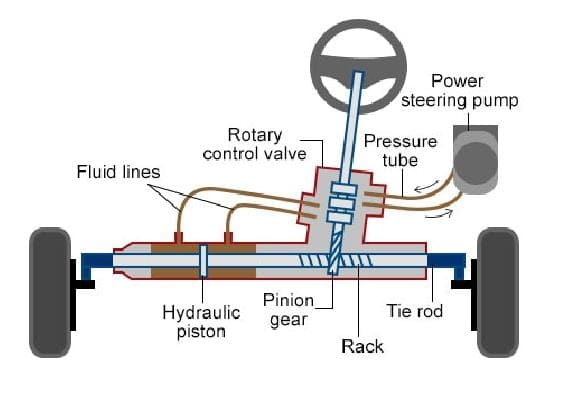
Construction or Main Parts of Rack and Pinion Steering system:
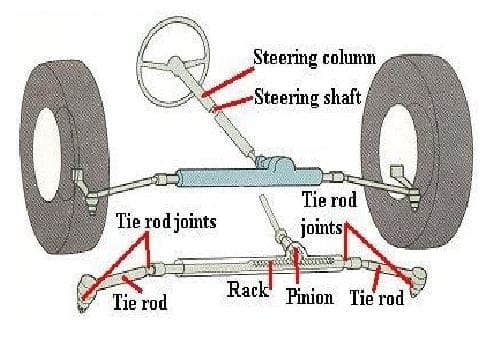
The rack and pinion steering system consists of the steering wheel, steering shaft, pinion, rack, tie rod, and tubular casing.
#1. Steering wheel:
The steering wheel is the part of the system accessible to the driver and is used to change the direction of the wheels. It is connected to the steering shaft at the other end.
#2. Steering shaft:
The steering shaft is the linkage between the pinion gear and the steering wheel. It rotates along when the driver rotates the steering wheel, which moves the pinion accordingly.
The shaft is enclosed in a section called the steering column. The pinion is fixed at the end of the steering column.
#3. Pinion:
The pinion is positioned over the rack. It moves along with the steering shaft when the steering wheel is rotated.
The pinion is a helical gear that rotates in a circular motion at a fixed axis. The teeth of the pinion mesh with that of the rack.
The size of the pinion gear decides the steering efficiency and stability. Smaller pinion offers lighter steering, so the number of turns needed is more and the vehicle stability is not compromised due to sensitivity (steering ratio).
A larger pinion offers better steering ability and decreases the number of turns but makes the steering too sensitive (higher steering ratio) which may compromise the stability. This is called gear reduction. Mild steel is the preferred material in the industry for manufacturing pinion.
#4. Rack:
The rack is attached to the pinion and in simple words, it is a straight bar with gear teeth. The gear teeth help it mesh with the pinion. When the steering wheel is rotated, the rotary motion of the pinion converts into linear motion on the rack.
To provide better driving feel to the users, automobile manufacturers have introduced a variable-steering ratio. This is a technique in which the rack and pinion system has a different tooth pitch at the center than it has on the outside. This provides a quicker response when starting a turn and also reduces the effort at the wheel’s turning limits.
Here also Mild steel is the preferred material in the industry for manufacturing racks.
Moreover, a spring-loaded pad is provided underside of the rack to reduce the backlash between the gears. Rack acts as the center of a three-piece rod, with ball joints called tie rod end at each end that allow the up and down movement of the wheels.
Note: Steering ratio is the ratio of the steering turned to the wheels turn. For example, if one complete revolution of the steering wheel (360 degrees) results in the wheels of the car turning 30 degrees, then the steering ratio is 360 divided by 30, or 12:1. Higher the steering ratio, less responsive is the steering.
#5. Tie rod:
The tie rod is connected to the spindle on each end of the steering rack. The tie rod end consists of two parts namely, the inner tie rod and the outer tie rod.
The inner tie rod is connected to the rack and is the longer of the two. The inner tie rod end is connected to the ball joint and the outer tie rod is connected to the steering knuckle.
The outer end is called the tie rod end. The tie rod is a major part as its function is to link the motion produced in the rack to the wheels to produce turning movement of the vehicle.
Moreover, the tie rod end helps with the stability of the steering knuckle. These are mostly made up of high-strength steel. Tie rods act as the pivot point between the steering shaft, rack, and steering wheel.
These are used to move the wheels when steered and make turning possible for the vehicle. The tie rod is responsible for the control and stability of the wheels.
#6. Tubular casing:
The tubular casing is provided as housing to the rack and pinion system. The rack and pinion gears are enclosed inside the metal tubes.
Step by Step Working of rack and pinion steering system in detail:
A rack and pinion steering system works on the principle of converting the circular motion on the steering wheel into linear motion on the rack.
This is made possible due to the meshing of the two gears (rack and pinion) which moves according to the steering shaft.
When a driver rotates the steering wheel, the steering shaft is rotated accordingly. Positioned at the other end of the steering shaft is the pinion gear, which also rotates along with the steering shaft.
The teeth on the pinion gear (helical type) mesh with the rack (straight bar type). When the pinion gear rotates, it moves the rack sideways in a linear motion.
The sideways movement of the rack transmits the motion to the tie rod end through the ball joint.
This allows for movement in the steering and suspension of the vehicle.
The tie rod end brings about change in the direction of the wheel thus assisting in turning the vehicle.
Functions of Rack and Pinion steering system:
The rack and pinion steering have three main functions:
#1. To convert the steering wheel’s rotational motion into linear motion is needed for the vehicle’s wheels to turn.
#2. To provide optimum steering ratio for easier turning of the wheels. This is done by varying the distance between the teeth at the center and the ends of the rack.
For better stability, the distance between the teeth at the center is wider and that at the ends is more closely spaced. Due to this steering causes relatively little movement at the start and increases momentum with the turn.
#3. To provide optimum gear reduction ratio for smooth turning of the steering wheel and decrease the effort needed to rotate the steering. This is done by selecting the optimum size of the pinion.
Smaller pinions provide lighter steering and more turns are required till the lock. Whereas, larger pinions provide sharper steering and less than required till the lock.
But the weight of the steering increases in case of a larger pinion and makes steering heavier.
How it is different from Recirculating ball steering system?
The rack and pinion steering system weigh less than the recirculating ball steering system, which helps improve the steering ratio. These systems are lighter because they don’t require the idler arms, pitman arms, center links, and tie rod sleeves found in the conventional steering systems.
Also, these systems are more straightforward and simple than the recirculating ball steering, due to less number of parts. So the friction is less with the rack and pinion system, as a result, the steering feels more compact and responsive.
Moreover, recirculating ball steering has a wide-ratio box which requires more revolution of the steering wheel to get the front wheel to turn lock-to-lock. Rack and pinion steering have a close-ratio box which requires less revolution of the steering wheel to get the front wheel to turn lock-to-lock.
This reduces the effort required by the driver to rotate the steering wheel from lock to lock. In a recirculating ball steering system, the worm gear and threaded rod are the vital parts for working in place of the rack and pinion gears.
Types of rack and pinion steering System:
There are two main types of rack and pinion steering systems, namely end take off and center take off.
- End take off: In this type of system, the tie rod is connected to the end of the steering rack via the inner axialrods.
- Centre take off: In this type of system, the bolts attach the tie rod to the centre of the steering rack.
Advantages of Rack and Pinion Steering System:
- Rack and pinion steering is a simple system with only two moving parts and as a result the friction in the system is very low.
- Rack and pinion steering system is light in weight due to less number of parts involved and hence provide a more compact system.
- This system works mainly with the help of the rack and pinion gears in contrast to the idler arms, pitman arms, center links and tie rod sleeves found in the conventional steering systems.
- The system has only four wear points in the linkage: the inner ball joints and the outer tie-rod ends.
- Rack and pinion requires lesser space to fit into a car which provides clearance for headers.
- This system provides a responsive and tight feel to the steering for the driver.
- It also requires less effort to steer in the rack and pinion system and the steering wheel requires lesser revolutions for the wheel to go from lock-to-lock.
- It also provides a constant and varying steering ratio at different ends of the rack. Mostly, there is little movement of the wheels at the start of the steering and it gradually increases when the steering is rotated.
- Since the parts involved are less, the rack and pinion system is cheaper compared to other systems in the industry.
Disadvantages of Rack and Pinion Steering system:
- Due to the limit on the number of teeth that can be cut into the rack, there is less travel available as compared to a recirculating ball system.
- Even though the amount of friction is less, it is concentrated on the same parts which as a result is under constant wear, possibly needing replacement after a certain time.
- Since there are fewer parts and the system has more connection with the road, the vibration and noise can be transferred to the driver and passengers.
- The impact force between the steering wheel and road surface can be transmitted to the steering wheel, which is called backlash. This phenomena happens due to the high reverse efficiency.
- The backlash also affects the durability of the steering system and its chances are more when the system is installed in a four- wheel drive vehicle.
- If the rack or pinion wears out, the steering wheel will feel loose or unstable at high speed and steering difficulty at slower speeds. The imperfections on the road will cause the vehicle to easily move sideways instead of staying in a straight line.
Application or Uses of rack and pinion steering system:
- Rack and pinion steering system is mainly used in cars, small trucks and SUVs, rather than recirculating ball steering system which is found in larger trucks, larger SUVs and other heavy-duty vehicles.
- BMW started using rack and pinion in the 1930’s.
- Later ford started using the system in 1974 mustang II and 1974 pinto.
- This system was also used by Hindustan ambassador Mark II.
- The other automotive companies which used the system are Maruti Suzuki, Toyota, Hyundai, Honda and Nissan among others.
Internal Resources:
- Clutch complete Notes
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Open Belt Drive vs Cross Belt drive
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Electronic Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Lubrication System Types
- Flywheel, Camshaft, Crankshaft
Reference [External Links]:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/rack-and-pinion-steering
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rack_and_pinion
Here we finally studied Rack and Pinion Steering system in detail. Let me know what else topic you are looking for?. And if this article information helps you then please do share it with your friends and family.





Discussion about this post