Hello, In today’s article we will study Difference Between Two-Stroke and Four-Stroke Engine in detail.
The PDF you can download at the end of every article.
There are three types of stroke engine exits in the world. The first and second is a Two-stroke engine and four-stroke engine. The latest engine that exists nowadays is the six-stroke engine.
In a two-stroke engine, we use one cylinder. In four-stroke, we use two cylinders whereas in a six-stroke engine the number of cylinders is more than two.
The stroke in the cylinder is defined as the distance of movement of piston up and down that is top dead center to bottom dead center.
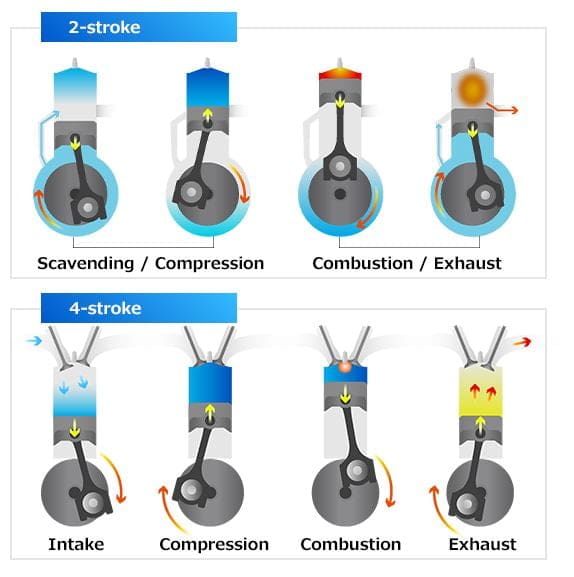
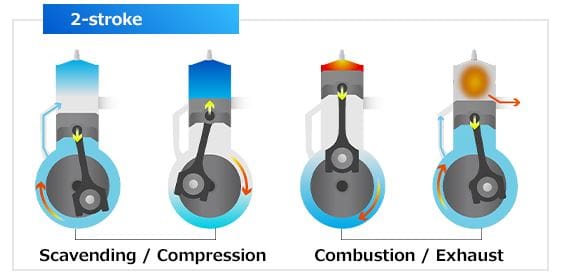
What is Two Stroke Engine?
The two-stroke engine is defined as the power stroke is available for every one revolution of the crankshaft or we can say In this engine the piston movements only two times in order to get yield power.
There are two ports and that is inlet and exhaust ports. Due to varying pressure, these two ports are open and closes.
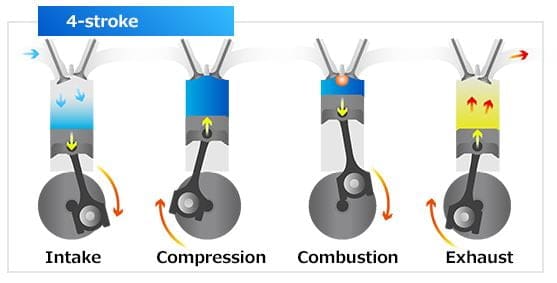
What is Four Stroke Engine?
The four-stroke engine is defined as the power stroke is available for every two revolutions of the crankshaft or we can say In this engine the piston movements four times in order to get yield power.
The four stroke engine has four steps to follow and those are:
- Intake Process
- Combustion Process
- Power stroke and
- Exhaust stroke.
The complete we will read in another four stroke engine articles.
Now lets see Difference Between Two Stroke and Four Stroke Engine. Let’s start,
Difference Between Two Stroke and Four Stroke Engine:
The following differences between Two Stroke and Four Stroke Engine are:
| Two Stroke Engine | Four Stroke Engine |
| The weight of the two-stroke engine is lighter. | The weight of the four-stroke engine is heavier. |
| The cost of a two-stroke engine is less compared to a four-stroke engine. | The cost of a four-stroke engine is high. |
| The two-stroke engine used in motorcycles, scooters, and many more. | The following example is a bus, truck, car, and so on. |
| Here more wear and tear happens while moving. | But in four-stroke less wear and tear. |
| The consumption of lubricating oil is more in two strokes. | The consumption of lubricating oil is less in four strokes. |
| The two-stroke has less thermal efficiency. | It has more thermal efficiency compared to a two-stroke engine. |
| This is an air-cooled engine which means when the engine gets heated it is cooled by air. | The water or air is used for cooling an engine. |
| In two stroke engine the mechanical efficiency is more because of less friction in the parts. | There is more friction in the parts therefore the mechanical efficiency is less. |
| There is only one power stroke for one revolution of the crankshaft. | Here two revolution of the crankshaft is required for one power stroke. |
| The cost of the engine is a less comparatively four-stroke engine. | The cost of the engine is more compare to the two-stroke engine. |
| The two-stroke engine consists of two ports inlet and outlet ports. | In four-stroke, there are inlet and exhaust valves. |
| There is a simple lubrication system. | Here the lubrication system is complicated. |
| A two-stroke engine takes less space and | the four-stroke engine takes more space. |
| In two-stroke, there is high torque generated. | But in four-stroke, there is less torque generated. |
| The two-stroke produces more smokes. | But The four-stroke produces fewer smokes compared to a two-stroke engine. |
| It requires more lubricating oil because some oil burns with the fuel. | Here it requires less lubricating oil. |
| In terms of power to weight ratio, it has more ratio than a four-stroke engine. | But in the four-stroke engine, the power to weight ratio is low. |
| The Air and fuel mixtures which are known as charges, first enter into the crankcase then enter into the cylinder. | Here in four-stroke The Air and fuel mixtures directly enter into the cylinder. |
| The two-stroke engine takes place scavenging process. | No scavenging process. |
| The output power is less. | The output power is more. |
| The maintenance cost for two-stroke is less. | Here there are more parts, therefore, the maintenance cost is more. |
| Engine starting is very easy compare to a four-stroke engine. | Starting an engine is not easy. |
So here we studied more than 15 point on two stroke vs four strong engine in detail.
Internal Resources:
- Drum Brake vs Disc Brake
- Battery Ignition System
- Magneto Ignition System
- Electronic Ignition System
- Different Types of Lubrication System
- Different Types of Clutch
- Types of Braking SYstem
References [External Links]:
So here we finally studied all the differences in detail. I hope you have understood this topic. If yes then please share it with your friends and family. Do let me know what further topic I can help you with. Till then Thank you so much for visiting. Bye.





Discussion about this post