In this article we will study Definitions, Parts, Working principles, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications of the Benson boiler.
Note: At the end of the article you can download whole article in PDF format.
So let’s start our topic,
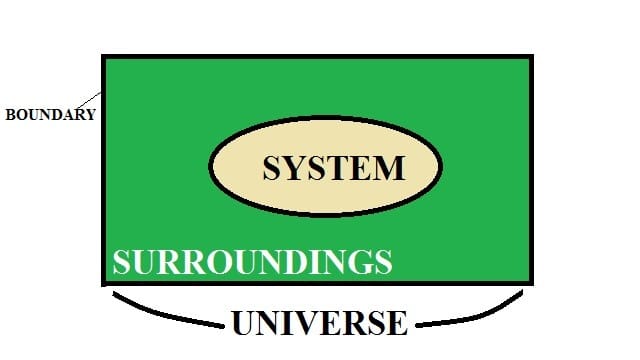
What is a Boiler?
A boiler is an enclosed vessel that provides a medium in the transfer of heat and pressure until it turns the water into steam. The heating surface of any boiler, like the hot gases, and liquid gets placed on either side. The boiler part that provides in making steam is the heating surface, expressed in square meters. The larger the surface, the more efficient it produces.
Now come to Benson Boiler,
The Benson boiler is invented by Mark Benson in the year 1922. It is a high-pressure, supercritical water tube steam boiler, that uses the method of forced circulation.
Benson Boiler Definition:
Benson Boiler is a high-pressure super critical water type boiler in which no bubble is formed because the water is compressed at super critical pressure and it directly converts into steam.
In other words, The formation of a bubble does not take place because of supercritical pressure, and at this pressure, the density of water and steam becomes the same.
As the water which is entered into the boiler is being compressed to supercritical pressure. Therefore the latent heat of water is reduced to zero. So the water directly changes into steam without the formation of bubbles.
You might be interested to know what is Latent Heat?
So the latent heat is defined as the energy absorbed or released by a substance during a change in its physical state without changing the temperature is known as Latent Heat.
Now come to the construction of Benson Boiler,
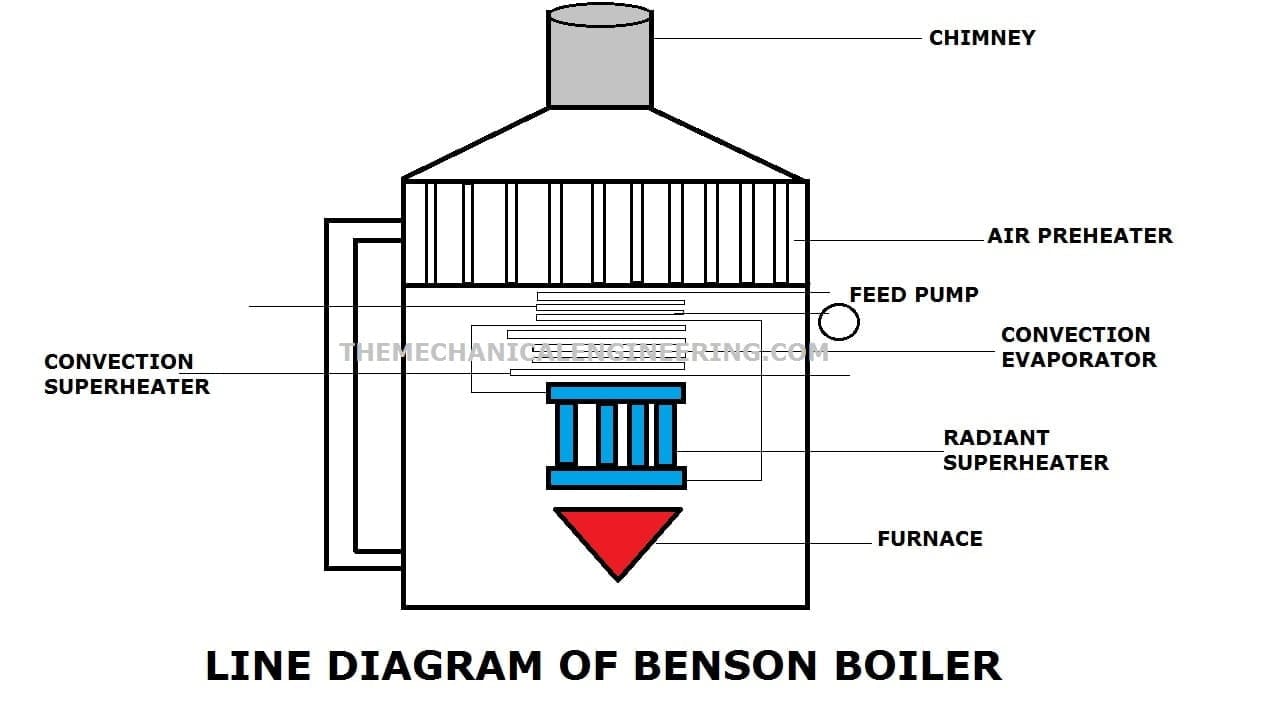
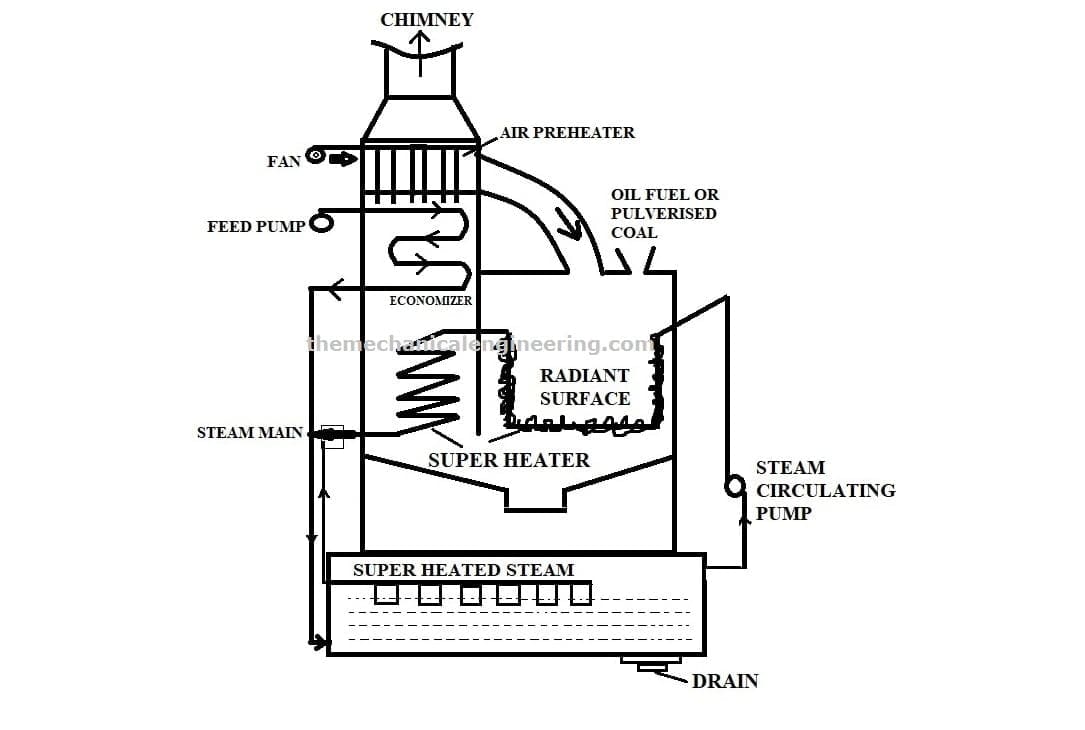
Benson Boiler Parts or Construction:
Benson Boiler consists of the following Main Parts:
- Chamber
- Water Feed Pump
- Blower
- Furnace
- Economizer
- Air Preheater
- Radiant Superheater
- Convection Evaporator
- Convecting Superheater
- Throttle Valve
- Chimney
Benson Chamber:
Benson chamber is the outer parts of this boiler where all the other parts of this boiler are kept.
Water Feed Pump:
The work of water feed pump is to supply the water from the hot well to inside the boiler at a supercritical pressure of 225 bars.
Blower:
As in general we know that the work of a blower is to blow the air in a particular direction at a very high speed. The blower is connected with the air preheater and its working is the same. The blower blows air into the air preheater and the air preheater will heat the air.
Furnace:
The furnace of any boiler where fuel is burnt and here it has a maximum temperature. The flue gases are passed to the tube and other places from here only.
Economizer:
Economizers’ contribution is to increase the efficiency of any boiler. Here The water which is entered through the feed pump now passes through the economizer and This heats the water at a certain temperature with the help of combustion gases inside it.
Air Preheater:
The name itself indicates “preheat” which means the air is being heated before entering the boiler so we can say it also helps to increase the overall efficiency of the boiler.
Radiant Superheater:
Again radiant superheater helps to heat the water with radiation produced by burnt fuel, therefore, the temperature of the water rises to supercritical temperature and It is connected to the convective superheater and that is finally connected to the turbine.
Convection Evaporator:
In this evaporator, the water evaporates completely. In other words, the Convection evaporator evaporates the superheated water and converts them into steam. The convection process of heat transfer is used to transfer heat from the flue gases to water.
Convection Super heater:
The conviction superheater work is to superheat the steam to the desired temperature which is at 650 degrees Celsius.
Chimney:
The burnt gases which are now became smokes will be released by the chimney to the atmosphere.
Throttle valve:
It is a type of valve that works is to stores and control the flowing passages of steam.
Now we will study Benson Boiler working in detail,
Benson Boiler Working Principle:
The water feed pump sends the water into the economizer (here it increases the pressure of the water to the supercritical pressure). Now In the economizer, the water is preheated using combustion gases that help to increase the efficiency of the boiler.
Now the water from From economizer which is already heated at a certain temperature passes to the radiant superheater for further heating.
In the radiant super heater, the water is heated using the radiant heat transfer method.
Here the heat is received from the combustion chamber. Now the water will partially convert into steam and some amount also remains in the liquid form which is not converted into steam completely. So from here, it is further sent to the superheater for converting completely into steam.
In the convective superheater, The remaining water or partial steam is fully converted into vapor or steam and this superheated steam will go to the prime mover for the rotation of the turbine. Further, it is being used for power generation.
Benson Boiler Video in English:
Now we will study Advantages, Disadvantages, and Applications.
Benson Boiler Advantages:
The main advantages of Benson Boiler are:
- The Benson boiler cost is cheaper as there is no presence of a steam drum.
- It produces higher power pressure, so there is no pressure limit to attain supercritical pressure.
- The attaining of high pressure avoids the bubble collection in the tubes and increases the maximum heat rate. The presence of bubbles in the boiler causes lower efficiency power of the boiler.
- It’s lightweight than any other boilers.
- The boiler is efficient in running, starts in 15mins due to welded joints.
- Boiler transportation is simple and easy.
- The boiler is efficient and achieves a thermal efficiency of up to 90%.
- The boiler consists of small tubes with lesser diameters. It helps in creating negligible situations prone to explosion hazard risks.
Benson Boiler Disadvantages:
The disadvantages of Benson Boiler is:
- An overheating of the tubes can cause insufficient water supply.
- Since the storage capacity is small, it requires close coordination between steam, feedwater, and feed inlet.
- The evaporation process gets accompanied by the salts and solid in tubes if the water present is impure. It can cause severe damage and blockage to the boiler tubes.
- You may face some problems and difficulties controlling the boiler for variable loads.
- Its movements require continuous inspection in every duration to prevent an explosion. It happens due to the presence of supercritical pressure.
Benson Boiler Application:
The main application of Benson Boiler is:
- The high-pressure supercritical boiler is used in various industry, to produce steam and generate electrical power.
- The boiler’s average optimum pressure is 250 bar with a temperature of 50 degrees celsius and a capacity to produce about 135 tons/ hour.
Benson Boiler Features:
The following features of the Benson boiler:
- The weight of this boiler is comparatively low than the other boilers. It makes it cheap and reduces production costs.
- The boiler consists of a lack of drums. It makes the parts transfer easy.
- They are transported easily without the need to preassemble them.
Internal Resources:
- Fire Tube boiler
- Lancashire Boiler
- Locomotive Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
- Cochran Boiler
- Water Tube Boiler
- Difference between Fire Tube and Water Tube Boiler
External Resources:
- https://onlinecourses.nptel.ac.in/noc22_me07/preview
- https://dte.karnataka.gov.in/Institutes/gptraichur/FileHandler/17-e97b863d-c699-45dc-a81a-73f88ec54d8f.pdf
Conclusion:
Here we finally studied the Benson Boiler and its sub-topic Definitions, Parts, Working principles, Advantages, Disadvantages, Applications in detail. I have also written many articles on boiler and types if you are interested then please do check out and Share it with your friends.
And let me know your doubt bout this topic in the comment section. And If there are any improvements needed do let me know or any further recommendations in the comment section.




Discussion about this post