Here we are going to study the Definition, Types In Detail, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application of Water Tube Boiler.
Note: At the end of every article you can easily download whole article in PDF format.
So let’s start with the definition first,
Water Tube Boiler Definition:
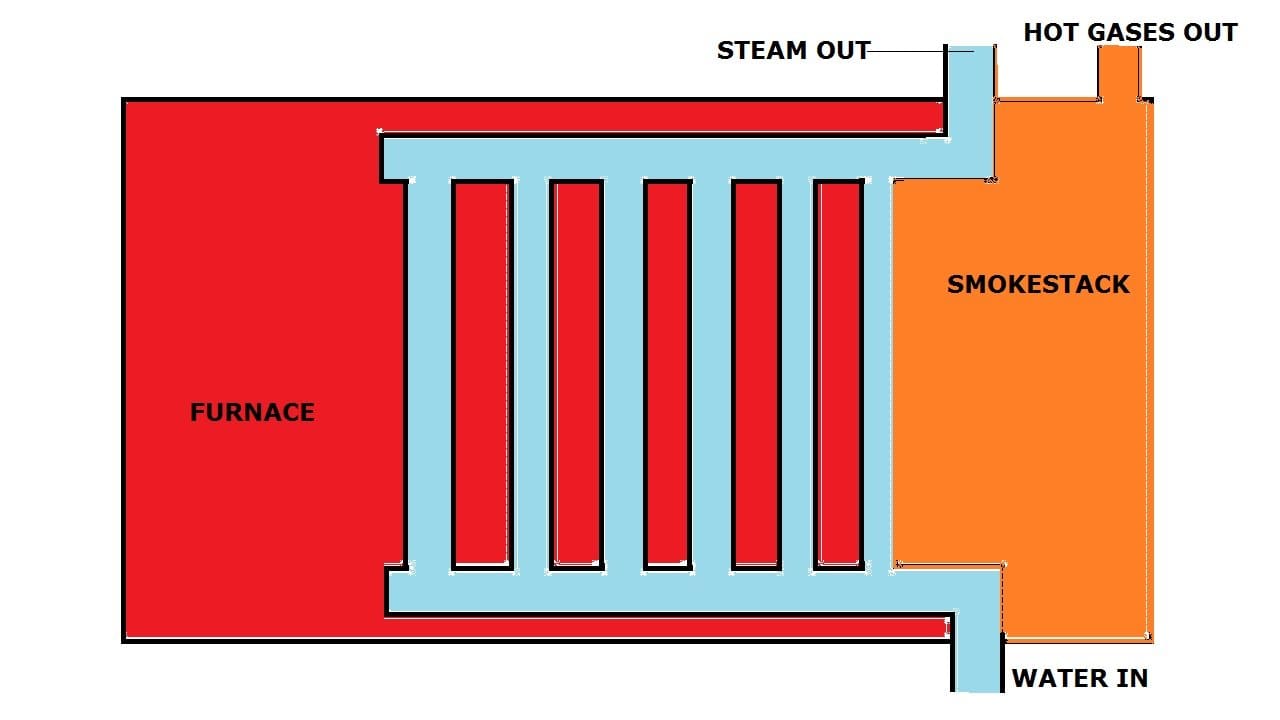
Water Tube Boiler is the type of boiler in which the water is flowing inside the tube and hot gases which are produced by the combustion chamber have surrounded the tube and the further boiler is used for the generation of electricity.
Now the types of water boiler in detail,
Water Tube Boiler Types:
The following water tube boiler are:
- Benson Boiler
- Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
- Loeffler boiler and
- Yarrow boiler.
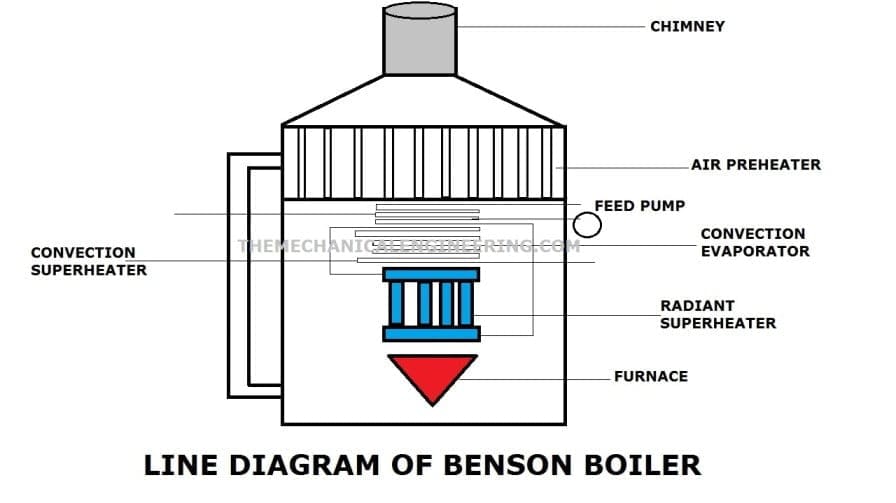
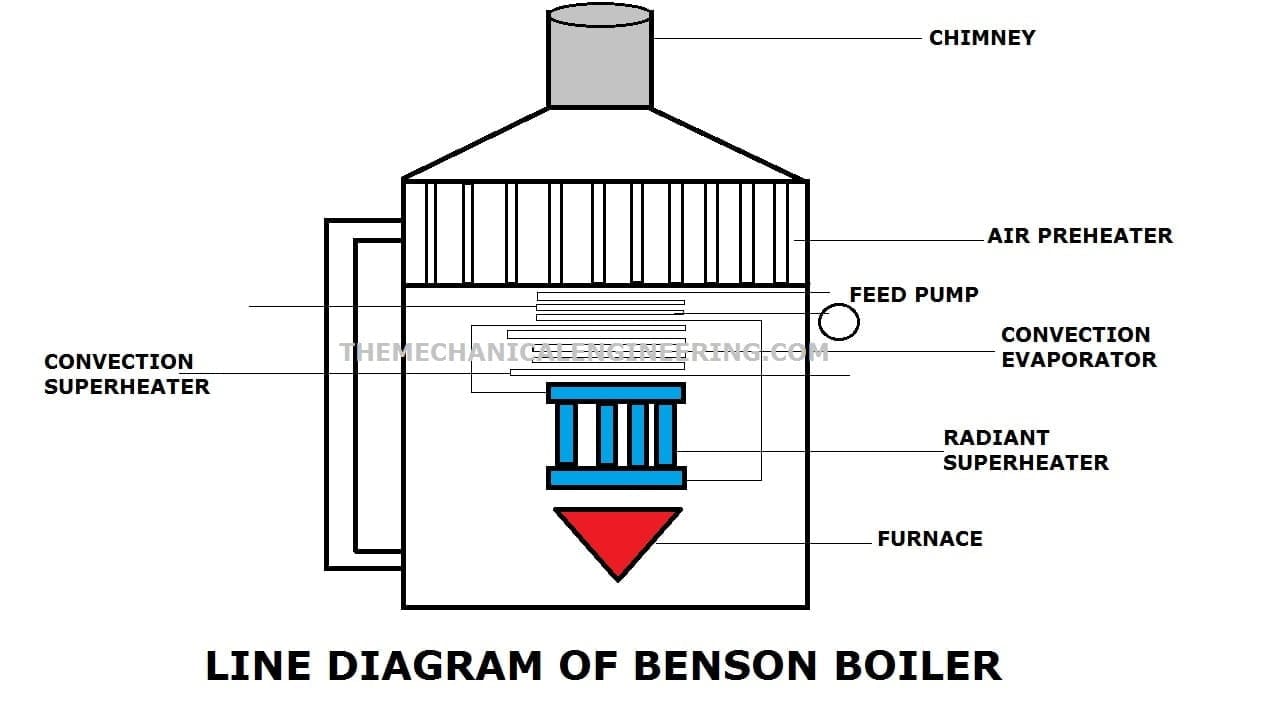
1. Benson Boiler:
The Benson boiler is developed in the year 1922 by Mark Benson. This is a high-pressure water tube boiler.
This is a supercritical boiler (Supercritical means There is no bubble formed). This Benson boiler also works on critical pressure that means high pressure and there is no drum used here.
This boiler works above the critical pressure which are 225 bar and can work up to 350 bar pressure and the water which is entered into the system is directly converted into steam because of Latent Heat. The efficiency of the Benson boiler is good.
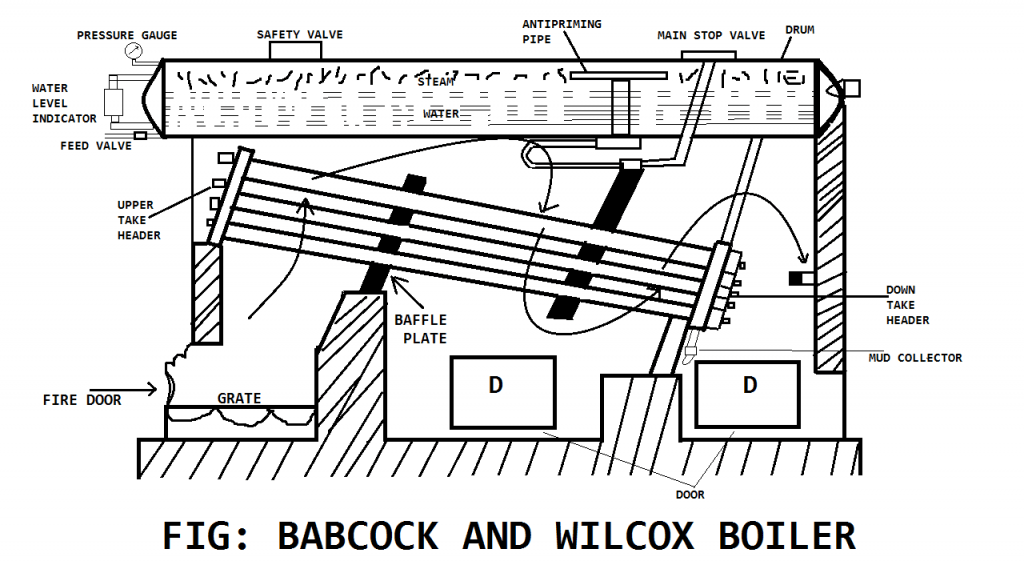
2. Babcock and Wilcox Boiler:
The Babcock and Wilcox boiler is invented by George Herman Babcock and Stephen Wilcox in the year 1967. This is a high-pressure and multi-tubular and externally fired water boiler.
The name kept of this boiler because of the inventor’s name. This boiler is also producing a high rate of steam almost more than 5000 kg per hour. The overall efficiency of this boiler is good.
The use of Babcock and Wilcox boiler is to produce high steam for use in industry.
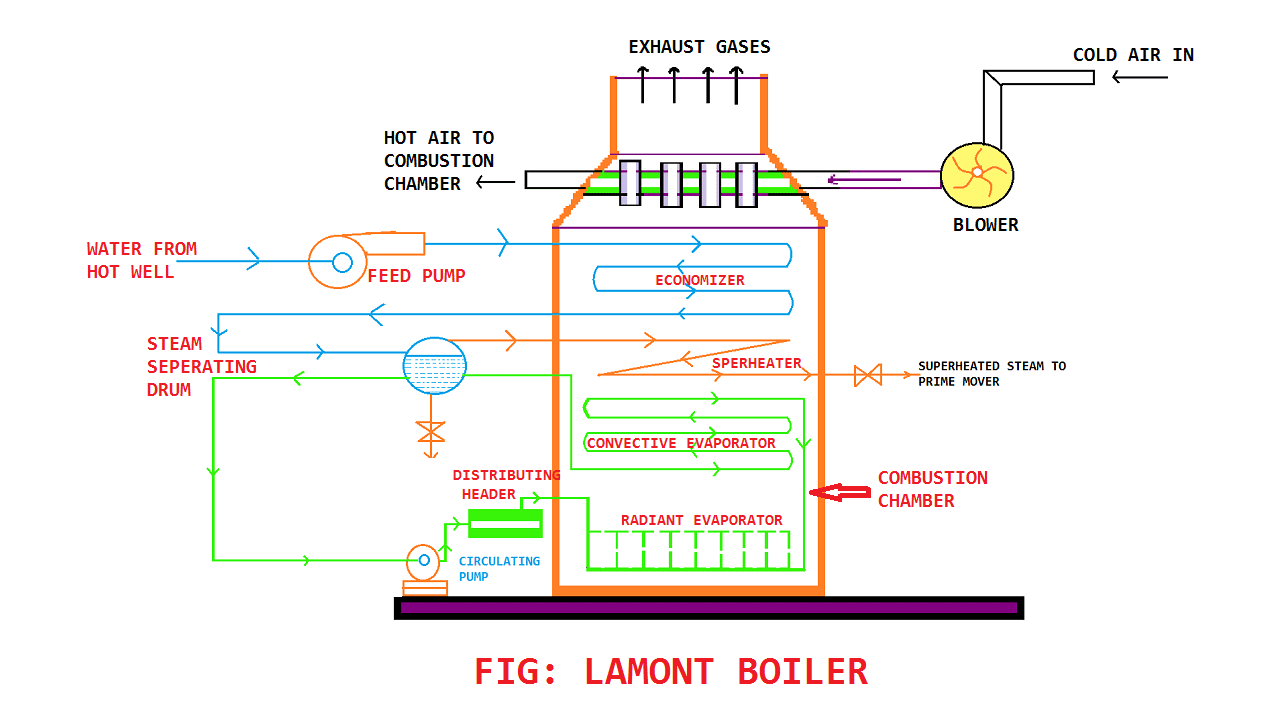
3. Lamont Boiler:
It is developed in 1925 by Walter Douglas La-Mont. The name of this boiler also kept because of the inventor’s name.
It is an internally fired furnace boiler. The Lamont Boiler is also a water boiler and working pressure is above 150 bar. So as you can see it works above 150 bar, therefore the production of steam is high 5000 kg per hour.
The Lamont boiler design is flexible. In Lamont Boiler the circulating pump is used to circulate the water into the furnace. The main advantage of this boiler is that it is very easy to start (No problem with the starting).
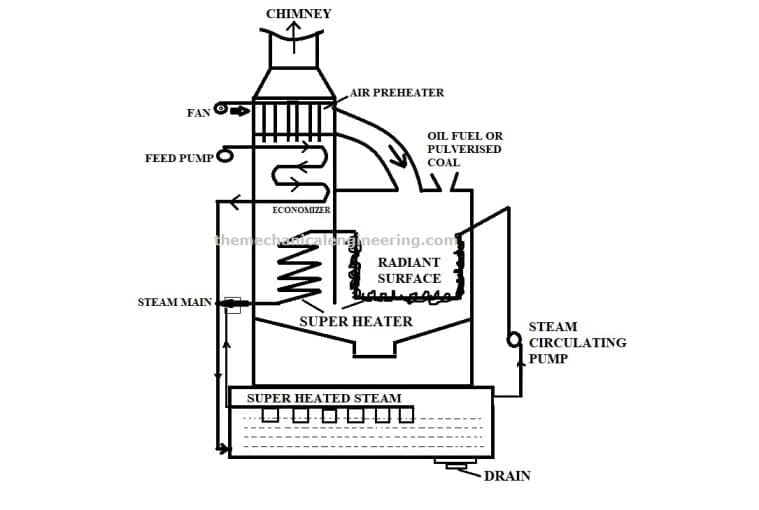
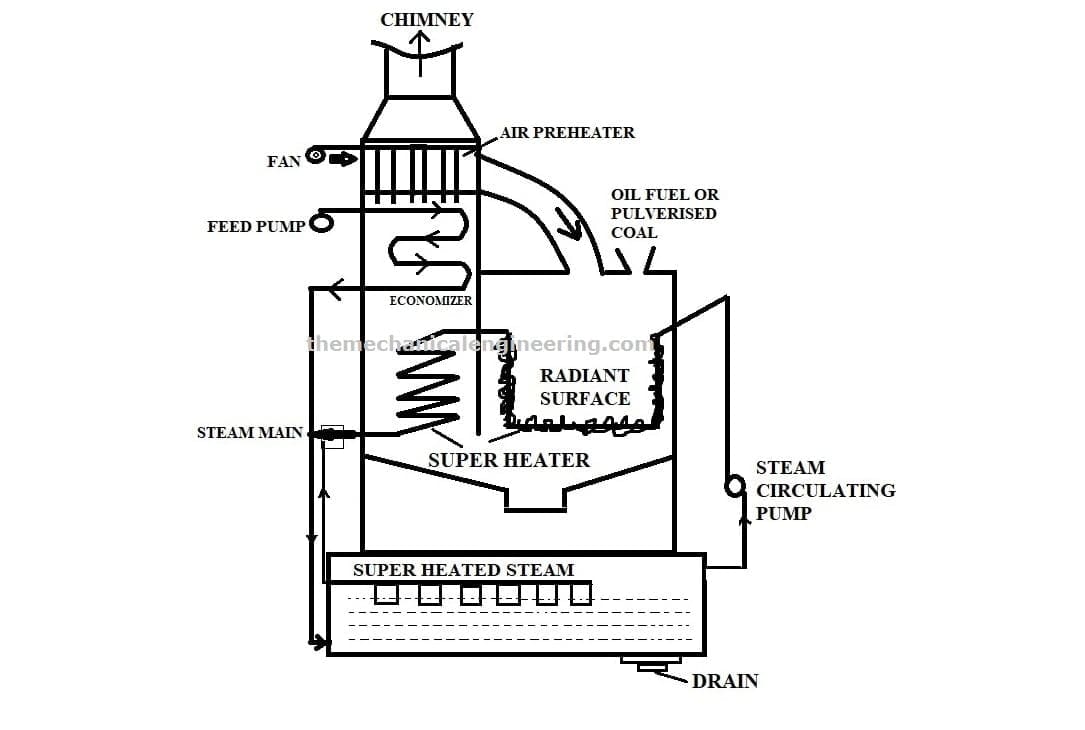
4. Loeffler boiler:
It is the extent of Lamont Boiler. The Loeffler boiler is also a water tube and the working pressure is around 100 bar which is high pressure. Normally you can not see a fire tube boiler works under this pressure.
The Loeffler boiler produces high steam at a rate of 90 to 100 tonnes per hour. The major parts of the Loeffler boiler are Economiser, Steam circulating pump or centrifugal pump, Radiant superheater, Evaporating drum, Convection superheater, and Mixing nozzle.
The major disadvantage of Loffler boiler bubble formation is that reduces the heat transfer rate.
It also has overheating problems due to salt deposits. To overcome these problems, we do preventing the flow of water in the tubes.
5. Yarrow boiler:
Yarrow Boiler is another type of water boiler. It was developed by Yarrow & Co in London. The Loeffler boiler is widely used on ships, particularly warships.
For Boiler repair, you can visit Unitary Engineering from Bristol, best for boiler repairs [Sponsored Link].
Water Tube Boiler Advantages:
The following advantages of water tube boiler are:
- The heating surface can be achieved much by using more numbers water tubes.
- The movement of water is much faster than the fire tube boiler because of conventional flow, hence the rate of heat transfer is high which results in higher efficiency.
- Water boiler: Overall efficiency is up to 90%.
- In the water boiler: The maximum working pressure is 250 bar or you can say 140 kg/cm2.
- The rate of steam generation is high.
- Less floor area required for the given output.
- The Steam quality is better comparatively fire tube boiler.
- A Water boiler can be used in a Large Power Plant.
- Load fluctuation or Fluctuation of load can be easily handed.
- Water Circulation direction is specified.
Water Tube Boiler Disadvantages:
There are some disadvantages of Water boiler:
- The Design is complex in the water boiler.
- For operation, a skilled operator is required.
- The maintenance cost is high.
- The cost of a water boiler is high for the same power output.
- As we studied it is used in large power plants therefore it is uneconomical to use in small industries.
- Feedwater treatment is very essential because small-scale deposits inside the tube cause overheating and bursting.
Water Tube Boiler Application:
The main application of the water-tube boiler is that it is being used at several places Such as paper mill, Sugar mill, a textile factory, Central heating enterprise, Chemical industry, A power plant, and so on.
Internal Resources:
- Babcock and Wilcox Boiler
- Fire Tube boiler
- Benson Boiler
- Locomotive Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
- Cochran Boiler
- Difference between Fire Tube and Water Tube Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
External Links:
- Boiler: Wikipedia
You can also read the Fire-tube boiler in detail I have written that article too. If you have any doubts regarding this article feel free to contact us. And if you like the article please do not forget to share it on social.




Discussion about this post