In this article, I will tell you about cutting fluid and its type in detail. In the beginning, you will learn about the definition, types, and properties. Afterward, we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of the Cutting Fluid.
So, let’s get started with definition,
What is Cutting Fluid?
Cutting fluid is the liquid used in the metalworking process like cutting, drilling, milling, turning to reduce the heat produced due to the deformation and machining process to lubricate for reducing friction and wear and tear on the workpiece.
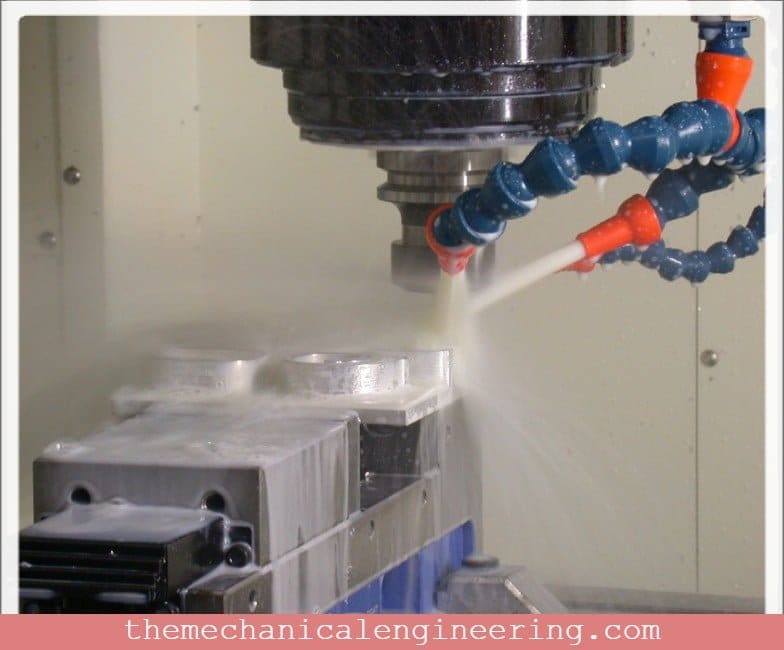

Sometimes, it is also known as a coolant or lubricant but, it is wrong because it performs many functions beyond cooling and lubricating.
It helps in achieving an excellent surface finish and great dimensional control.
Did you know? Cutting fluid is evolved from water. Initially, during the metalworking process water, was used as the cutting fluid. You might have seen a blacksmith using water for shaping metal. Water is excellent at cooling but, it lacks lubricating capabilities and not good at decreasing friction while cutting.
This lead to the formation of cutting fluid. It is the mixture of water and oil with an emulsifier that forces to mix water and oil. It can go even further by adding a chemical to form synthetic fluid.
Purpose of Cutting Fluid:
The following four purposes of cutting fluid:
- Temperature control
- Lubricating
- Cleaning the machine and
- Prevent harmful contamination
Temperature Control:
Cutting fluid support to minimize the friction & heat produced between tool and workpiece as an increase in the temperature can reduce the tool’s life.
Lubricating:
Cutting Fluidshelps in lubricating the tool and the workpiece to reduce the friction and cutting forces to increase the tool’s life and surface finish.
Cleaning the Machine:
Cutting Fluids helps in cleaning the chips, particles, and debris which can further damage the surface finish.
Prevents Harmful Contamination:
Cutting Fluids develops a thin layer on the workpiece thus, prevent contamination from harmful gases like SO2, O2, H2S2 in the atmosphere.
Properties of Cutting Fluids:
Here is the list of properties of cutting fluids :
- High Heat Absorption Capacity
- Good lubricating quality
- Very High Flash Point
- High Stability
- Neutral Properties
- Must be odorless
- It must be harmless
- Transparent
- Low Viscosity and
- Low Price.
Let’s understand one by one,
High Heat Absorption Capacity: The fluid must have a high heat-absorbing capacity so that it can reduce the heat produced by metalworking( or cutting process)
Good lubricating quality: Reduces the coefficient of friction between workpiece and tool hence reducing the wear of the tool.
Very High Flash Point: Having a lower flash point can lead to inflammation so, cutting fluid must have a high flash point to avoid accidents.
High Stability: The oxidization of cutting liquid with the air present in the atmosphere must be very less.
Neutral Properties: The cutting liquid must not react with the other chemicals.
Must be odorless: The cutting liquid must not produce a bad odor.
It must be harmless: The cutting liquid should not harm any human being or worker. It must be safe to use.
Transparent: The fluid must be transparent so the tool’s operation on the work piece can be easily visible.
Low Viscosity: The cutting fluid must have a low viscosity to provide smooth fluidity on the workpiece surface or the tool.
Low Price: The cutting liquid must be affordable so that it reduces the production cost.
Methods of Applying Cutting Fluid on the Workpiece or Tool:
Manual Application- Under this method, a worker pours the cutting liquid manually on the workpiece or tool with the help of a container or oil can. It is the simplest and economical method that requires the least effort. But it is also the least used method in the machining process due to inconsistency inflow.
Flood Application- This technique uses a pipe, hose, or nozzle system for delivering the cutting fluid to the tool or the workpiece. To produce maximum results fluid is flown by the nozzle under high pressure.
Mist Application- This method is used to atomize & blow the cutting fluid over the surface of the workpiece/tool. For the implementation of this technique, there should be appropriate ventilation to protect the worker. For the successful application of this technique, the pressure and direction of mist are critical.
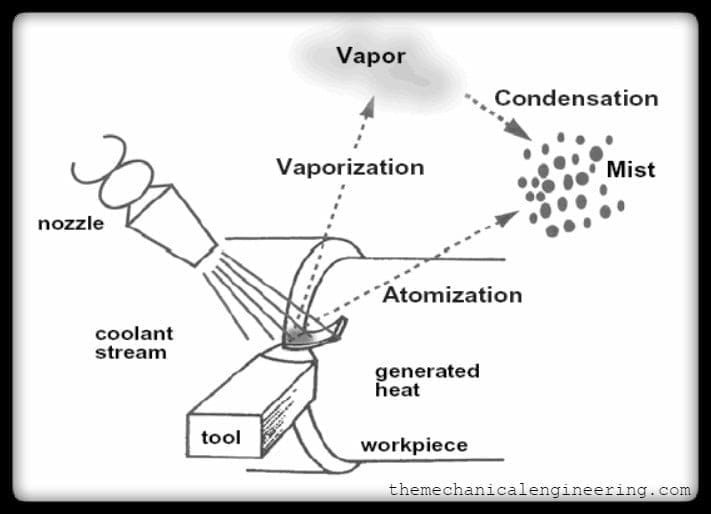
Types of Cutting Fluid:
The following different types:
- Liquid Type or Semi-Synthetic Fluid
- Synthetic Cutting Fluid
- Semi-Solid
- Gaseous
- Soluble Oils
- Mineral Oils and
- Straight Oils Cutting fluid
Liquid Type Cutting Fluid Or Semi-Synthetic Fluid:
Emulsification of oils with the water base forms a liquid coolant. Water alone is a good coolant but, it cannot be used as a cutting fluid because of its corrosive and non-lubricating properties.
Mineral oils are added to the water to make proper cutting fluid also called as Semi-Synthetic Cutting Fluid. Examples of liquid-type are kerosene, motor oil, etc.
Synthetic Cutting Fluid:
These are water-based fluids without mineral oils. These are of particulate measurement 0.03mm. Water has excellent cooling properties but lacks lubricating properties and leads to corrosion So, rust inhibitors are added to prevent rust formation.
Semi-Solid Cutting Fluid:
Gel or pasted-based cutting fluid is known as semi-solid cutting fluids. There are certain operations like drilling, boring, tapping where it is complicated to use liquid-type cutting liquid.
So here, the semi-solid cutting liquid is applied. These fluids are generally expensive than liquid type but, these are used in little quantity without a continuous supply.
Gaseous Cutting Fluid:
These are the best and cheapest as it includes atmospheric air as cutting fluid. Sometimes, At the cutting edge, a mist supply is given with the liquid and compressed air.
The compressed air works best as a coolant as it has good thermal properties and also blows away the chips.
Soluble Oils:
Soluble oil is the most commonly used cutting fluids used in machining operations. This is made of soluble oils, emulsifiers, additives, and water (1%-20%).
It is suitable for machining operations like a light cutting operation that requires low metal removal rates.
Mineral Oils:
These are suitable for heavier metal operations due to their excellent lubricating ability. These apply to production machining operations where high metal removal rates are required.
These should not be applied to copper or its alloy due to its corrosive property.
Straight Oils:
Vegetable oils or Petroleum oils that are used without mixing water are called straight oils. Examples of straight oils are Paraffin oil, naphthenic oils, vegetable oils.
These have excellent lubrication ability. Vegetable oils were generally used due to their environment-friendly properties like biodegradability but they are little in use because of their bad smell.
Advantages of Cutting Fluids:
The following advantages of cutting fluid is:
- Higher surface finish and better dimensional quality is obtained due to the use of cutting fluid in machining operation.
- Reduction in the cost of the tool as cutting fluids increases the life of the tool by reducing the wear and tear of the tool.
- The production speed increases as cutting fluid reduce fiction and heat produced due to deformation so cutting functions can be performed at a higher speed.
- Power consumption reduces as fiction reduces so less power is required in the machining operation.
- Cutting fluids helps in avoiding corrosion on the surface of the workpiece.
- It has low toxicity so does not harm the workers.
Cutting Fluid Disadvantages:
The following disadvantages of cutting fluid is:
- For certain machining processes, it requires a costly engineering system for the application of cutting fluid.
- Disposal of the fluids prepared is not an easy task as it requires a long time and can cause environmental issues.
- The fluid prepared needs to be prepared and after use needs to be filtered for reuse or disposal.
- Some fluids cause health hazards due to chemicals and additives added while preparation. If not used properly can cause health issues.
- Some metal is affected due to the use of cutting fluids so, we have to use it carefully.
- Some of the materials get affected due to thermal shock so again use it carefully.
Application Of Cutting Fluids:
Cutting fluids are used in many industries but specifically in the metalworking industry. Cutting with the tools having low strength as high-speed steels requires the use of cutting fluids. This is because cutting at high speed increases the temperature of the tool, reducing its mechanical strength thus reducing the life of the tool.
In this example, using cutting fluids can help in reducing the temperature of the tool allowing it to function properly. Operations were using cutting fluids are essential are drilling, broaching, milling, threading, with huge momentum.
Operations that require a smooth surface and tight dimensional tolerance require the use of cutting fluids because in these cases lubricant can provide a good surface finish and cooling can provide tight dimensional tolerance.
Application of cutting fluids becomes necessary in the operations like drilling that generates chips continuously. In these cases, the main function of cutting fluid is to remove chips away from the cutting tool otherwise the chips can cause damage to the tool.
Selection of Cutting Fluids:
The selection of the cutting fluids depends on the following parameter:
- It depends mainly on the material of the workpiece and the material of the tools used in operation.
- What kind of operation you are performing is also a major factor responsible for deciding the cutting fluids.
- Lastly, it depends on the cooling effect required in the machining operation.
Internal Resources:
- Milling Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Shaper Machine
- Slotter Machine
- Lathe Machine
- NC Machine
- Hot Working Process
- Cold Working Process
Conclusion:
Cutting fluids are an important element of manufacturing that helps the manufacturing industries in metal cleaning and producing processes. There are different types of cutting fluids like gaseous, synthetic, semi-synthetic, straight oils, etc.
Hope, So this article has helped you to get a clearer view of Cutting fluids and their purposes and applications. Make sure to comment on all of your queries regarding the topic.



![Steel: Properties, Different Types and Applications [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Steel](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Steel-300x168.jpg)
![Pneumatic System: Definition, Components, Working, Advantages [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Pneumatic System](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Feature-Image-of-Pneumatic-System-300x155.jpg)
![Different Types of Measuring Tools and their Uses [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Types of Measuring Tools](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Feature-Image-of-Types-of-Measuring-Tools-300x171.jpg)

![What is Pulley? Different Types of Pulley [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Pulley](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/Feature-Image-of-Pulley-300x267.jpg)
![Aluminum: Introduction, Characteristics, Different Types, Application [Notes & PDF] Feature Image of Aluminum Types](https://themechanicalengineering.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/Feature-Image-of-Aluminum-300x150.jpg)




Discussion about this post