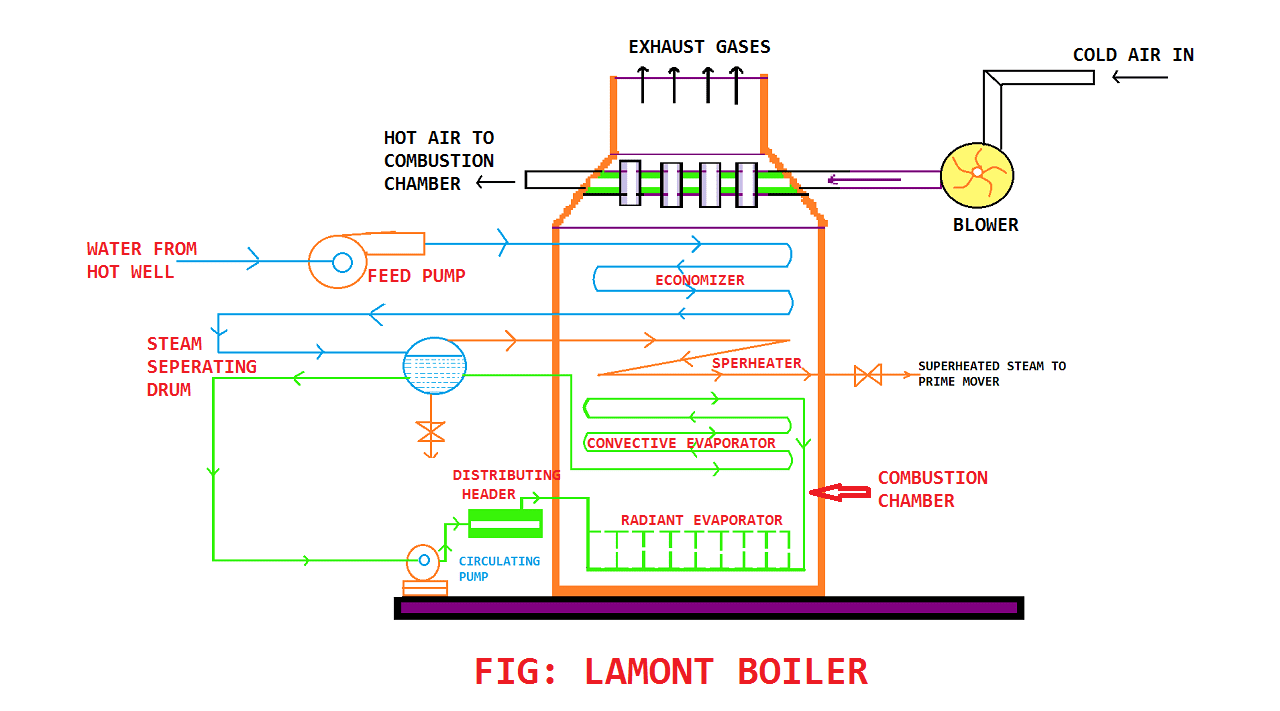
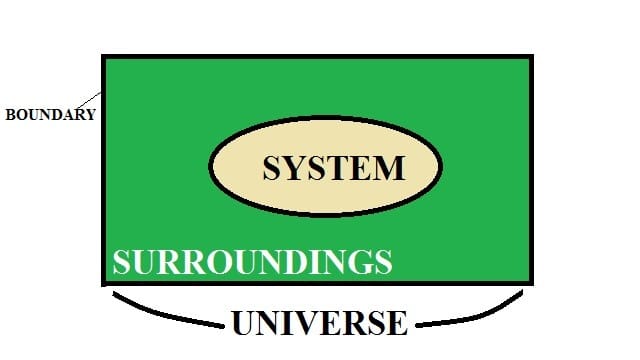
Lamont boiler is a forced convection boiler. It is a vertical furnace water tube boiler in which the water flows inside the pipe tube and fire or flue gases surround them.
Today we will study Definition, Parts, Working Principle Diagram, Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Lamont Boiler.
You can download PDF just at the end of the articles.
So let’s start with the definition first,
Lamont Boiler Definition:
Lamont boiler is a type of water tube boiler in which steams are generated from water by the burning of fuel which is coal and later that steams are used for the generation of electricity and so on. It is a high-pressure boiler.
Lamont Boiler Parts or Construction:
A Lamont boiler consists of the following parts or construction as you can see in the diagram below:
- Feed Pump
- Grate
- Economizer
- Circulating Pump
- Distributing header
- Radiant Evaporator
- Convective Evaporator
- Steam separating drum
- Superheater
- Blower
- Air preheater and
- Combustion chamber
Let’s start one by one,
Feed Pump:
Feed Pump is one of the important types of pump which is used at the boiler for supplying the feed water. It increases the pressure so that the feed water can enter into the boiler.
Grate:
The grate is located bottom side of the furnace. At the grate, we supply coal for burning at the combustion chamber.
Economizer:
Economizer is a device for increasing boiler efficiency. So the work of the economizer is to preheat the water by the use of remaining heat flue gases of the combustion chamber.
In the repetition, the feed water is first entered into the economizer before entering into the boiler because it will preheat the water that is the major advantage of it.
Circulating Pump:
A circulating pump is a centrifugal pump and it is driven by the turbine. The turbine takes steam from the boiler. It takes water from the steam separating the drum and sends it to the Distributing header to the radiant evaporator section.
Distributing header:
It is a component having an inlet at one end only and more than one outlet end.
Radiant Evaporator:
The water starts changing phase from liquid to saturated liquid and to the saturated steam. The heat receives here from the burning of fuel that is coal.
Convective Evaporator:
Here the complete saturation of water into the saturated steam process takes place.
Steam separating drum:
The main work of the steam separating drum is to separate the steam and water. Further, the steam is sent to the superheater and water is sent to the circulating pump.
Superheater:
A name itself indicates “superheater” which means more heat will supply to the steam so that there should not be any tiny liquid particles and it will fully convert into the steam and for rotating the turbine blades.
Here we can say superheater increases the temperature of the steam.
Blower:
Here it is an external component that receives the air and sends it to the air preheater.
Air preheater:
Air Preheater also helps to increase boiler efficiency. Here the air is preheating and then preheating air sends to the combustion chamber.
Combustion chamber:
In the combustion chamber, the coal is burned and produces hot flue gases that help to heat the water.
Lamont Boiler Working Principle Diagram:
Lamont Boiler works on the principle of forced circulation of water in the boiler with the help of a centrifugal pump.
This is a high-pressure boiler and works above 170 bar and temperature around 773k.
we will be understanding here in pointwise in depth so let’s start,
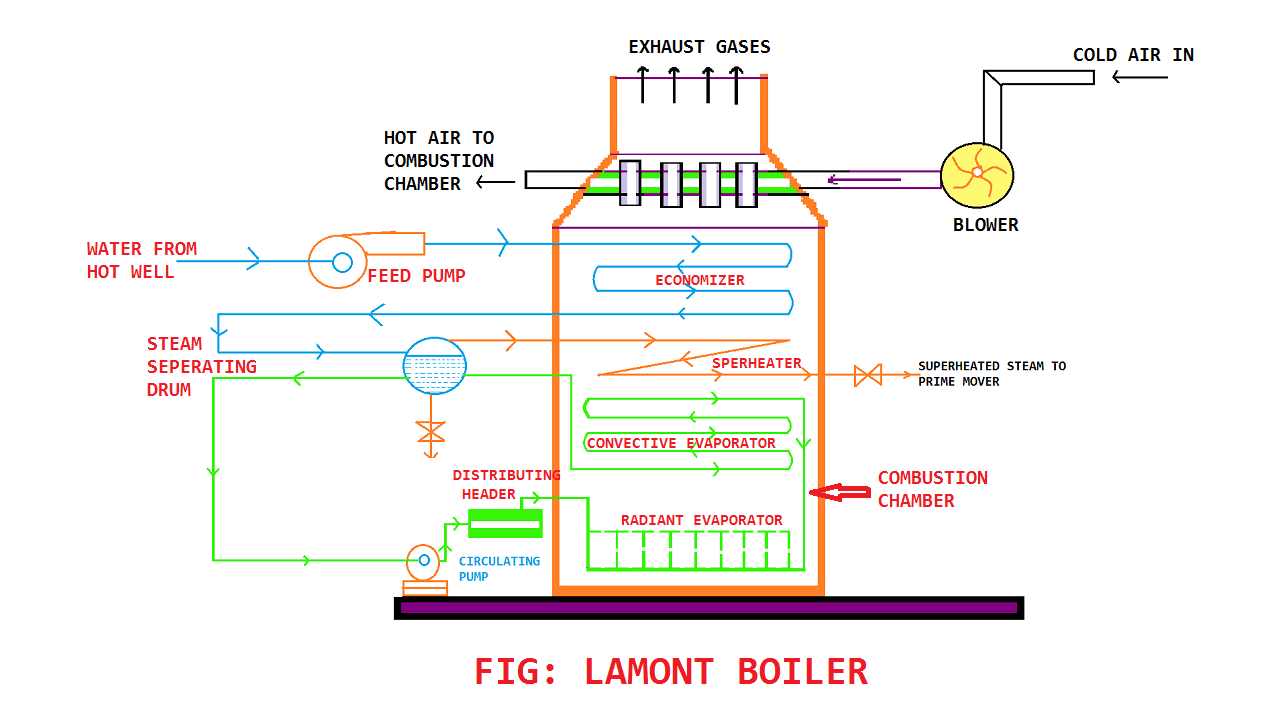
The water is first supplied to the feed pump from a large water tank. From the feed pump, the water is entered into the economizer.
As we know it is a boiler efficiency increasing device so here if heat is available then the water will get heated before entering into the combustion chamber.
From the economizer, the water comes to a steam separator device where the separation of steam and water takes place.
The water is circulated by the centrifugal pump from the separator drum. Here distributor header is kept for controlling the water level entry into the boiler.
Now water reaches into the combustion chamber where flue gases surround them and it starts getting heating.
Now the water comes in the phase of radiant evaporator here major amount of water is converted into steam and then it sends to the convective heat transfer.
Here the remaining water is further converted into saturated steam. Now, this saturated steam is further sent to the separator drum for separating steam.
After separating steam now further sent to the superheater to superheat the saturated steam and make use of it further for the generation of electricity and more.
Lamont Boiler Video:
Lamont Boiler Advantages:
A Lamont Boiler has the following advantages:
- In terms of the design of the boiler are very simple and understandable.
- The drum size is small.
- It is easy to start. There is no such problem with starting.
- Steam generation capacity is very good and it is 50 tonnes per hour.
- The transfer rate of heat is also good and the major drawback is bubble formation.
Lamont Boiler Disadvantages:
The major disadvantages of the Lamont boiler are bubble formation at the surface of the tubes that reduces the transfer rate of heat and causes low steam generation.
Lamont Boiler Application:
A Lamont Boiler has the following application or uses:
- Lamont Boiler is mostly used in Power plants for producing steam which helps to run a turbine for the generation of electricity.
- It is also used in other industries like Sugar Mill, Chemical industry, and more.
Related Article
Cochran Boiler
Lancashire Boiler
Water Tube Boiler
Fire Tube Boiler
Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
So this is all about Lamont Boiler. Let me know if you understood or not in the comment box. And If you find this article helpful then do check out our other article too.



Discussion about this post