In this article, I will tell you about the casting process and its methods in detail. In the beginning, you will learn about the definition, methods, and detailed working.
Afterward, we will discuss the advantages, disadvantages and applications of the casting process.
So, let’s get started,
What is the Definition of the Casting Process?
The casting process is the manufacturing process in which molten material such as metal is poured into the casting cavity or mold of the desired shape and allowed to harden or solidify within the mold, after solidification the casting is taken out by ejecting or by breaking the mold.
This is one of the oldest and widely used methods of the manufacturing process used to make many types of equipment, tools, materials that would be rather difficult or expensive to make using any other method.
Did you know? In the historic era, many of the weapons and defense equipment were made using the casting process. And, India is termed as the first civilization to use this process for the bulk production of coins.
Major Parts like a bed of the Lathe machine, milling machine bed & IC engine equipment are made by using this method.
Casting Process Working Principle in Detail:
In this part, we will learn the detailed working process and Basic terminologies of Casting.
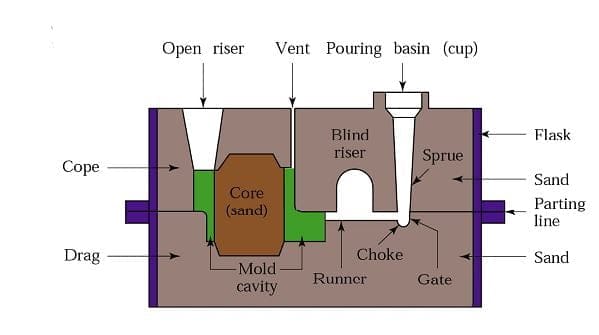
Basic Terminologies Of Casting Process:
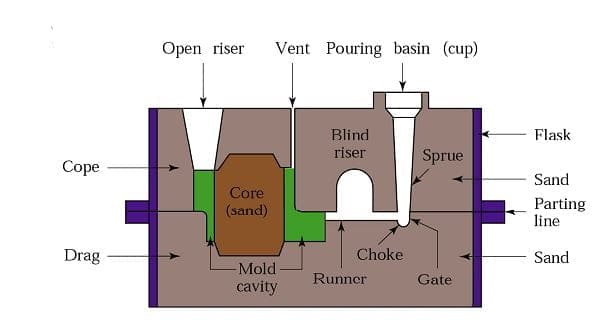
- Flask: A metal or wood frame in which mold is formed.
- Cope: The upper half of the flask is called cope.
- Drag: The lower half of the flask is called drag.
- Core: Core is used to create an internal hollow cavity in the final product.
- Vents: These are the places created in the mold to carry off-gases produced when the molten metal comes in contact with the sand.
- Mold cavity: This is the hollow space in the mold where the metal part is formed.
- Riser: It is the reservoir of molten metal that supplies additional metal in case of any reduction.
- Runner: It is the passage from where the molten metal can be regulated before reaching the mold cavity.
- Pouring Cup: It is the cup or basin from where molten metal is poured in the metal.
- Pattern: It is the duplicate of the shape needed to form.
- Sprue: It is the cavity through which molten metal flows downward.
- Parting Line: This is the line that separates the cope and drag.
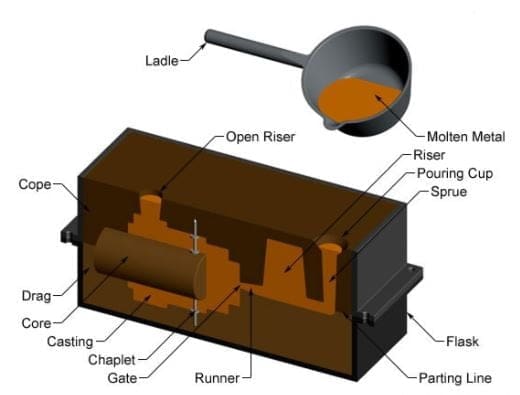
Steps Involved in Casting Process:
There are five steps involved in the casting process:
- Pattern Forming
- Core Forming
- Mold Making
- Pouring Process and
- Solidification Process
Pattern Forming:
The First step of this process is to select the shape that we have to cast. Then we have to make the dummy material of that equipment that we have selected to cast. The dummy material is also called the pattern. The dummy material can be made of wax, wood, metal, plastic, etc.
Core Forming:
After making the pattern then comes the core making. The core is made when the casting requires some internal features like a hole. The core is made from the sand of higher purity. Now after making the core comes the mold making.
Mold Making:
To make the mold we take a wooden box, and then place the pattern in the wooden box. After that, we will put the drag above the wooden box and fill the drag with the sand. We will fill the sand tightly in the drag.
Note: There are two types of sand used in the casting process that are green sand & dry sand. Greensand is a mixture of silica sand, clay, other additives & moisture. Whereas dry clay is the mixture of sand & fast curing adhesive.
After the sand sets, we will reserve the drag as the pattern pointing upward. Now we will remove the pattern. As we remove the pattern we can see the mold cavity has formed. Now we can create a runner and a gate that regulate the flow of molten metal to the cavity.
Now we will place the cope above the drag and attach it tightly with the help of locating pins. In the cope, we will make sprue and riser.
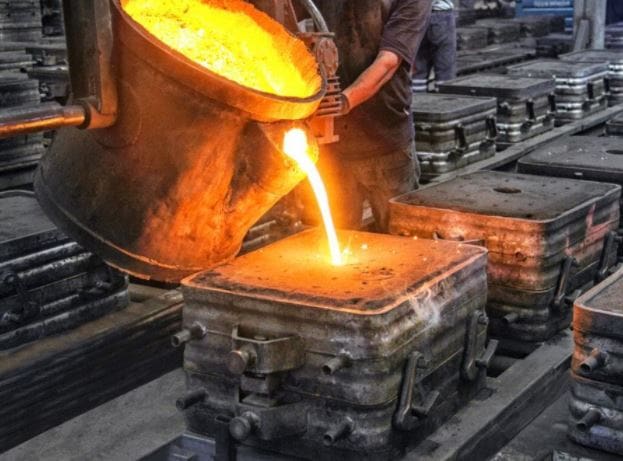
Now comes the most important step is pouring.
Pouring Process:
The first step of this method is to select the type of metal to be used for the casting purpose. Then the selected metal is melted to remove all the impurities and gases. While melting the treatment of the metal is done like degassing, fluxing, etc.
Then the molten metal is filtered and this step can be directly in the mold or before pouring in the mold. This is done to remove impurities, dross, traces, etc.
And then this molten metal is poured into the mold in such a way that the release of gases produces due to contact of the sand mold with the molten metal is the least. As well as the gases present in the mold get enough time to exit from the vents.
Note: To avoid any gaseous defect all the gases must escape. To avoid erosion and interaction with atmospheric gases, the gases must escape with the least turbulence.
Solidification Process:
This process depends upon the gating system and the temperature gradients after pouring molten metal. Efforts always made to raise the raiser or use the chills to get suitable temperature gradients.
Casting should be designed in such a way so, that directional solidification( from one end to another end) takes place to avoid defects. Chills & Padding are useful for directional solidification.
The molten metal solidifies it is ejected from the casting mold either by breaking the mold or by using tools for ejection.
After the ejection of the casting, it is cleaned to remove all the undesirable parts by cutting, sandblasting, tumbling, etc.
Now we get our final and finished product.
So, this was the detailed process of casting hope so you gained a lot from these processes or steps.
Classification of Casting Process:
Casting Process has been categorized into three process:
- Expendable Mold
- Permanent Mold and
- Composite Mold Casting
Expendable Mold Casting:
This is the type of casting process molds are made of sand and cannot be reused. This method is used to produce expensive parts or equipment at less cost. These are also called temporary mold. As this is a temporary mold so, the surface finish & accuracy is not so clean.
Permanent Mold Casting:
In this type, the mold is made of metal and it can be reused again & again. This process is used for the bulk production of the product. In this process, the product produced has a smooth & accurate finish. The product produced has more strength. The cost of the die will be more.
Composite Mold Casting:
This casting is the combination of the permanent and expandable mold casting where some part of the mold is made up of sand that is temporary and some part is made up of permanent metal.
Now moving to different types,
Types Of Casting Process In Detail:
Here I will explain all the types of the casting process:
- Shell Casting
- Investment Casting
- Full Molding
- CO2 Molding
- Sand Casting
- True Centrifugal Casting
- Gravity Die Casting
- Pressure Die Casting
- Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Cold Chamber Die Casting and
- Slush Casting
Shell Casting Process:
Shell molding is the casting process that uses mold like a shell made up of material like fine-grain silica, thermosetting resin, and alcohol. In this method, the pattern is heated up to 250-degree celsius.
This mold has high strength and light-weighted. The mold is suitable for automatic casting. This method can be used for both ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Merits of Shell Casting:
- This process can be performed by semi-skilled labor.
- The products have a smooth finish.
- Higher-dimensional Accuracy is obtained.
- Easily Automated
Demerits:
- Shell casting is more permeable so the chances of gas defect increases.
- It is not suitable for a small batch of production.
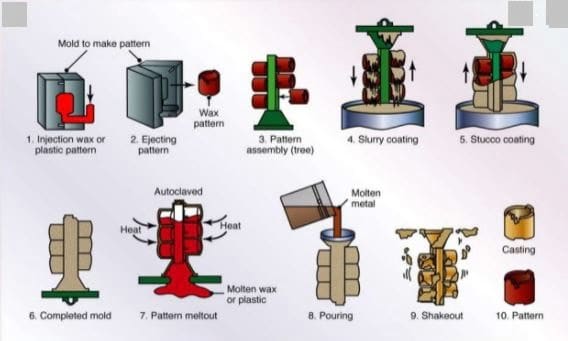
Investment Casting Process:
This is the type of casting process in which casting is formed around a pattern made of wax or similar material. In this casting, the pattern is used is made up of wax and the casting is formed around the pattern by dipping it into the slurry made of silica flour, ethyl silicate & water.
This method of forming a casting around a pattern is called stuccoing. After the casting formed the pattern is melted this process is called dewaxing. And this forms the hollow cavity and molten metal is poured into the cavity for products.
Merits:
- Fine surface finish
- Complex & intricate material can be formed.
- Higher-dimensional Accuracy is obtained.
- Low wastage of material.
Demerits:
- High Cost.
- Parts having a core are difficult to cast.
Full Molding Process:
This method is also known as cavity-less molding or evaporative pattern technique. In this process, the pattern used is made up of plastic, Pvc, polystyrene, foam, etc.
And when the hot liquid metal is poured into the mold the pattern placed inside the mold starts evaporating and gets converted into gases forming the hollow cavity.
Then the molten metal is poured into the cavity to form a product. It is generally used in making a motor casing.
Merits of Full Molding:
- Can cast lightweight parts
- Complex & intricate material can be formed without core or cast.
- Higher-dimensional Accuracy is obtained.
- It offers high smoothness.
Demerits of Full Molding:
- High costing if the die to create the pattern is large.
- Cost of the pattern if the finished product to be produced is big increases.
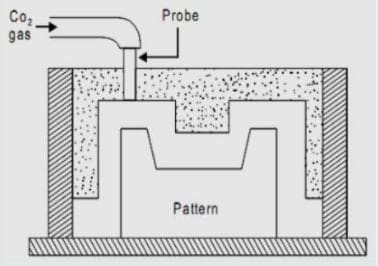
CO2 Molding:
This method is used to increase the strength & hardness of the large-size molding. In this technique, the strength of the casting is increased by passing CO2 gas through the mold.
While preparing the mold we add a special type of additive called sodium silicate. This is added about 2%-6%. And when CO2 gas is passed through the mold this additive reacts with CO2 and forms silica gel.
And this silica gel has better bonding properties which further increases the strength & hardness of mold. Hence CO2 molding is used to produce a casting of the larger shape which requires good strength.
Merits of CO2 Molding:
- The cost of raw material is less.
- Can be performed by semi-skilled labor.
- Can be mechanized easily.
- Faster production rate.
Demerits of CO2 Molding:
- Not suitable for non-ferrous material.
- The minor fault can lead to gas defects and poor surface finish.
Sand Casting Process:
Sand casting is the widely used method of casting. This method is known as sand casting. In this technique, the pattern is placed in the drag and filled with sand.
In addition to sand certain bonding agents are mixed like clay. More than 60% of metal casting is done using the sand casting method.
Merits:
- Wider choice of material as any kind of metal alloy can be cast.
- The cost of tools & equipment needed to perform the process is certainly lower than other metal casting processes.
- As it has a short lead time so, it is perfect for production in the short-run.
- It can be used to create complex & intricate shapes.
Demerits:
- It cannot produce large casting as it has low strength.
- Poor surface finish.
- Increases the efforts as requires post-production finishing.
- Chances of occurring defects as tools & equipment are of low cost.
Centrifugal Casting Process:
Centrifugal or roto casting works on the principle of centrifugal force to produce hollow cylindrical parts or products. During this casting operation, a cylindrical mold revolves at a high velocity around its central axis as melted metal pours into it.
This rotation of the cylindrical mold creates centrifugal force, which pushes the molten metal to the circumference of the mold. Resulting in forming hollow cylindrical parts & products.
Merits:
- The high-density object will be produced.
- No chances of the gas defect.
- Due to fast rotation, the object obtained is of fine grain structure.
- No riser & No gating system required
Demerits:
- Skilled labor is required.
- This expensive process.
- Only some shapes can be formed by this process
- The inaccurate diameter of the inner surface of the product.
Gravity Die Casting Process:
Gravity die casting is a type of permanent casting in which the molten metal is poured into the die with the ladle. While filling the mold with the melted metal no force will act other than gravity force. The material that has high fluidity is made by gravity die casting.
Merits:
- The surface finish of the material produced is high.
- Excellent accuracy of the product produced.
- Mechanical & physical properties are higher than other types of casting.
- Parts can be made of internal inserts and core.
Demerits:
- Certain alloys have a lower production rate.
- Tools and equipment required are of higher cost.
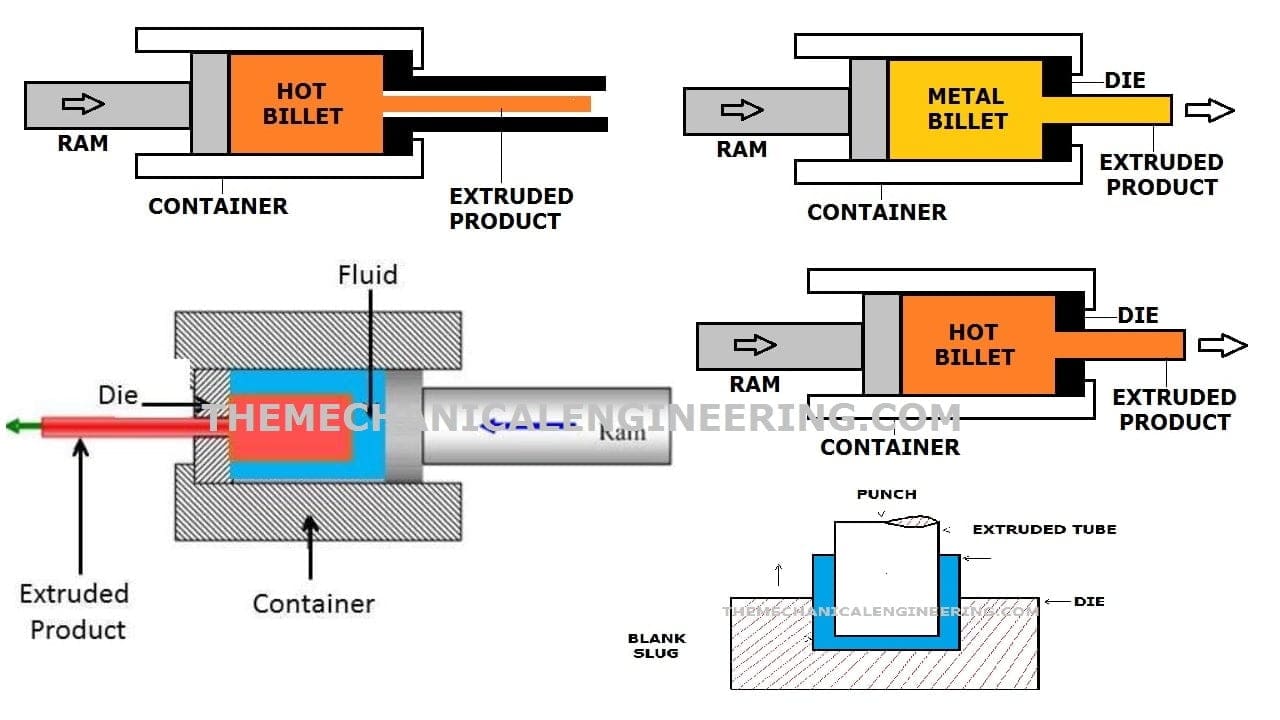
Pressure Die Casting Process:
Pressure die casting is the type of permanent casting in which the molten metal is poured into the mold under high pressure. In this, technique force is applied to the melted metal using a plunger. There are generally two types of die casting-
Hot Chamber Die Casting:
This method is only applicable for the metal like zinc & other alloys that have a low melting point. In this process, the furnace is attached to the gooseneck.
Cold Chamber Die Casting:
The difference between a hot chamber and a cold chamber is in the cold chamber gooseneck is not attached to the furnace. And molted metal is poured with the help of a ladle through the hole in the gooseneck. generally, stell casting along with copper & aluminum is done through a cold chamber.
Merits of Cold Chamber:
- Produces high-volume equipment with higher accuracy.
- Excellent accuracy of the product produced.
- Molten metal solidifies in the second of time even milliseconds.
- Suited for large production in long run.
Demerits of Cold Chamber:
- Complex equipment used.
- Tools and equipment required are of higher cost.
- Not suited for individual products in the short run.
Slush Casting Process:
Slush casting is the type of permanent casting used to produce objects that are thin-walled and hollow. This technique is commonly used to produce decorative objects, components, and ornaments.
In this method, the molten metal is not allowed to solidify completely. When the desired thickness is achieved the remaining molten metal is poured out.
Merits:
- A wide range of ornaments and decorative products can be produced.
- Preferred thickness can be easily achieved by pouring excess molten metal.
- Good surface finish.
- Faster cooling rates.
Demerits:
- Requires manual labor.
- The thickness of the material can vary.
- Time-consuming.
Advantages of Casting Process:
The following advantages of Casting Process is:
- Complex and intricate shapes can be formed.
- We can cast any type of material.
- The tools and equipment used in the casting process are inexpensive.
- It is possible to make the casting of any shape and size.
- The casting of any size can be performed up to 200 tons
- It is the cheapest way to produce shapes and sizes with different mechanical properties.
Disadvantages of Casting Process:
The following disadvantages of Casting Process is:
- High chances of defects.
- The dimensional accuracy of casting is not so good.
- Generally, sand casting the popular technique of casting is labor-intensive.
- In some cases, it is not possible to overcome defects.
Application of Casting Process:
The casting process is used to manufacture different products in industries like a cylindrical hollow cylinder, piston used in automobiles, pulley, engine manifolds, valves, nuts, defense equipment, etc.
The casting process is used in multiple industries like aerospace, defense, automobile, railways, construction, farming, mining, chemical, etc. It is also used in the manufacturing of home decor and ornaments.
Internal Resources:
- Injection Molding Process
- Drilling Machine
- Shaper Machine
- Slotter Machine
- Lathe Machine
- NC Machine
- Hot Working Process
- Cold Working Process
Conclusion:
Casting is an important method of manufacturing that helps the manufacturing industries to produce a different variety of products. There are different methods of casting like sand casting, die casting, full molding, investment casting, etc.
Hope, So this article has helped you to get a clearer view on the Casting process and its advantages & disadvantages. Make sure to comment on all of your queries regarding the topic.








Discussion about this post