The main difference between Otto and Diesel cycle is that The otto cycle explosion process takes place at a constant volume process and the Diesel cycle explosion process takes place at a constant pressure process.
In this article, we will be studying the differences between Otto and Diesel cycle in very detail.
Note: At the end of the articles, you will find the PDF which you can easily download.
Otto Cycle:
- The cycles are mostly found in an automobile engine. The fuel used in the Otto cycle is Petrol fuel.
- The heat addition takes place at a constant volume process and It is also known as the Isochoric process.
Diesel Cycle:
- The fuel used in the diesel cycle is diesel fuel.
- In the diesel cycle, the heat addition takes place at constant pressure and It is also known as the Isobaric Process.
- Here you can read Diesel Cycle in detail.
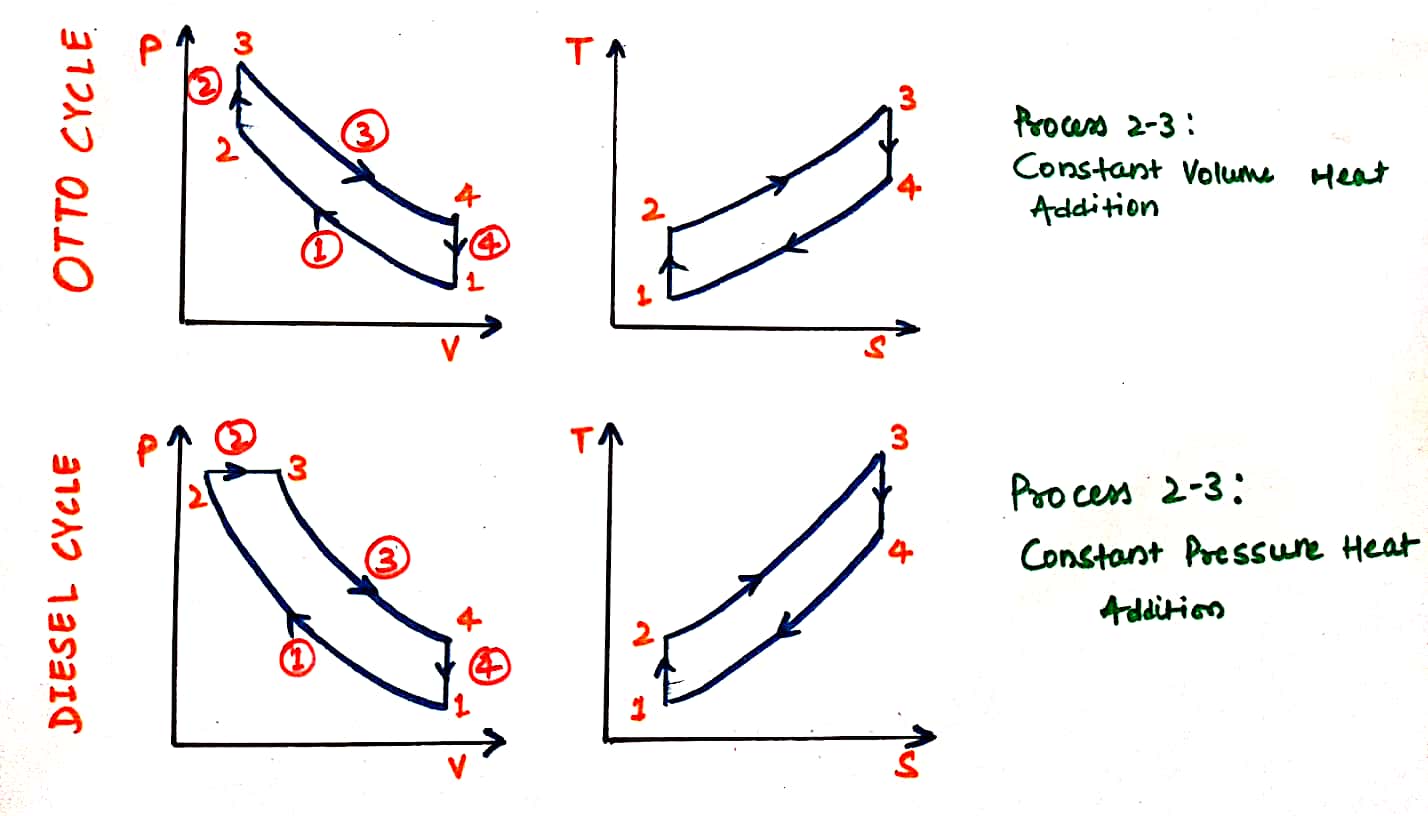
The below figure is attached PV and TS Diagram of Otto and Diesel cycle.
| Otto Cycle | Diesel Cycle |
| 1-2: Isentropic Compression | 1-2: Isentropic Compression |
| 2-3: Heat Addition at constant volume | 2-3: Heat Addition at constant Pressure |
| 3-4: Isentropic Expansion | 3-4: Isentropic Expansion |
| 4-1: Heat rejection at constant volume processes. | 4-1: Heat rejection at constant volume processes. |

Difference Between Otto Cycle and Diesel Cycle:
| Sl No. | Otto Cycle | Diesel Cycle |
| 1. | Otto cycle has low thermal efficiency. | The diesel cycle has high thermal efficiency. |
| 2. | It has a low compression ratio. | But This one works on a high compression ratio. |
| 3. | Otto cycle is also called a Constant volume cycle. | The diesel cycle is called a constant pressure cycle. |
| 4. | Otto cycle system is light in weight. But | The diesel cycle is heavy in weight. |
| 5. | The explosion process takes place at constant volume process and | In the diesel engine, the explosion process takes place at a constant pressure process. |
| 6. | The Spark Plug is used here for igniting the charge. | A fuel injector is used here for igniting the charge. |
| 7. | A mixture of air and fuel is entered in suction stroke. | Only air is entered in suction stroke. |
| 8. | Here the working fuel is used as Petrol. | The working fuel is used as Diesel. |
| 9. | Otto cycle engine is the high-speed engines. | Diesel cycle engines are not high-speed engine comparatively Otto cycle. |
| 10. | The engine starting is easy in cold weather too. | But here it is difficult comparatively Otto cycle. |
So These are the 10 Points on differences between the Otto cycle and Diesel cycle. Let me know by using the comment box have you understood or not?
I have also written on the Difference between Spark Ignition vs Combustion Ignition Engine.
Related Resources:
Piston
Connecting Rod
Lubrication System
Here you can download PDF by just clicking Download PDF.


![Different Types of Measuring Tools and their Uses [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Types of Measuring Tools](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Types-of-Measuring-Tools-300x171.jpg)
![Steel: Properties, Different Types and Applications [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Steel](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Steel-300x168.jpg)

![Pneumatic System: Definition, Components, Working, Advantages [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Pneumatic System](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Feature-Image-of-Pneumatic-System-300x155.jpg)
![What is Pulley? Different Types of Pulley [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Pulley](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Feature-Image-of-Pulley-300x267.jpg)
![Aluminum: Introduction, Characteristics, Different Types, Application [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Aluminum Types](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Feature-Image-of-Aluminum-300x150.jpg)

Discussion about this post