In this paper we will discuss What is Electronic Ignition System? and its subtopic like Definition, Parts or Construction, Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application in detail.
At the end you can download whole article in PDF format.
Let’s start with the definition,
What is Electronic Ignition System?
In an internal combustion engine, the electronic ignition system is used to ignite air-fuel. Basically, this provides heat in form of spark for ignition. This system works inside the engine for creating a spark in the spark plug.
Why do we need an Electronic ignition system?
There are already three different types of ignition systems are Battery Ignition System, Glow plug ignition system, and Magneto Ignition System.
It is because there are certain limitations in all the given ignition system for example, If we are talking about the Glow plug ignition system then this system electrode was used because that combustion was uncontrolled.
Because of that, the exhaust emission rate was very high and there was also some limitation in the battery and then magneto ignition system which is replaced by other system and the best one was the electronic ignition system. This provides high performance, better mileage, and reliability to this system.
By replacing all the other ignition system, an electronic ignition system is introduced in the market and it replaced all other.
When we are talking about the magneto ignition system, the electrode is replaced by a spark because that emission rate decreases but the magneto system depends upon the speed of the vehicle, and vehicle speed can never be constant on road because of traffic and many other situations, which is not fulfilling the need.
That’s why the battery ignition system is introduced. Even today in most of vehicles, a battery ignition system is used because it has high accuracy and high efficiency.
But there are certain limitations with the high-speed engine as it is less efficient, because of that the electronic ignition system is introduced which fulfills all the requirements for an efficient engine.
Now moving to construction,
Parts or Construction of Electronic Ignition System:
Electronic Ignition System consists of following main Parts:
- Battery
- Ignition Switch
- Electronic control module
- Ignition coil
- Ignition distributor and
- Spark plug
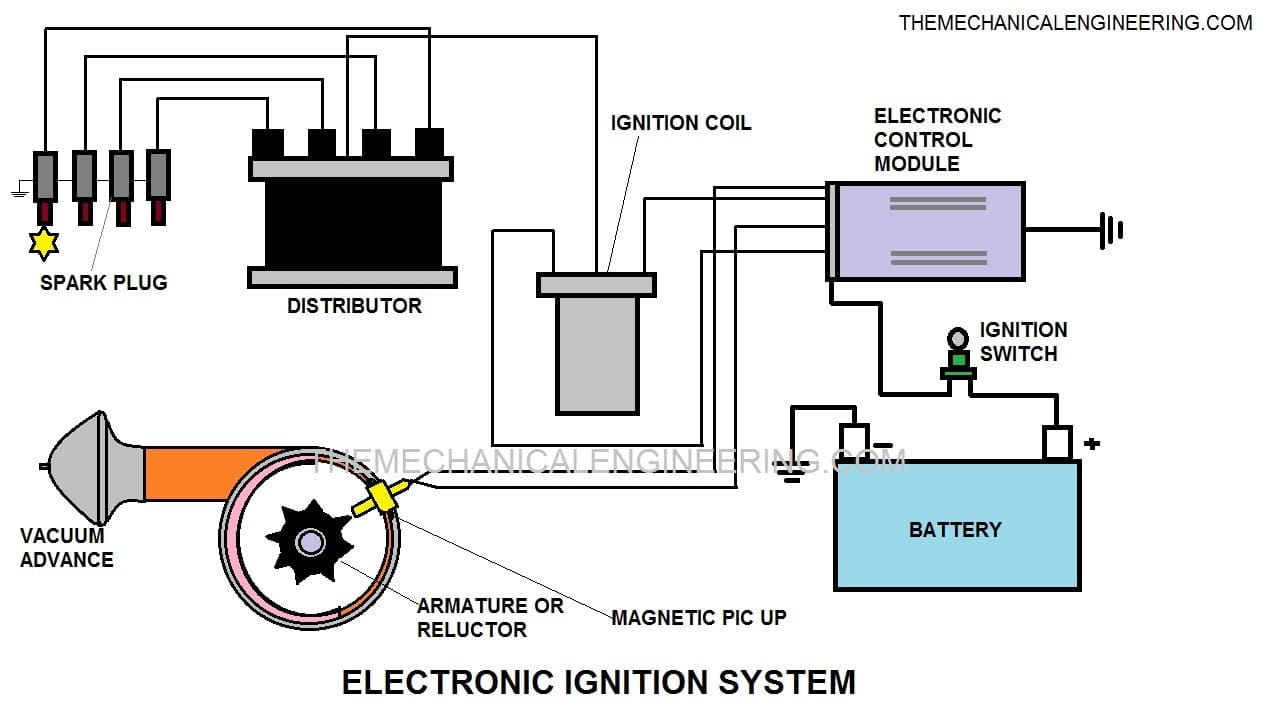
Battery:
It works as a powerhouse of the whole system and the energy which is necessary for the working of the whole system is provided by the battery.
A lead-acid battery is used in this system to provide electrical energy. This battery is rechargeable and it gets recharged through the dynamo through the engine.
Ignition switch:
This is the main switch of the whole system. You can on/off with this switch. The negative side is grounded and the positive side is connected to the primary winding of the coil.
Electronic control module:
A control module is the brain of an electronic ignition system. All the instructions are already programmed in this module and it also controls or monitors the timing and intensity of the spark.
This is one of the important parts of the whole system. The whole system is controlled by an electronic control module.
Armature:
This consists of reluctor which is the rotating part of the armature which consists of the tooth. To make or break the circuit armature takes a regular supply of voltage through the electronic control module.
When the armature tooth comes in contact with the pickup coil, voltage is generated and it stops the flow of current from the primary circuit.
Ignition coil:
It consists of the primary winding and the secondary winding. This produces high voltage for the spark plug. The coil is having a soft iron core.
Both the end of the primary winding is connected with exterior terminals. The primary winding is having 200-300 turns but the secondary is consists of 21000 turns and another end is connected with high tension wire.
Ignition distributor:
Distributor helps to distribute current for spark plug when there is the use of multi-cylinder or more that one then sparks plug is used. It consists of the metallic electrode on the periphery and the rotor in the middle of it.
The metallic electrodes are connected with spark plugs also known as ignition harness. The rotor is connected with the secondary winding, which is driven by the camshaft.
When the rotor starts rotating, it passes high tension current to the ignition harness which is carried by high tension currents with spark plugs.
Spark plug:
The plug emits sparks for the Ignition of fuel. It has two wires first one is connected with a high-tension current-carrying wire and the other one is grounded, because of the potential difference it creates sparks and combustion takes place.
Electronic Ignition System Working Principle:
When the driver inserts the key into his car for switching on the ignition switch, just after that battery starts and it supplies current to the system.
Current passes through the ignition switch and move toward the ignition coil on the system then, start passing through the primary winding of the coil.
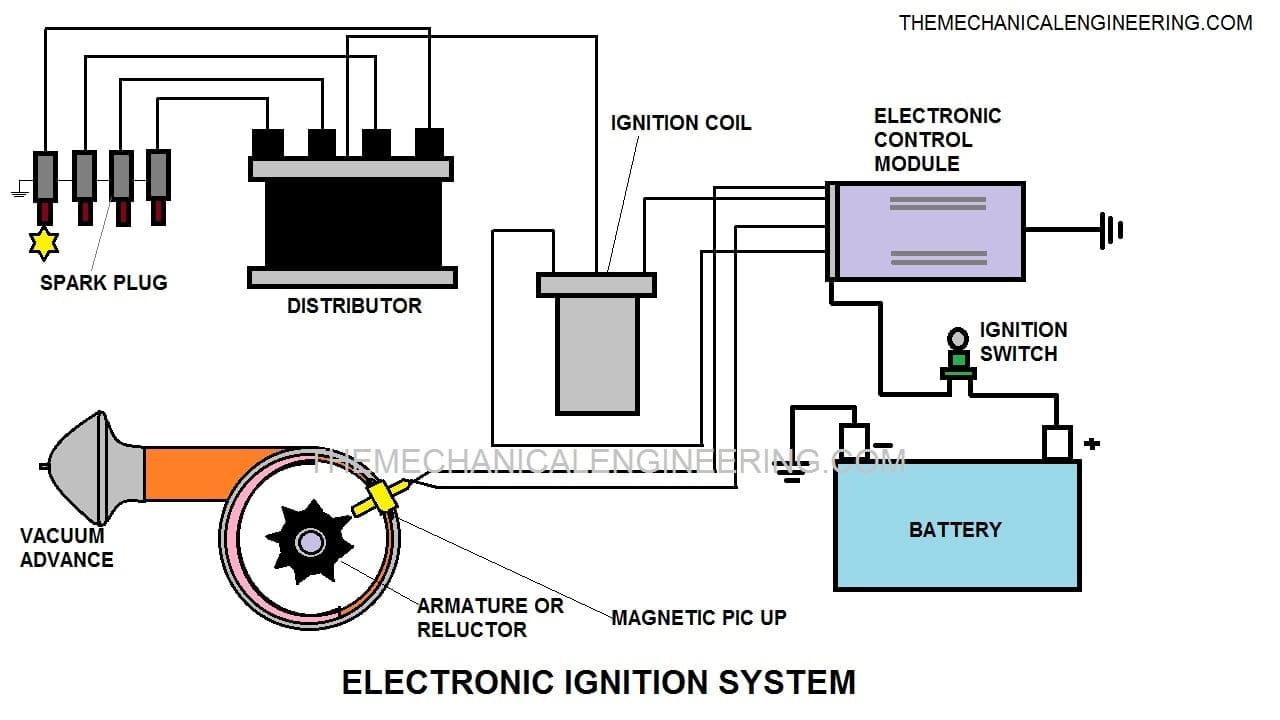
As the current passes through the primary coil, the pick-up coil got activated which is in the armature. It receives current as a voltage on the pick-up. Just after receiving voltage, the reluctor starts rotating which consists of the tooth.
When the tooth comes in front of the pick-up coil exactly at the same time the pick-up coil starts sending a signal to the electronic control module.
After receiving a voltage signal, it stops the current supply from the battery up to the primary coil. When the tooth deviates from the point, it senses the change in voltage, and then again it sends a signal of change in voltage to the electronic control module.
We all know that the electronic control system is already a programmed system, so exactly after sending a signal of change in voltage it again starts supplying the current in the primary winding.
Because of this continuous make and break of the current circuit, it creates a magnetic field inside the ignition coil because of that, the secondary winding emf is induced.
This emf increases voltage up to 50000 V. The voltage is supplied to the distributor.
It consists of a rotating rotor and distributor points, which is programmed as per the ignition. When there is a jump of voltage between the air gap of the rotator and the distributor of high voltage, after that it reaches to spark plug through high tension wire.
Spark is generated because of the voltage difference between the central electrode and the ground electrode because the combustion is possible in air-fuel.
Electronic Ignition System Working Video:
Application of Electronic Ignition System:
The electronic ignition system has a lot of applications in the 21st century.
- It is mostly used in modern and hypercars.
- It is mostly used in Audi, Mahindra XUV, KTM bikes, Ducati, and many more.
- It is also used in aircraft engines.
Advantages of Electronic Ignition System:
The following advantages of Electronic Ignition System includes:
- These are low maintenance systems as compared to others like Battery Ignition System, Glow plug ignition system, and Magneto Ignition System.
- It has no moving parts because it is controlled by the electronic control unit(ECV).
- Emission is less as compared to other means because this system is environmentally friendly.
- It increases the efficiency of the engine and also it is fuel-efficient.
- It is more accurate as compared to the magneto system.
- The vehicles having this system have a long life and also reliable.
Disadvantages of Electronic Ignition System:
The main disadvantage of electronic Ignition is that this system is very expensive because all cannot afford the vehicles having an electronic ignition system.
Internal Resources for You:
- Engine Manifolds
- Flywheel, Camshaft, Crankshaft
- SI Engine vs CI Engine
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Air Suspension system
- Clutch complete Notes
- Single Plate Clutch
- Multi-Plate Clutch
- Lubrication System Types
Reference [External Links]:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/ignition-systems
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ignition_system
- https://osme.co.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Ignition-system.pdf
- https://auto.howstuffworks.com/ignition-system.htm
Here we finally studied the Electronic Ignition System in detail. Let me know what else topic you are looking further to explain. If this article help you then Please share to your friends and family.





Discussion about this post