Many experts were working on electron beam technology in the late 1940s. It was in the year 1949 when german physicist Karl-Heinz Steigerwald developed Electron beam welding.
After 9 years of patience and hard work, the first practical electron beam welding machine was developed in 1958 by the same person.
On the other hand American inventor James.T.Russell has also been given the credit for the invention of electron beam welding.
In this article, we will study the Definition, Working Principle, Construction, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application of Electron Beam Welding. And at the end, You can download a PDF of this article.
Let’s start with the definition first,
What is Definition of Electron Beam Welding?
Electron beam welding is a liquid state welding process used to weld two or more metals together. As the name suggests electron beam welding is a process of welding in which a high-velocity electron beam is focused on the workpiece to generate heat, the heat produced melts the metal which in turn creates a weld.
It is a non-traditional method of welding that is used to create strong welds in several industries. The acceleration of electrons depends on the potential difference applied, hence high voltage is used in the order of a few thousand volts. While the current applied is of a low order of around 0.05amps to 1amps.
Working Principle of Electron Beam Welding:
The working principle of electron beam welding is an energy conversion principle. The high voltage electrical energy is first converted to the kinetic energy of electrons through an electron gun. Then this kinetic energy is then converted to heat energy which is used to melt the workpieces and weld them together.
Now we will look step by step how it works?
At first, the workpieces are clamped inside the vacuum chamber on the CNC-controlled worktable, with the help of fixtures.
Vacuum is created inside the chamber using mechanical or electrical pumps.
The workpiece is brought to the correct position using computer numerical controls. As soon as the workpiece is situated in the correct position the power supply is switched on.
A very high voltage is created between the anode and cathode of the electron beam welding machine.
The electron beam is released due to the heating of the filaments at the top. This beam is then accelerated due to the EMF generated at the anode.
The high-velocity electron beam then reaches the pair of focusing coils, where the diverging beam is converged using Lorentz force.
Now, the high velocity converged electron beam reaches the deflection plate. Here the beam is directed to the correct position.
As the electron beam hits the workpiece, its kinetic energy is converted to heat energy which is used to melt the workpieces. Which in turn creates the weld.
Once the weld is initiated the area to be welded is controlled using computer numerical control. Once the welding is done the power supply and pumps creating vacuum are switched off.
The welded joints are unclamped manually by the operator.
Construction of an Electron Beam Welding Machine:
Part and construction are much similar to electron beam machining which is a non-traditional machining process.
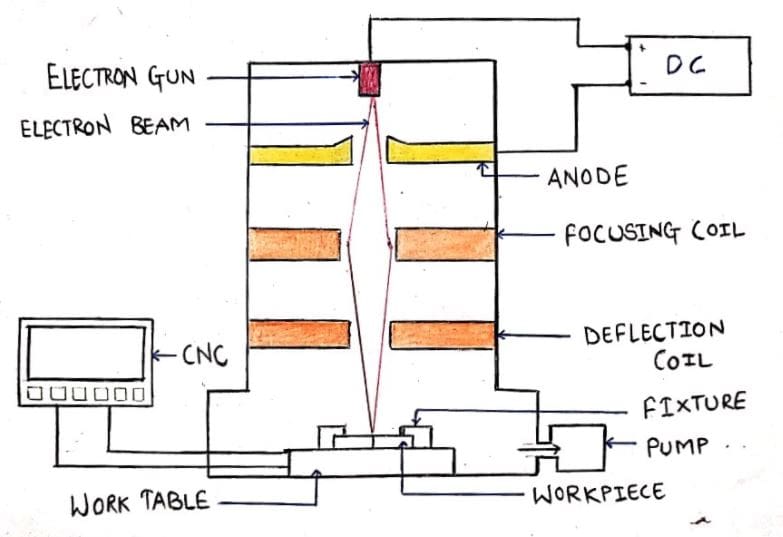
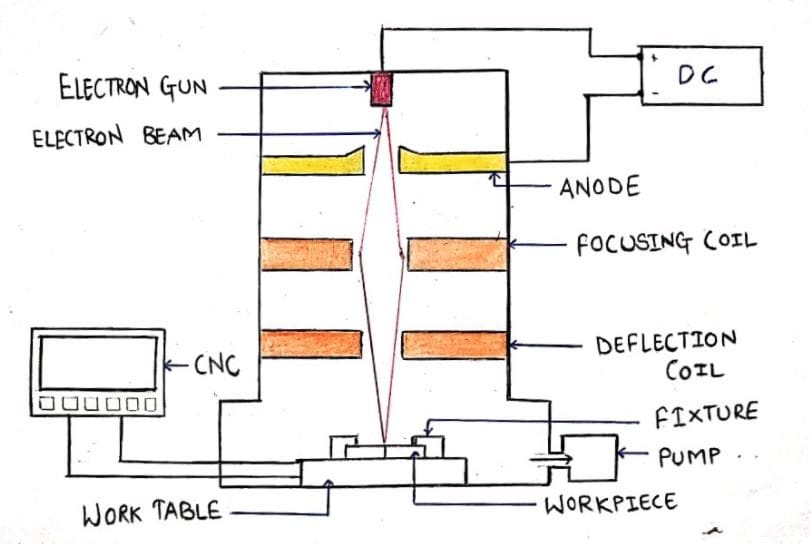
The electron beam welding machine has two parts. The upper part is called an electron beam tower and the lower part is known as the vacuum chamber.
The electron beam tower consists of an electron gun at the top which also acts as the cathode and is connected to the negative terminal or the power supply. Right below the cathode, there’s an anode that is connected to the positive terminal of the Power supply.
There is a pair of focusing coils under the anode followed by a pair of deflection coils. The electron beam tower is connected to the vacuum chamber in which a CNC-controlled worktable is situated. Workpieces are clamped on the table using fixtures.
Numerous elements involved in the construction of Electron Beam Welding are as follows:
- Power Supply
- Electron Gun
- Anode
- Focusing Coil
- Deflection coil
- Vacuum Chamber
- Fixtures and
- Work Table
Power supply:
A DC power supply is used in the case of electron beam welding. This supply line creates a very high voltage across anode and cathode.
The Range of voltage created by the power source varies from 5kV to 30kV for thin welding and 70kV to 150kV for thick welding. Such a high supply is required to generate high-velocity electrons, discharging from an electron gun.
Electron gun:
The electron gun is that element that produces low-velocity electron beams. The electron gun is said to be the heart of electron welding. An electron gun is a cathode tube with a filament of either tungsten or tantalum.
When the cathode tube is given electrical energy in the order of a few kV it converts this energy into an electron beam. This takes place due to the heating of the filaments at about 2500oC.
The electron gun is the only source of electrons in the setup and is the most important part of an electron beam welding machine.
Anode:
Anodes are the positive terminals used in an electron beam welding setup. The main function of an anode is to increase the velocity of the electron beam coming from the cathode or electron gun.
The acceleration of electrons coming from the electron gun depends upon the anode. Besides increasing the velocity of electrons, anode also gives the beam a direction and avoids unnecessary scattering of the beam.
Focusing coil:
The high-velocity electron beam coming from the anode always tends to diverge. If the beam diverges it won’t focus on a single point this would not generate enough heat for Melting the metal surface.
Hence magnetic coils known as focusing coils are used to converge the electron beam. This uses the principle of Lorentz force to deviate from the diverging beam.
It also absorbs low-energy electrons and diverging electrons.
Deflection coil:
Deflection coils are also magnetic lenses used to deflect the electron beam on the required area. The coils work on the same principle as that of focusing coils.
Vacuum chamber:
The workpiece to be welded is kept in a vacuum chamber. Vacuum is created using mechanical or electrical pumps. The pressure varies from 0.1 to 10 pascals.
Vacuum is created because the electron beam should not get scattered by the air particles. There can be a scattering of the beam if a vacuum is not created.
Fixtures:
Fixtures are the devices used for holding the workpiece in the required position.
Worktable:
The worktable used in electron beam welding is CNC driven. And allows movement of the workpiece in XYZ directions. This is because of the sealed vacuum chamber which does not allow any human interference.
Advantages of Electron Beam Welding:
The following advantages are:
- Flexibility: It is a flexible welding process that can be used for welding both similar and dissimilar metals.
- Low running cost: The running cost of this machines is low as there are no filler metals or flux used for welding workpieces.
- Surface finish: The surface finish obtained after welding is excellent. Better surface finish results in increased strength of the weld.
- Delicate materials: Another advantage of electron beam welding is that it can be used for welding delicate materials. This is due to the low heat produced during the welding operation.
- Clean process: There is an absence of flux and filler metals which makes the process clean. There are no waste products formed during machining. Hence waste management is not necessary, unlike traditional welding methods.
- Accuracy: Industries, where electron beam welding is used, rely on accuracy and precision. The process of electron beam welding is carried out with the help of a computer numerical controller hence the welds formed are highly accurate and precise.
- Welding speed: Welding speed refers to the linear area being welded in a given time. It is generally expressed in mm/s. The Welding speed is high ( 30mm/s) which results in a faster production rate.
Disadvantages of Electron Beam Welding:
The following disadvantages include:
- Initial cost: There are several expensive parts used in an electron beam welding machine such as an electron gun, magnetic coils, vacuum pumps, CNC system, etc. The use of expensive parts makes the initial cost of the equipment quite high making it a disadvantage of electron Beam welding.
- Complex structure: The machine is very complex as it involves parts working on electric and magnetic radiation. Also, the CNC systems used in the process involve complexities. This requires a professional technician in case of any breakdown.
- Skilled labor: Unlike traditional welding methods, this welding machines cannot be handled by unskilled labor due to the complexities involved. Hence there’s always a requirement of skilled labor to weld workpieces using electron welding.
- High vacuum: To run the equipment in an effective way the vacuum created using pumps must be high. This results in high power consumption by the pumps to create a vacuum.
- Safety: Harmful radiations such as X-rays and other radiations are generated at the time of working of an electron welding machine. This requires high safety measures to overcome any health-related issues. This is not the case with traditional welding methods.
Applications of Electron Beam Welding:
The following application is:
- Electron beam welding is widely used in aviation industries for various purposes. The parts framed by electron beam welding are used in engines, sensors, gears, etc. This process of welding gives effective results in the aviation industry and is considered very important.
- It also has great importance in power generation industries. The process is used to create shallow as well as deep welds. It is used for welding large components such as steam turbine diaphragm to small components such as nozzles.
- This process of welding is also used in automobile industries for welding different functional parts like gears, turbochargers, clutch plates, etc.
- Electron beam welding is also used in electronic industries for welding different connectors. This is due to the ability of electron beam welding to weld aluminum and copper.
- This welding is of great importance in medical industries as it does not change the chemical structure of the parent material. It is used for welding orthopedic implants in medical industries.
- Besides all these applications it is also used for welding hard materials like titanium and its alloys.
Internal Resources:
- Plasma Arc Welding
- Casting process
- Forging vs Casting Process
- NC Machine
- Milling Machine
- Drilling Machine
- Shaper Machine
- Planer Machine
- Slotter Machine
- Hot Working Process
- Cold Working Process
- Different Parts of An Engine
Reference [External Links]:
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/resistance-welding
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/electron-beam-welding
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_resistance_welding
This is all about Definition, Construction or Parts, Working Principles, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of Electron Welding.
Let me know have you understood or not by the use of the comment box. Till then Thank you so much for reading the article and share with your friends too.






Discussion about this post