In this article, we are going to study What is Thermodynamic System? and Its Type with Examples in detail. So let’s start with the definition first,
What is Thermodynamic System?
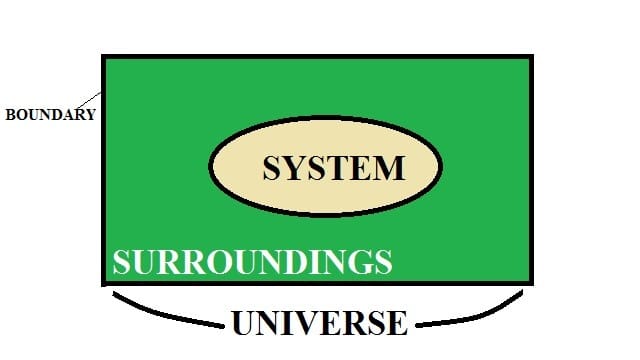
A thermodynamic system is defined as a fixed mass in a region of space under consideration to analyze a problem.
Let also understand the terms system, surrounding, and boundary.
What is a System?
The system is defined as the region or quantity of matter which is taken into consideration for analysis.
What is Surrounding?
Surroundings: Surrounding is the region located outside the system. There is a boundary between the surroundings and system which keeps them separated from each other.
Note: The system and surroundings together make up the universe.
What is Boundary?
It is a surface in which the system is contained and separated from the surroundings. It can be movable or fixed.
Classification of Thermodynamic System:
Thermodynamic systems can be classified into three categories on the basis of heat and mass transfers between the system and the surroundings:
- Closed system
- Open system and
- Isolated system
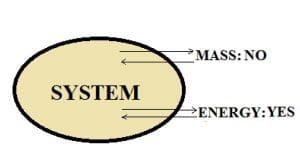
Closed system:
In this type of system, the transfer of mass does not take place across the system boundary. However, energy transfer can place in the form of heat or work.
For example, We have a piston-cylinder arrangement.
The volume of gas is 1 m^3, and the mass is 3 kg. The boundary is closed i.e. gas can’t escape out of the cylinder into the atmosphere, When the cylinder is heated from below, the piston moves upwards. The gas in the cylinder heats up and transfers work in the form of piston movement.
However, the mass remains constant as only expansion is taking place. Thus, we can say that this is a closed system.
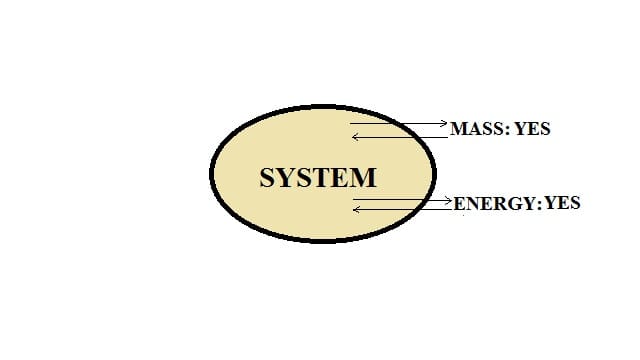
Open system:
In this type of system, the transfer of energy, as well as mass, takes place across the boundary of a system.
For example: Heating a pan.
When a pan containing water is kept on a stove and heated, water molecules get evaporated and convert into steam. Thus, mass transfer is taking place. Water gets evaporated and water can be added to the pan. Heat energy is transferred to the water by the gas flame and heat energy is also lost to the surroundings. Hence, we can say that this is an open system.
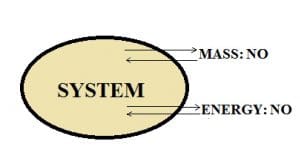
Isolated system:
If there is no mass and energy transfer between the system and the surroundings, then such a system is said to be an isolated system.
Example: A thermos flask.
When a liquid is poured inside the thermos flask whether it is hot or cold, the flask is built in such a way that it maintains the temperature of the liquid present in it. It does not allow the transfer of mass and energy because the lid is closed so nothing comes in and nothing goes out of the flask. So, we can conclude that the thermos flask is an isolated system.
Internal Resources for You:
- Fire Tube boiler
- Water Tube Boiler
- Difference between Fire Tube and Water Tube Boiler
- Benson Boiler
- Locomotive Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
- Cochran Boiler
Reference [External Links]:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/thermodynamic-system
- https://www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/cellular-energetics/cellular-energy/a/the-laws-of-thermodynamics
Conclusion:
Here we finally studied the Thermodynamic System in detail. I have also written many articles on Thermodynamic subjects if you are interested then please do check out and share them with your friends.
And let me know your doubt bout this topic in the comment section. And If there are any improvements needed do let me know or any further recommendations in the comment section.




Discussion about this post