The turbojet engine is another example of a Gas turbine engine. The working fluid is air or gas. Turbojet engine works on the principle of Newton’s third law of motion How? Just scroll down I have added and explained all the terms.
In the early 1930s there are two engineers from America (Frank Whittle) and Germany (Hans von Ohain) developed the concept independently into practical engines.
In today’s article, we will study Definition, Parts and their function, Working principles with images, Advantages, Disadvantages, and Application of Turbojet Engine in detail.
Turbojet engine Definition:
The turbojet engine is a closed cycle gas turbine engine that is used in aircraft and other industries by the burning of fuel and the use of several components like the compressor, Turbine, propeller, and more.
Open cycle Gas Turbine:
Here the working fluid is air or gas. It is an internal combustion engine. It involves four processes:
- Suction of air
- Compression and Combustion of air
- Expansion and
- Exhaust.
Here You can check Information on Open Cycle Gas Turbine
Let us know four processes in brief,
- Suction: The suction process intake the air into the system.
- Compression: It compresses the air and so pressure and temperature are increased.
- Combustion: Here the compressed air and fuel together burns
- Expansion and Exhaust: After burns, it makes a charge and the remaining again cycle starts.
There are three types of Gas turbine engines: Turbojet, Turboprop, and Turbofan.
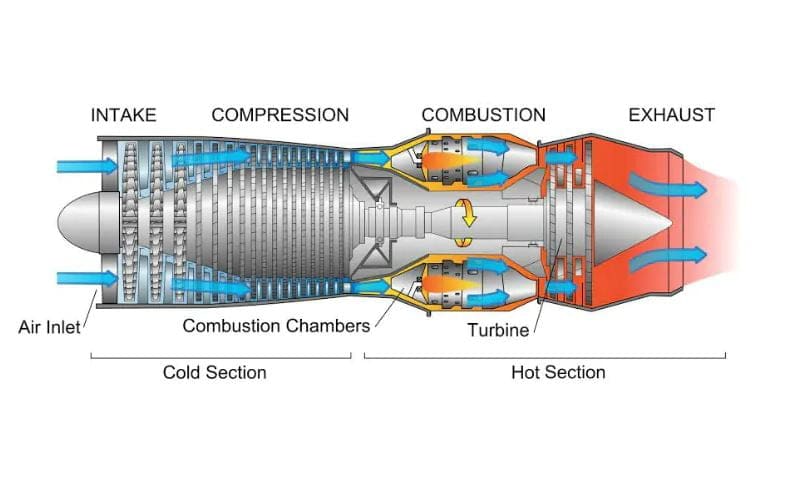
Turbojet Parts or Construction:
Turbojet Engine consists of following main parts:
- Diffuser
- Compressor
- Pump
- Fuel Injector
- Combustion chamber
- Shafts
- Turbine
- Nozzle
Let’s know one by one,
Diffuser:
Air is supplied here. The area is such a way that the kinetic energy of air is reduced and pressure energy starts increasing.
The air molecules get compressed. It is an isentropic (Entropy remain constant) component. In simple Diffuser main work is to diffuse the air.
Compressor:
The main function of the compressor is the compress the air that comes from the diffuser hence it increases the temperature and pressure of the air.
Kinetic energy gets reduced. It is an isentropic (Entropy remain constant) component.
Pump:
The pump gets the compressed air and air the lean amount of fuel is provided for a mixture of air and fuel.
Fuel Injector:
Its main works are to ignite the mixture of air and fuel.
Combustion chamber:
In the combustion chamber, the complete burning of air and fuel takes place at constant pressure heat supplied.
Shafts:
The shaft is connected between the compressor and the turbine.
Turbine:
Here the burned charges come with high-pressure energy and it rotates the turbine blades and also compressor gets rotates. It is an isentropic (Entropy remain constant) component.
Nozzle:
The nozzle is like sending the exhaust gas to the atmosphere. Here the charge coming the pressure energy is reduced and Kinetic energy is increased and thus thrust created more.
Which is useful for sending the jet in the forward direction.
Newton’s third law of motion: For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. At the end of the nozzle, the power supplied for creating thrust to move the engine forward.
Now working,
Turbojet Engine Working:
The working of Turbojet Engine, Air is first supplied into the diffuser. The diffuser work is to diffuse the air hence the molecular of the air get together.
Now from the diffuser, air comes into the compressor. The compressor compresses the air hence the pressure energy is increased.
Now from the compressor it sends to the combustion chamber where a pump is fitted and with the help of the pump there is a small hole or you can say the fuel injector is fitted. The fuel is supplied here with very less amount (lean mixture the ratio of air to fuel is 50:1).
In the combustion chamber, the mixture of air and fuel gets completely burned. The burning gas has high-pressure energy which is directly send to the turbine.
Here the turbine blades rotate and shafts are connected between the compressor and the turbine. The charges of pressure energy are reduced and kinetic energy increased.
The turbine also works s for a rotating compressor for getting much air from outside.
Then from here it directly comes to the nozzle here with the thrust of the charge is created.
Thrust moves the engine into the perpendicular direction and From nozzle, the exhaust gases are released.
Note: after the turbine process it works Newton’s third law of motion. It creates thrust and moves the engine forward and releases the exhaust gases from the nozzle.
Advantages of Turbojet Engine:
The following main advantages of Turbojet Engine are:
- The low-grade fuel type can be used.
- The chances of parts wear and tear are very less.
- Turbojet engines produced more thrust comparatively propeller engines.
- The operating temperature can be high which means it can operate at a high temperature.
- The speed operation is very high.
- Simple in construction.
- The weight to power ratio is very less in this system.
- The maintenance cost is low.
- This type of engine does not have any unbalance force which causes a problem which is also a major advantage of the turbojet engine.
- It can be highly efficient for supersonic aircraft.
It has some disadvantages’ too so let’s discuss,
Disadvantages of Turbojet Engine:
The following main disadvantages of Turbojet Engine are:
- The efficiency reduces at a lower speed of the system.
- It produces noise. So the system is like a noisy system.
- Low thrust is available at takeoff and climb.
Application of Turbojet Engine:
The following main application of turbojet engine:
- This type of system used in the aircraft industry.
- It also used in the Automobile sector:
- In vehicles: Motorcycle, racing cars
- It also used in a water jet engine.
- Used in Military aircraft and much more.
Difference Between Turbojet and Turbofan engine:
| Turbojet | Turbofan |
| The power produce from the turbine is used to drive the compressors in turbojet engine but | Here the power produce from the turbine is used to drive the propeller and compressor. |
| The frontal area is less comparatively. | The frontal area is more because of use of centrifugal compressor. |
| In this lower weight per unit thrust. | Turbofan has high weight per unit thrust. |
| It has low propulsive efficiency. But | Turbofan has high propulsive efficiency. |
| Take of thrust is low comparatively Turbofan. | Take of thrust is more here. |
| The gear reduction is not needed. | Here reduction gear is needed. |
| Low space as compared to a Turbofan engine. | More space is required. |
This is all about the Turbojet engine from my side. Let me know what other topics you are looking for?
Here you can check all the articles on Thermodynamics.
Here you can download PDF.



Discussion about this post