In this article, we will study the Definition, Layout, Working, Site Selection, Advantages, Disadvantages [Notes and PDF] of Thermal Power Plant.
Note: At the end of the article you can download PDF version.
Let’s start with the definition first,
Thermal Power Plant Definition:
Thermal Power Plant is an electric producing power plant in which fuel (such as coal, liquefied fuel, uranium, and natural resources) is used to generate heat and that heat is further utilized to heat the water to make steam and that steam is used to rotate the turbine and further electricity generates with the help of 3 phase supply generator.
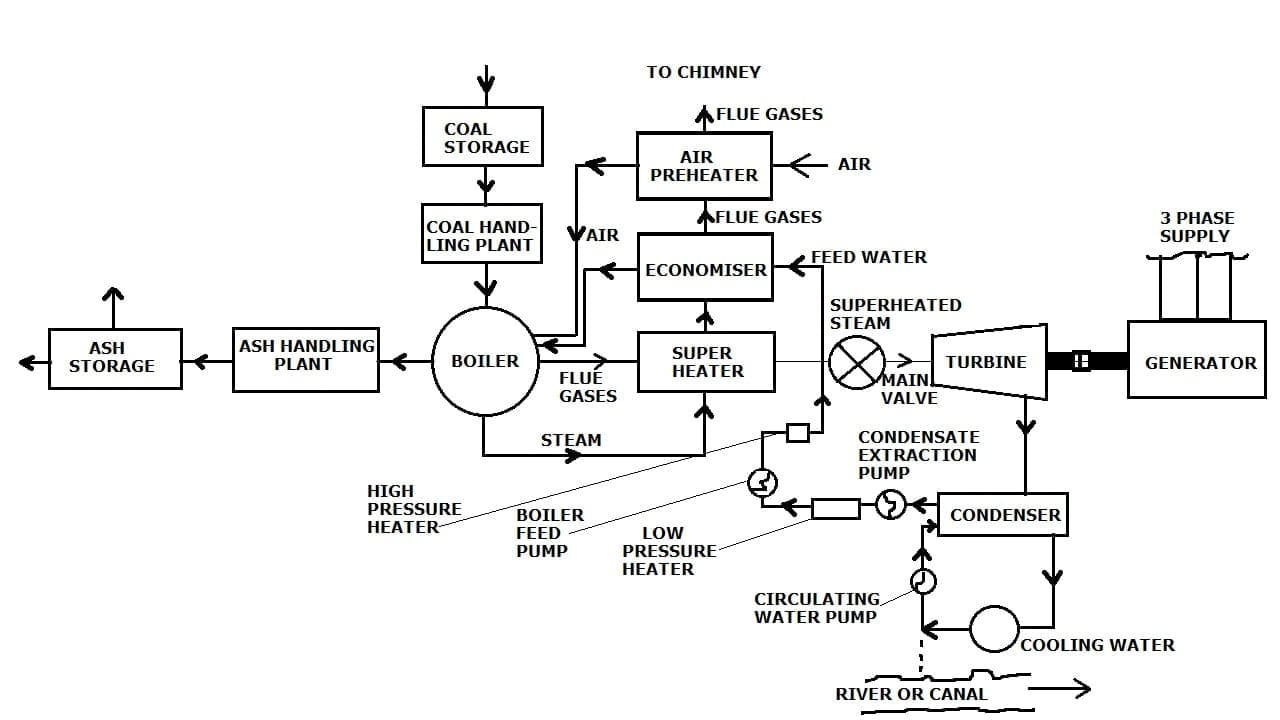
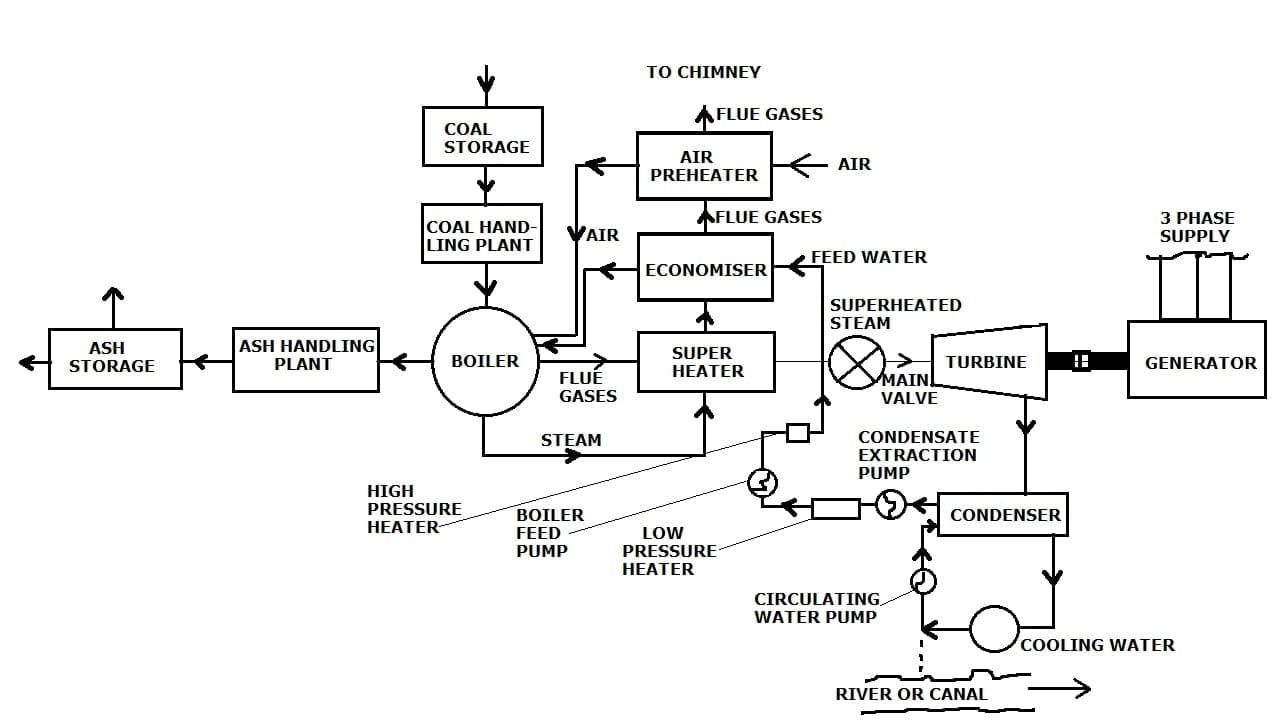
Thermal Power Plant Layout:
The construction of Thermal Power Plants is Coal Storage, Coal Handling, Boiler, Boiler feed Pump, Superheater, Economiser, Air Preheater, Ash handling and Storage, Feed Water, Turbine, Generator, and 3 Phase Supply, Condenser, Low and High-pressure heater, River.
Let’s study these terms in very detail,
Coal:
It is the most common source of energy that is being used since industrialization. The modern steam boiler burns coal mainly as the primary fuel in any of its available forms. Different ranks of coal available are peat, lignite, bituminous, and anthracite.
Coal Storage and Handling Plant:
As name suggest storage and handing it means that the coal is stored in the storage and as per the demand it supply to the next.
Boiler:
Boiler is a closed vessel in which fuel burn and produces flue gases that flue gases is further used to heat the water to make steam.
There are two main types of boiler: Fire Tube boiler and Water Tube boiler.
Boiler Feed Pump:
The feed water is supply to next accessories by the boiler feed pump.
Super heater:
Name itself indicates that it increases the temperature of any substances. Super heater is a external system which helps to increases the temperature of substances and to improve boiler efficiency.
Economizer:
It is also used here to preheat the fluid. It helps to increase boiler efficiency.
Air Preheater:
The work is same as an economiser.
Turbine:
Here some baldes are attached. The amount of steam generated from the boiler will strike the blades and balde will rotates hence PE is converted into KE and then It attached to generator.
Generator:
Generator used for generating electricty with the help of turbine.
Condenser:
Some amount of wet steam that is not used will come to condenser and the further cycle repeats.
The main function of condenser is to condense the fluid from gaseous state to liquid state.
Ash Handling and Storage:
After burning of coal it is in the form of Ash, which is being stored and release to the field.
Now let’s study working,
Thermal Power Plant Working:
As you can see the above diagram is general layout of Thermal Power Plant. The coal is inserted into coal storage. Here coal is being crushed and send to the boiler.
In the boiler there is feed water supplied through economizer. Coal is being heated here it produces flue gases, that flue gases is used to heat the feed water to make change the phase of water into steam.
From the boiler the coal which is burnt and becomes ashes will now send to the ash handling plant and further ash storage.
The steam generated in the boiler is now sends to the superheater here it again gets heated at high temperature to becoame only steam. This steam is now send the the turbine.
In turbine there is blades are attached. The tubine further attached to the generator for generation of electricity.
Now the steam strikes to the turbine blades, the turbine blades starts rotating [PE is converted into KE and further used for generation of electricity]
Here some amount of steam which is not used will now come to the condenser and here it looses his heating properties. Now again with water it sends to the economizer for repeation process.
Thermal Power Plant Video In Hindi:
Thermal Power Plant Video In English:
Thermal Power Plant Site Selection:
The factors to be considered for site selection of steam power plants are:
- Availability of Coal
- Transportation facilities
- Availability of land
- Supply of water
- Availability of labors
- Geology and soil type
- Distance from populated area
Availability of coal:
As the power plant consumes a large amount of coal, enough quality, must be available either in the vicinity, Proximity to sea route and rail transport are the major criteria.
Transportation facilities:
A typical power plant with 1,000 MW capacity approximately consumes more than ten thousand tons of coal per day. Hence the necessity for continuous supply and storage capability of coal in the power station by rail, by sea, and by road must be ensured.
It is also essential to have easy and enough access to transportation networks during power plant construction and operation periods.
Availability of land:
In addition, enough space must be available for the storage of coal, disposal of ash, the building of the power plant, township or residential colony of workers, markets, etc.
Normally for every 1 MW of power generated at least 3-4 acres of land available for this purpose.
Supply of water:
A large amount of water is required for the cooling and ash handling system in the power plant. Hence it is essential to have water resources In the form of rivers, lakes, sea, etc.
Availability of labors:
Apart from these, the major requirement availability of skilled labour is also essential in the plant locality as the semi and unskilled labour requirement are very high. Proper transportation facility is very high. Proper transportation facility is very vital for the arrangement of labours.
Geology and soil type:
The power plant should be built on land that is not prone to vibrations generated by rotary equipment. Proper inspection and testing of soil and rock layers are essential.
In addition, the site should be away enough from the faults and earthquake-prone areas as weak and small earthquakes can damage many parts of a power plant intensively.
Distance from the populated area:
The location of the plant must be chosen in such a way that it has minimal or no impact on the surrounding environment. Plant location should be away from the national park’s wildlife, protected area, etc.
As nearby forest ecosystems etc. Are very sensitive to the pollution caused by a power plant, the ideal location should be away from them. Similarly, for the same reason, the site should be away from population centers.
Thermal Power Plant Advantages:
The various advantages of thermal power plant compare to other plants are:
- The fuel used coal which is quite cheap and available.
- The initial cost is low.
- It can be installed anywhere.
- The generation cost is quite less.
Thermal Power Plant Disadvantages:
- Overall efficiency is low [below thirty percent].
- The handling of ash is a major problem in steam plants.
- It pollutes the atmosphere due to the production of a huge amount of smoke therefore Global warming increases.
- This cubic capacity of the building required for gas turbine plants is about 50 percent of the steam plant. The total weight of the material required for the gas turbine plant is also 50-60 percent of the steam plant. Therefore considerable savings in capital cost is possible having the same efficiency as a steam plant.
- The site of the steam power plant is dictated by the availability of large cooling water, whereas an open-cycle gas turbine plant can be located near the load center as no cooling water is required.
This is all about Thermal Power Plant in detail. Let me know in the comment box what I can help you further.
Related Resources:
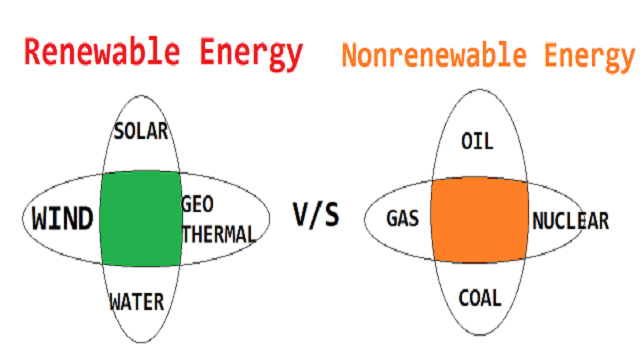
Renewable vs Non-Renewable Energy
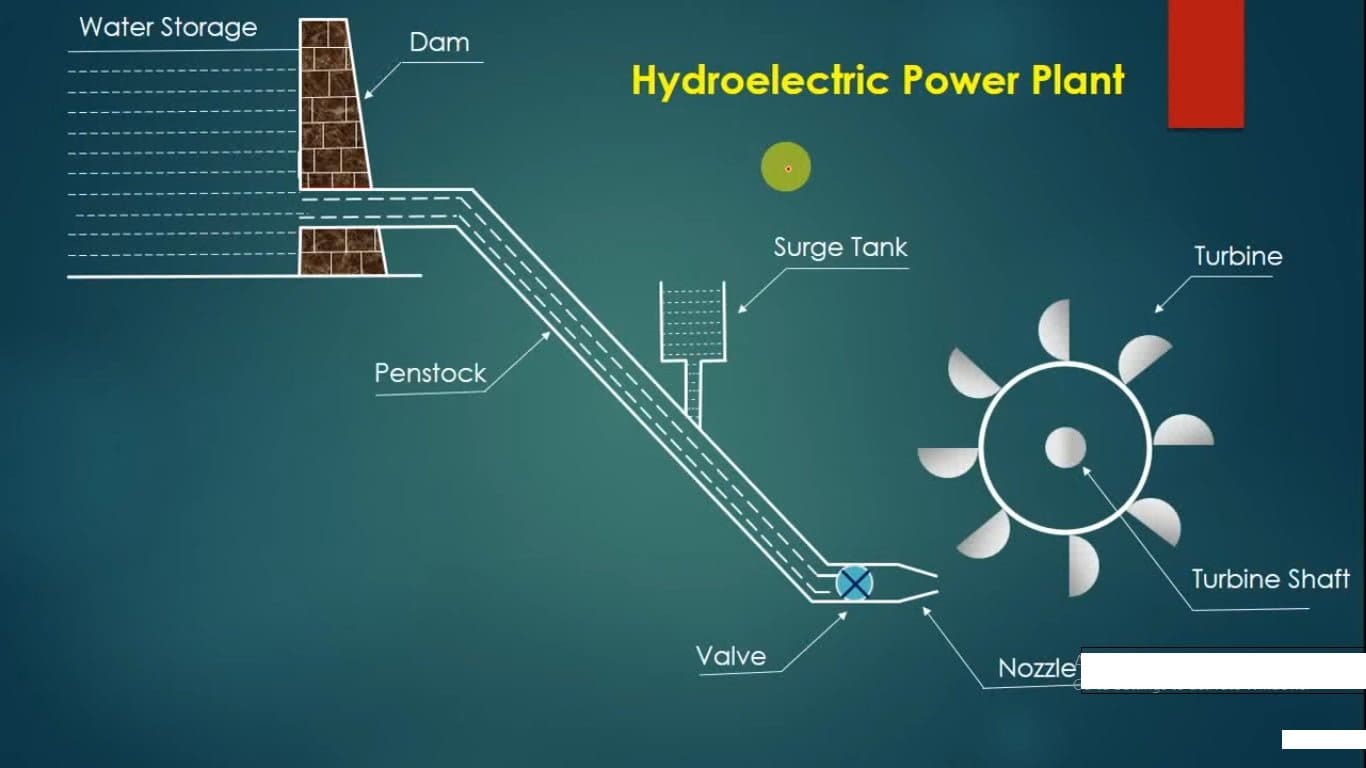
Hydro Power Plant
If you like the article do not forget to share on Social Media.




Discussion about this post