Hydraulic Clutch is a device used in automobiles that use hydraulic fluid to operate the clutch. Hydraulic clutch utilizes the fluid which is stored in a reservoir in place of the cable to move the clutch plate.
This clutch is preferred in the modern automobile industry because it does not require pedal height adjustments and they self-adjust automatically due to the presence of the clutch fluid.
It requires optimal pedal effort and provides a smoother clutch pedal feel to the driver as they are manufactured from much lighter materials and have a stronger clutch mechanism due to highly pressurized fluid and cylinders.
The fluid is also called brake fluid or mineral fluid. Most cars made from the start of the ’90s have a hydraulic clutch system.
Hydraulic clutch Definition:
The hydraulic clutch is a type of automotive clutch that uses hydraulic fluid rather than a cable to move the clutch plate. These clutches have a master cylinder linked to the clutch pedal, which moves the fluid inside the clutch lining with high pressure when the driver presses the clutch pedal to disengage the clutch.
Hydraulic clutch Construction or Parts:
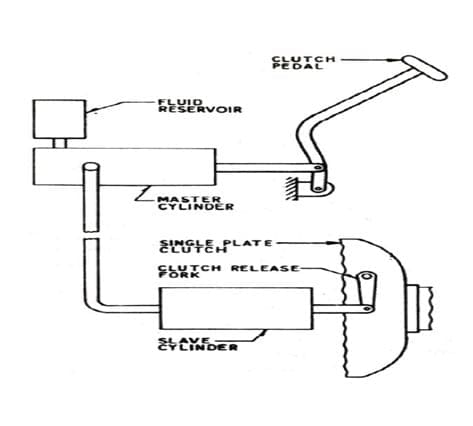
The figure given below shows the basic diagram of a Hydraulic clutch.
The hydraulic clutch consists of various parts, such as the clutch pedal, master cylinder, hydraulic pipe, slave cylinder, release fork, release bearing, diaphragm spring, pressure plate, splined sleeves, clutch plate, and flywheel.
Now we will study one by one in detail,
#1. Clutch pedal:
The clutch pedal is the primary part that engages a clutch in a vehicle. The clutch disengagement process starts when a driver presses the clutch pedal.
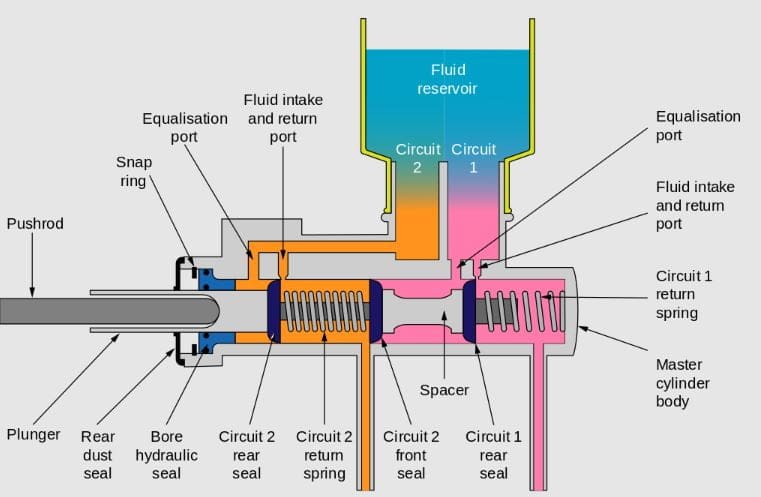
#2. Master Cylinder:
As the name suggests, it is a primary hydraulic cylinder in which the clutch fluid is applied at high pressure with the help of a piston present inside the cylinder.
The clutch fluid reservoir is connected to the master cylinder which supplies the clutch fluid when the clutch pedal is pressed.
#3. Pressure Pipe:
It supplies the fluid from the master cylinder to the slave cylinder at high pressure to operate the clutch.
#4. Slave Cylinder:
The slave cylinder is the second hydraulic cylinder present in the system. It consists of a push piston rod that is connected to the clutch release fork.
The fluid from the master cylinder enters the slave cylinder and presses against the push piston rod which in turn actuates the release fork.
#5. Release fork:
The clutch release fork is connected to the slave cylinder at one end and another end is connected to the clutch shaft which has the clutch release bearing mounted on it.
When the clutch pedal is pressed, it is used to press the release bearing on the diaphragm to apply pressure on it.
#6. Release bearing:
The clutch release bearing is mounted on the clutch shaft. It presses against the middle of the diaphragm spring when the clutch pedal is pressed.
#7. Diaphragm spring:
The diaphragm is a semi-circular or ‘C’ shaped spring. It is mounted on the pressure plate and is used to maintain pressure on the clutch plate.
When the clutch pedal is pressed, the middle of the diaphragm spring is pushed in and the spring pulls the pressure plate away from the clutch plate.
#8. Pressure plate:
The purpose of the pressure plate is to push the friction plate against the flywheel. It is kept under pressure with the help of the diaphragm spring.
When the clutch pedal is pressed, the diaphragm spring pulls away from the pressure plate clutch plate, which causes disengagement of the engine from the transmission.
#9. Splined sleeves:
The splined sleeves are located between the friction lining of the clutch plate and the pressure plate. The pressure plate keeps the splined sleeves under pressure to keep the clutch engaged.
When the pressure plate releases pressure the splined sleeves to pull away and it disengages the engine from the transmission.
#10. Clutch plate:
The clutch plate is held between the pressure plate and the flywheel. It has friction lining on both sides of its surface. The frictional surface creates friction between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
The friction between them is responsible for producing or interrupting the power flow between the engine and transmission.
#11. Flywheel:
The flywheel is a part that is connected to the engine crankshaft at one end and the clutch plate at the other end. The flywheel is responsible for transferring the flow of power from the engine to the transmission through the clutch plate.
When the clutch pedal is pressed, the linkage between the flywheel and clutch plate is interrupted. This causes disengagement of the power transfer and permits the change of gears smoothly.
Working principle of a Hydraulic Clutch:
The basic function of a clutch is to produce the flow of power from the engine to transmission and interrupt the flow of power to enable the change of gears without slippage. This is done by separating the linkage between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
The Hydraulic Clutch utilizes the fluid stored in the reservoir when the clutch pedal is pressed. The pushing force on the clutch pedal will force the piston inside the master cylinder and the fluid will be compressed to high pressure.
Pressure pipes are used to transfer the high-pressure fluid from the master cylinder to the slave cylinder.
Working of Hydraulic clutch Step by step in detail:
The working procedure of hydraulic clutch is divided into two categories:
- Disengagement and
- Engagement
Disengagement:
The clutch is engaged when the engine and transmission are rotating together. In simpler words, a clutch is engaged when the flywheel and clutch plate are rotating together under pressure at the same speed.
The transmission needs to be separated from the engine for a smooth change of gears. This process is called clutch disengagement. The disengagement process starts when the driver presses the clutch pedal.
The clutch pedal is linked to the master cylinder. The purpose of the master cylinder is to compress the fluid, which is present in the reservoir, to a high pressure using the piston present inside it.
This highly pressurized fluid is transferred from the master cylinder to the slave cylinder using the hydraulic pipe.
The high-pressure fluid from the master cylinder causes the slave cylinder to push out the push piston rod present inside it.
The push piston rod actuates the clutch release fork, which is connected to the clutch shaft. This pushes the clutch release bearing mounted on the clutch shaft.
The clutch release bearing is connected to the middle of the diaphragm spring. Diaphragm spring is used to contract and expand its surface on the pressure plate.
When the release fork pushes the release bearing, the middle of the diaphragm pulls the pressure plate away.
The pressure plate causes the splined sleeves to pull away and it releases the pressure on the clutch plate. This results in loss of frictional force between the clutch plate and flywheel.
Since the power flow occurs due to friction, it is interrupted when there is no frictional linkage between the plates and flywheel.
Hence, the clutch disengages and permits changing of gears.
Engagement:
The Clutch is engaged when power flows between engine and transmission. This happens when the driver releases the clutch pedal after a change of gear.
The release of the clutch pedal causes the fluid to release pressure in the cylinders.
This brings back the fork, bearing, and diaphragm spring to their respective original positions.
As the diaphragm moves back to its original position, splined sleeves move into the original position to bring the pressure plate into contact with the clutch plate.
The pressure plate presses the clutch plate against the flywheel causing friction. This makes the plates rotate along with the flywheel at the same speed. Thus the power flow between the engine and the transmission occurs.
Function of a Hydraulic Clutch:
- To produce or interrupt the power flow between the transmission (driven shaft) and the engine (driver shaft).
- To protect the transmission and engine from overloading and self the lubricating system.
- Possible to drive off smoothly from a standstill.
- To use the force of the hydraulic fluid to engage and disengage the clutch.
- To self-adjust the height of the clutch pedal using the hydraulic mechanism just like in the braking systems and maintain the engagement point of the clutch at the same point throughout the lifespan of the clutch.
- To keep the system between the master cylinder and slave cylinder a closed system and not have any air inside.
- The clutch master cylinder should act according to the force generated by the clutch pedal action.
- The hydraulic pipe should transfer the pressurized fluid between the cylinders without any leakage, as it may cause air to get trapped in the system and affect the clutch mechanism.
- The clutch engagement mechanism when the pedal is released should be optimal so that the linkage between plates and flywheel is stable and the clutch plate doesn’t wear out.
How it is different from other clutches?
Hydraulic clutch works on the principle of the highly pressurized clutch fluid. It consists of a fluid reservoir, a master cylinder, and a slave cylinder as compared to a cable in a mechanical clutch.
These are easier to modulate and have a more consistent lever pull due to the presence of a master cylinder and slave cylinder.
The hydraulic force in the fluid is used instead of a cable to get a smooth and consistently springy clutch pedal.
In the case of a hydraulic clutch, the clutch pedal returns to its original position even after the clutch plates wear out. But in the case of a mechanical cable clutch, the wire or cable used to actuate may break or corrode after aging.
The engagement point of the clutch remains the same throughout the lifespan of the clutch due to the self-adjusting nature of the hydraulic clutch.
Advantages of a Hydraulic clutch:
Some advantages of the hydraulic clutch are stated below:
- Hydraulic clutches offer smoother and consistent lever pull. It takes less time to react and does not require much force from the driver as in the case of mechanical clutches.
- Hydraulic clutches are considered to be low friction clutch since work is done using fluid.
- Low maintenance is required as these are self-lubricating and have low friction.
- Clutch pedal height is self-adjusted due to hydraulic action and hence, it does not need periodic adjustment like a mechanical cable clutch.
- These are self-lubricating clutches since they have hydraulic bearing oil. Cable wires require lubrication from time to time.
- Moreover, due to the hydraulic system, there is no presence of cable inside the system which may require periodic maintenance due to damage.
- Longevity is more in hydraulic clutches because there is less friction and will not cause a sudden cable snap like in a mechanical cable-actuated clutch.
- The quality of hydraulic clutches is more as compared to mechanical clutches.
Disadvantages of a Hydraulic clutch:
Some disadvantages of the hydraulic clutch are stated below:
- Hydraulic clutches have pipes and the system has a number of parts which require a very large area.
- The major problem that occurs in a hydraulic clutch is leakage as the clutch fluid is transferred in large quantities inside the system.
- The slave cylinder outflows the fluid sometimes due to hydraulic error, which may damage the clutch plate.
- The hydraulic pipe in the system consists of plastic metals, which will rot after a certain period of use. So it needs periodic checking to avoid any major damage.
- The clutch fluid gets contaminated with impurities after a certain time of use. Also, an optimum level of fluid needs to be maintained in the reservoir to avoid damage to parts. So periodic change of fluid is required for functioning.
- The clutch fluid requires bleeding to avoid trapped air during the replacement process, which is time-consuming.
- The standard clutch fluid should be used in the system. Incorrect fluids can damage the seals in the system.
- The hydraulic clutch is a complex system as compared to a mechanical clutch. The hydraulic clutch is based on the master cylinder, slave cylinder, hydraulic pipes, and fluid, whereas the mechanical clutch needs only a cable wire to operate.
- The clutch fluid used in hydraulic clutches is costly as compared to the mechanical cable wire. The cable wire is also easier to set up and maintain.
- Hydraulic clutches can be costly if the seals of the cylinders leak since the whole system would need to be replaced.
Applications of a Hydraulic clutch:
Hydraulic clutches are preferred by reputed car manufacturers as they ensure quality and require less effort.
These are also used in heavy vehicles nowadays.
Hydraulic plates can be used in both single plate and multi-plate clutch.
The self-adjusting and self-lubricating features are widely used for various applications in the industries.
Internal Resources:
- Clutch complete Notes
- Different Types of Clutch
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Open Belt Drive vs Cross Belt drive
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Electronic Ignition System
- Lubrication System Types
- Magneto Ignition System
- Battery Ignition System
- Flywheel
- Camshaft
- Crankshaft
Reference [External Links]:
So here we finally studied Hydraulic clutch in detail. I hope you have understood this topic. If yes then please share it with your friends and family. Do let me know what further topic I can help you with. Till then Thank you so much for visiting. Bye






Discussion about this post