The Magneto Ignition system does not require a battery. It generates its own voltage for the primary. Magneto Ignition system is being extensively used in mopeds, scooters, wheelers, motorcycles, stationary engines, and aircraft reciprocating engines.
Here I have discussed the Definition, Construction or Parts, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of the Magneto Ignition System.
At the end you can easily download whole documents in PDF format.
So let’s start with the definition first,
Magneto Ignition System Definition:
Electricity is obtained from the magneto and that electricity is further used to drive the engine is known as Magneto Ignition System. The system has got its own current generating unit without the assistance of a battery and ignition coil.
The electric current that is required for it and is generated by the Magneto due to the low-speed efficiency of the system the starting quality of spark is poor and it will improve as the engine speed rises due to high-intensity spark.
It will occupy less space that’s why used in racing cars and two-wheeler.
Now we will study Construction,
Magneto Ignition System Construction or Parts:
The following main parts or components of the Magneto Ignition system are:
- Rotating Magnets
- Primary Winding
- Secondary Winding
- Fixed Armature
- Condenser
- Breaker-points or Contact Breaker
- Distributor
- Ignition Switch and
- Spark plug
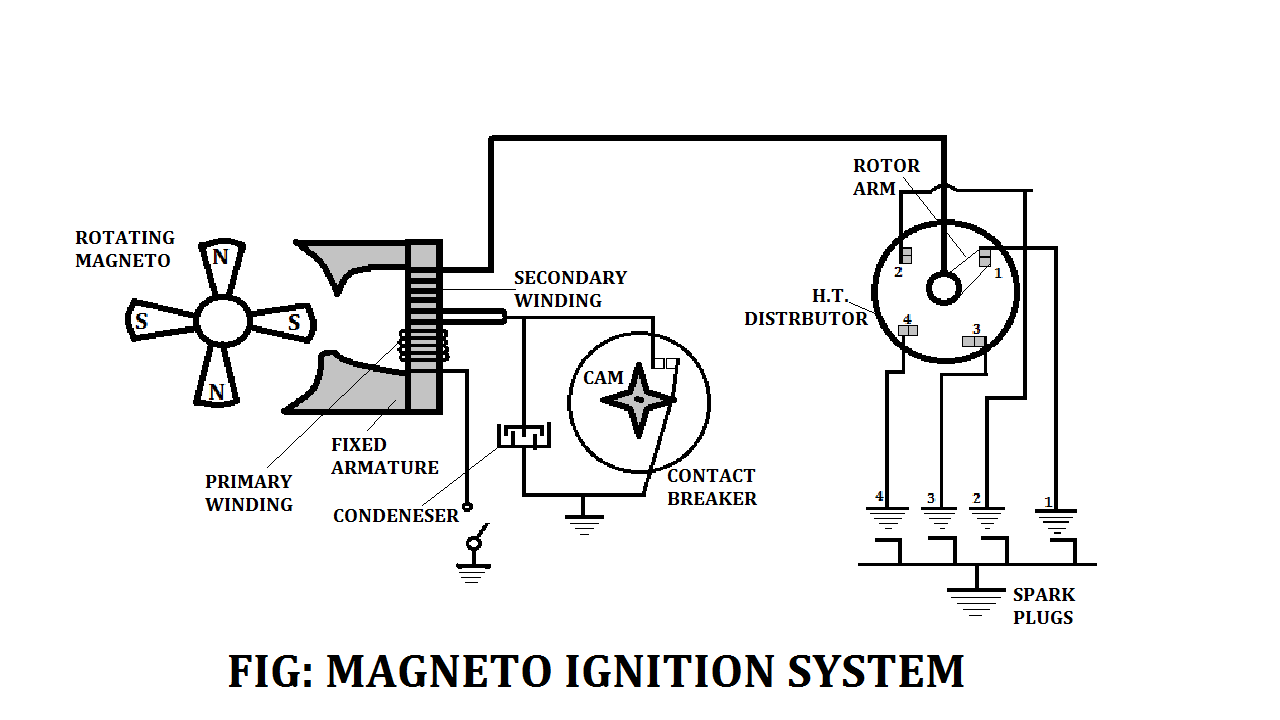
Rotating Magnets:
The magnets substituting the battery and ignition coil, have a four-pole magnet, two pole shoes, the primary and secondary coils.
When the magnet rotates, the direction of the magnetic flux through the soft iron core of the coil reverses direction. As a result of which a voltage is an inductor of the primary and secondary coils.
Primary Winding:
It draws power from the source and is usually more in number.
Secondary Winding:
It delivers the energy at the transformed or changed voltage to the load.
Fixed Armature:
fixed armature carries an alternating current.
Condenser:
The highly charged condenser discharges itself into the primary circuit and this produces a rapid change in the magnetic flux.
Due to this rapid change in the magnetic flux, a very high voltage is induced in the secondary coil and that will be sufficient to produce a spark, discharge, and ignite the fuel-air combustible mixture.
Breaker-points or Contact Breaker:
The breaker points and the condenser produce an increase in the rate of change of magnetic flux.
When the breaker points are opened by the cam mounted on the rotor shaft the condenser gets charged by currents from the primary coil.
Capacitor:
The Capacitor used in the magneto ignition system is a simple capacitor in which two metal plates are separated by insulating material between them.
Mostly air is used but for a particular application, high-quality insulating material is used.
Distributor:
The distributor is an enclosed rotating shaft that has mechanically timed ignition.
The distributor’s main function is to route secondary voltage from the ignition coil to the spark plug so that the correct firing order and correct amount of time occur.
Ignition Switch:
It controls the magneto ignition system.
Spark plug:
It is used to ignite the air-fuel mixture.
Electrical energy is thus transmitted from the spark plug to the fuel mixture and it will ignite so that power stroke will be obtained.
Magneto Ignition System Working Principle:
The working principle of the Magneto ignition system will be the same as that of the coil ignition system.
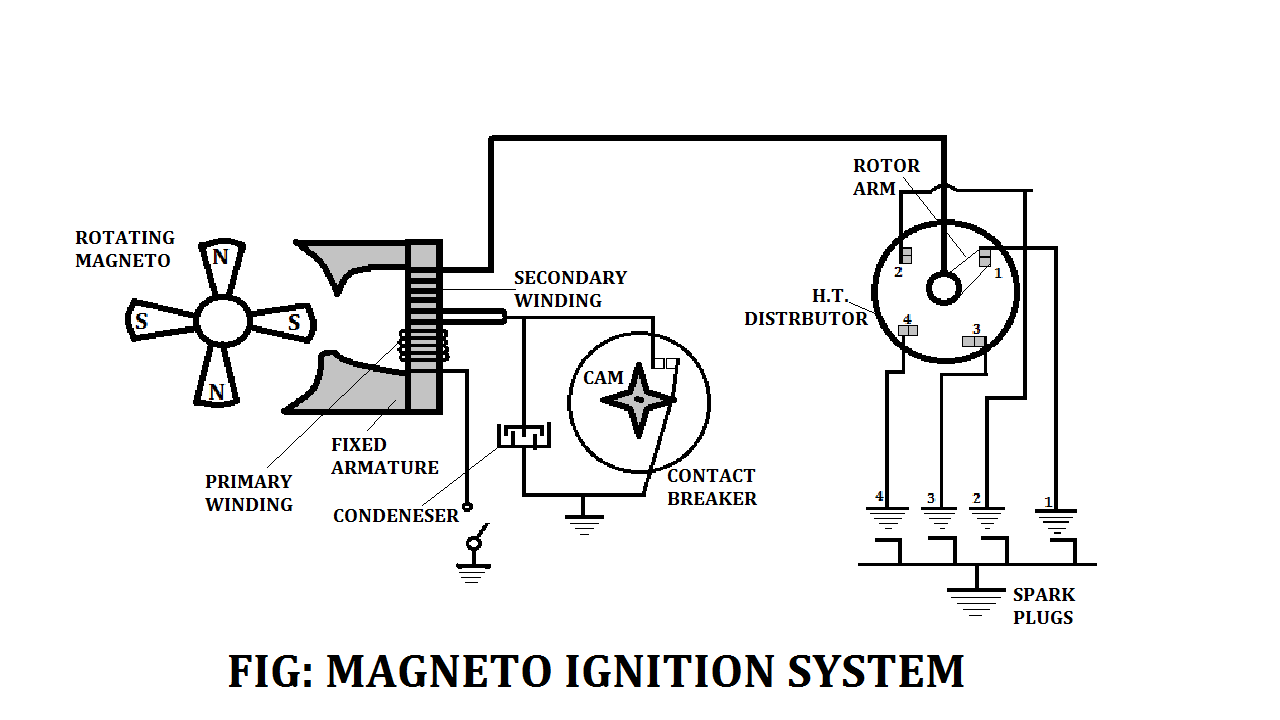
The primary circuit flux is changed and a high voltage is produced in the secondary circuit With the help of a cam.
The variation of the breaker current with speed for the coil ignition system and the Magneto ignition system.
Armature having wound upon it in the primary coil of a few hundred turns of enameled copper wire and the secondary coil of several thousand turns of fine insulated wire rotates in a permanent magnetic field.
The modern trend is to keep the armature stationary and the magnets rotating.
By this action, the primary voltage is generated in accordance with the laws of the electric generator which is then transformed into a very high secondary voltage exactly on the lines described in the battery ignition system.
It can be seen that since the cranking speed at the start is low the current generated by the Magneto is quite small.
The engine speed will increase as we increase the current. Thus, with Magneto there is always a starting difficulty and sometimes a separate battery is needed for starting.
Magneto is better for high speeds and therefore is widely used for sports and racing cars, aircraft engines, etc.
Magneto Ignition System Working Video:
Magneto Ignition System Types:
There are three types of Magneto Systems:
- Rotating Armature or Rotating Magnet Type
- Rotating Coils Type and
- Polar Inductor Type
Rotating Armature or Rotating Magnet Type:
The armature consists of the primary and secondary winding. All rotate between the poles of a stationary magnet.
Rotating Coils Type:
The magnet revolves and the winding is kept stationary.
Polar Inductors Type:
In the polar inductor type, both the magnet and the windings remain stationary but the voltage is generated by reversing the flux field with the help of soft iron polar projections called inductors.
Magneto Ignition System Advantages:
The following advantages of the Magneto Ignition system are:
- More reliable as there is no battery of connecting cable. Moreover with the coil ignition unit, if the battery has run down, the engine cannot be started unless a spare battery is available.
- It is more suitable for ignition at medium to very high engine speeds although there is a tendency to give excessive voltages in the latter case unless the Magneto is designed specifically for these high speeds.
- In modern designs of Magneto, using the more recent cobalt steel and nickel aluminum magnet metals very light and compact units can be made which occupies a very limited space.
- The more recent Magnetos with modern magnet alloys are capable of giving very low starting speed ignition characteristics
- The automatic timing of the ignition can now be affected as readily as with coil ignition.
- The powerful spark at high engine speeds that previously caused the plug electrodes to burn away can now be prevented by the use of suitable shunts on the Magneto.
Magneto Ignition System Disadvantages:
The following disadvantages of the Magneto Ignition system are:
- Not better sparks for low-speed starting.
- It is costly to manufacture and to replace its component parts.
- The half-speed engine driver is usually complex as compared to the coil ignition system.
- It has an effect over the complete ignition timing range, and with the ordinary Magneto, the spark timing adjustment affects the voltage or energy.
- It cannot be easily maintained.
Magneto Ignition System Application:
The following application of the Magneto Ignition system are:
- In the engine where other electricity means not available such as lawnmowers and chainsaws.
- Aviation Piston Engine and
- Racing Cars.
- In the engine where other electricity means not available such as lawnmowers and chainsaws.
- Aviation Piston Engine and
- Racing Cars.
Internal Resources for You:
- Flywheel, Camshaft, Crankshaft
- Piston, Connecting Rod
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Electronic Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Clutch complete Notes
- Lubrication System Types
- SI Engine vs CI Engine
Reference [External Links]:
So This is a small presentation on Magneto Ignition System. If you like the articles do share them with your colleague and on social platforms too.





Discussion about this post