The Grinding Machine is another most important machine in the manufacturing Industry. Today we will study the Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Operation, Advantages, Application of the Grinding machine in detail.
Lets start with the definition first,
Grinding Machine Definition:
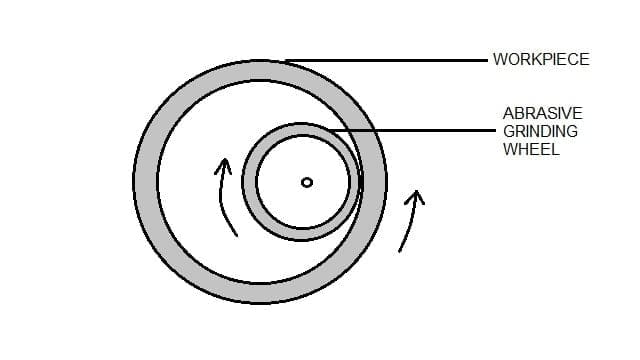
A grinding machine is a production machine tool used in the manufacturing industry in which the grinding wheel is attached in the tool post and the workpiece is fixed to the work table and when the operation starts it removes the unwanted material to get the desired surface finish, correct size, and accurate shape of the workpiece.
It is also known as the Abrasive Grinding Machining Process. Why Abrasive Grinding Machining Process? Because the abrasives are placed on the surface to do the finishing process with much more accuracy.
The grinding machine is widely used to finish the workpiece. Do you know why? Because the work removal rate is low between 0.25 to 0.5 mm. (This can be advantages or disadvantages also for various types of works).
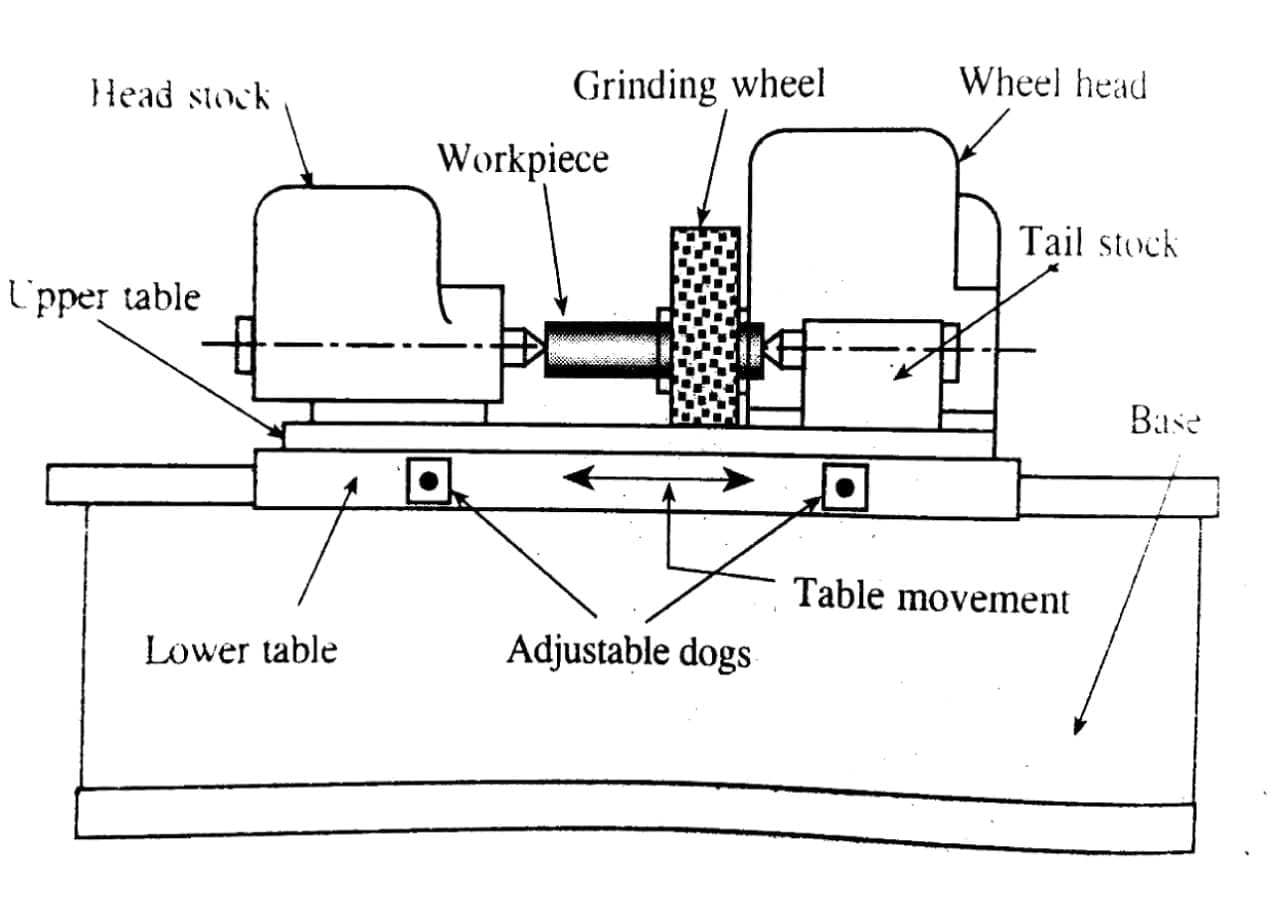
Grinding Machine Parts and Function:
The Grinding Machine Consists of Following Main Parts:
- Base or Bed
- Column
- Headstock
- Tailstock
- Worktable
- Wheel Head
- Grinding or Abrasive Wheel
- Crossfeed or Traversing Wheel and
- Coolant Supply Nozzle
Base or Bed:
The base or Bed is made up of cast iron. It is situated horizontally and it is the bottom part of the grinding machine, provides support to all the grinding parts. When machine operation starts some vibration occurs therefore base acts as an absorber of vibrations.
Column:
Colum is like a vertical pillar of the machine in this section the abrasive wheel, wheel head, and wheel guard are kept. The column is also made up of cast iron.
Headstock:
In Lathe Machine this section is known as live center Do you know that? The headstock work is to match the center and helps to grip the workpiece.
Tailstock:
Tailstock is know as dead center. It also provides gripping to the work piece.
Work Table:
Nowadays In the new grinding machine, the headstock and tailstock are replaced with work tables. A worktable is like a magnetic chuck that holds the workpiece.
Wheel Head:
In this section, the abrasive wheels which are our tool for operation are placed and this is moved vertically up and down. With the use of a Feed hand, we can adjust the wheel head. Moving this wheel head down so that the grinding wheel can touch the workpiece. The wheel head consists of a grinding wheel and driving motor.
Grinding or Abrasive Wheel:
Grinding or Abrasive wheel is our main tool used here to remove the unwanted material from the workpiece to get desired smoothness and surface finish. The wheels are coated with an abrasive particle. The abrasive wheel comes with various types and properties which I have discussed here : Grinding or Abrasive Wheel.
There are four commonly used abrasive materials for the surface of the grinding wheels are Aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, cubic boron nitride (CBN), and diamond.
Crossfeed:
Cross feed is also an important parts of this machine used for moving up and down or left and right of Wheel head and work table and so on.
Traversing Wheel:
There are three types of Traversing wheel.
- Hand Traversing Wheel: This wheel is used to move the table in the horizontal direction either left or right according to the tool and the workpiece.
- Cross Side: It is used to move the worktable in forwarding and backward directions and
- Vertical Feed Hand Wheel: The vertical feed hand traversing wheel is used to move the wheel head in the vertically upward and downward direction.
Coolant Supply Nozzle:
The main work of the coolant supply nozzle is to cool or reduce the temperature generated while performing the operation. If this part is not there then there are many chances of wear and tear happen because of the high temperature between the wheel and the workpiece. The coolant may be water or any other oil.
Now let see How does grinding Machine works?
Grinding Machine Working Principle:
In brief, we can say the working of the Grinding Machine is the Workpiece is fed against the rotating abrasive wheel. The action of rubbing or friction generates between wok price and tool therefore the material removes.
Lets see step by step,
- First, clean the machine with a clean brush.
- The workpiece is fixed in the worktable. And tool which is the grinding wheel is also fixed in the tool holder section.
- Now with the help of the traversing wheel, we adjust the tool and workpiece and bring it into the contact and make sure there is little gap available as you have not started the machine.
- After all, set between workpiece and tool make sure to check the coolant supply nozzle and fill the liquid into it So that when operation starts it automatically or manually can supply.
- Now supplying the power to the system, The wheel starts rotating and Now brings the tool in contact with the workpiece. Gradually provide the feed as per the dimension you want.
Grinding machine is used for providing good surface finish to the work piece.
This is how grinding Machine works.
Grinding Machine Working Video:
Now let see operation
Grinding Machine Operations:
The following different types of Operation that can be performed on Grinding Machine:
- Surface Grinding Operation
- Cylindrical Grinding Operation
- Thread grinding Operation
- Internal and External Grinding
- Centerless Grinding
- Form Grinding Operation
- Wet and Dry Grinding Operation
The relative movement of the wheel may be along the surface of the work or it may be radially into the work piece.
Now lets start with the surface grinding operation,
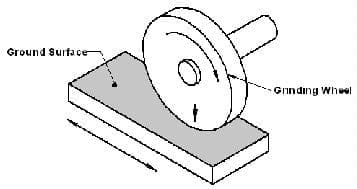
Surface Grinding Operation:
Surface grinding involves grinding flat surfaces and is one of the most common grinding operations. Typically the workpiece is secured on a magnetic Chuck attached to the worktable of the grinder. Nonmagnetic materials generally are needed by vises special fixtures, vacuum Chuck’s.
A straight wheel is mounted on the horizontal spindle of the grinder. Transverse grinding occurs as the table reciprocating. Longitudinally and feels latterly after each stroke. In plunge grinding the wheel is moved radially into the workpiece as it is when grinding a groove.
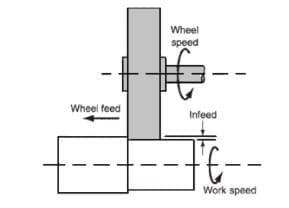
Cylindrical Grinding Operation:
The rotating cylindrical workpiece reciprocates laterally along its axis in a grinder used for the large and long workpieces. The grinding wheel reciprocate called a roll grinder cylindrical grinders are identified by the maximum diameter and length of the workpiece that can be ground similar to engine lathes.
In universal grinders, both the workpiece and the wheel axes can be moved and swiveled around a horizontal plane permitting the grinding of tapers and other shapes. This typical applications include crankshaft bearing spindles pins , bearing rings and rolls for rolling mills.
Thread grinding Operation:
It is done on cylindrical grinders with specially dressed wheels matching the shape of the thread as well as using a centerless grinder. Although costly thread produced by grinding is the most accurate of any manufacturing process and has a very fine surface finish.
Internal and External Grinding:
In an internal grinding, a small wheel is used to grind the inside diameter of the part, such as bushings and bearing races. The workpiece is held in a Rotating Chuck. The headstock of internal grinders can be swiveled on a horizontal plane to grind tapered holes. Whereas
In an external grinding, a small wheel is used to grind the outside diameter of the part, such as bushings and bearing races. The workpiece is held in a Rotating Chuck.
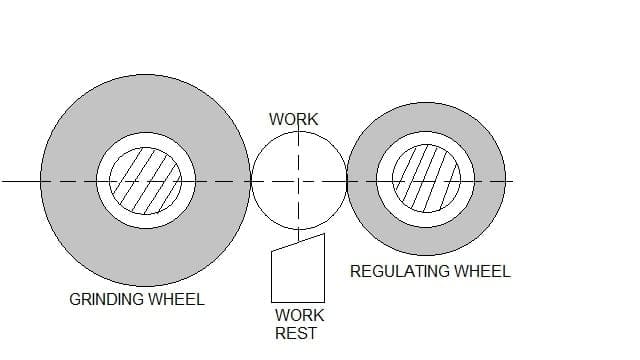
Centerless Grinding Operation:
In this operation there are two wheels are fitted parallel with a 5-10 degree angle, and this angle is provided to get a longitudinal motion of the workpiece.
Here the work piece is supported blade, not by centers or chucks.
A cylindrical rod is placed between the two-wheel due to the tilted angle the workpiece is automatically passed through the wheels, and we got a smooth surface.
Wet and Dry Grinding Operation:
Here In Wet, we sprayed coolant generally water or any other coolant to cool the surface so that the longevity of the grinding wheel increases and also we get a fine surface finish.
But In case of Dry Grinding operation Here In Wet, we do not use any coolant to cool the surface.
Grinding Machine Advantages:
The following advantages of Grinding Machine are:
- With the help of this machine, we can obtain a good surface finish on the workpiece.
- Grinding can machine hard material.
- The surface smoothness is good and it can be obtained from this machine.
- The work operation can be done at maximum temperature also.
- In a grinding machine, the abrasive particles are self-sharpened action.
- The semi-skilled operation can work on this machine. The work can be performed easily.
- The machine productivity is good.
- One major advantage of this machine is the manual and automatic operation can be performed.
Grinding Machine Disadvantages:
The following disadvantages of Grinding Machine are:
- The Grinding Machine is a little costly. The cost of this machine is more than 2.5 lacks.
- Unlike another machine (Lathe Machine) the material removal rate is not fast.
- It takes more time for removing the material.
- Once the grinding operation starts the wheel can not rotates in the reverse direction and The wheel is constantly degrading and it requires much spindle power.
Grinding Machine Application:
The following application of Grinding Machine are:
- The Grinding Machine is used in various industries for grinding. The first and foremost industry where this machine is used in Manufacturing Industry.
- The Grinding Machine is used for finishing the cylindrical and flat surfaces. In other words, we can say it is used for grinding various materials.
Internal Resources:
- Lathe Machine
- NC Machine
- Milling Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Shaper Machine
- Planer Machine
- Slotter Machine
- Hot Working Process
- Cold Working Process
Conclusion:
Here we have discussed the Definition, Parts, Working Principle, Operation, Advantages, Application of the Grinding Machine in detail. I have also written many articles on Manufacturing Technology you can check that too.
If you like the article then please do share it with your classmate and social media. Thank you for reading we will meet in another article.







Discussion about this post