Any thermodynamic system can be identified at any time by certain observable and measurable parameters like pressure, volume, temperature, mass, density, physical composition, etc. These parameters are known as the properties of a thermodynamic system.
Thermodynamic state: It is described as the condition of a system which is denoted by parameters like volume, pressure, temperature, etc.
For example: Let’s take an example of a piston-cylinder arrangement. The gas inside the cylinder is at a temperature of T1, pressure P1, and volume V1. We will call this state 1 (initial state).
When we push the piston downwards, the gas will get compressed so the temperature, pressure, and volume will change let’s say to T2, P2, and V2. This will be state 2.
Thus we can see that the parameters (that is temperature, volume, and pressure) in both states are different. These systems are uniquely defined and this helps us to distinguish one system from another.
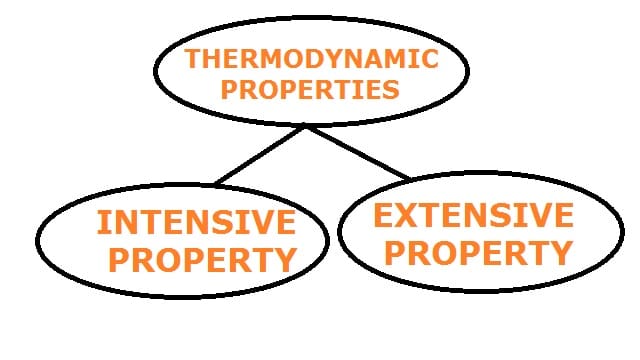
Classification of Thermodynamic Properties:
Thermodynamic properties can be classified into two categories as follows:
- Intensive property and
- Extensive property
Intensive property:
Intensive properties are those properties that do not depend on the mass of the system.
Example: Temperature, Viscosity, etc.
Consider a room where the pressure is p. If the room is divided into a number of parts, we find that the pressure at any point is the same and it is equal to the original pressure p though the mass in each part has changed. It shows that the intensive property has a definite value and it is independent of mass, it represents a point function
Extensive property:
The property of the system which depends upon the size and mass of the system is called an extensive property.
Example: length, volume, density.
For example, density equals mass per unit volume. Here, density is dependent on mass hence it can be termed as an extensive property.
Now we will study Path function and Point function in brief,
Point function:
Point functions are those functions whose values are dependent on the initial and final value of the system and independent of the path taken.
For example; Consider an 8-story building. You are standing on the ground and your potential energy is zero. You want to get to the top of the building so either take the stairs, lift, or climb your way up to the top of the building.
Either way, you are reaching the same spot, and your potential energy upon reaching the top is going to be mgh in every case.
So, here we see that irrespective of whichever route you are taking, or whichever path you are taking to go from initial to the final position, you are ultimately gaining a potential energy equivalent to mgh Common examples of point function are pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, etc.
Path function:
Path functions are those functions whose values are not dependent on the initial and final value of the system but on the path taken.
Now consider the same situation in the example of point function. There is an 8-story building and you want to reach the top of the building. You can either use the stairs or the lift.
In the case of stairs, you climb 8 floors and you are utilizing a lot of energy. In the case of stairs, you are not moving and within seconds you have reached the top.
Hence, in both cases, work done by your body is different. So, if we talk about the work done here, taking the stairs required more energy than taking the lift. Hence, we can say that energy that is being used to reach the top of the work which is being done by your body depends on the path you are taking.
Internal Resources for You:
- Thermodynamic System
- Fire Tube boiler
- Water Tube Boiler
- Benson Boiler
- Locomotive Boiler
- Lamont Boiler
- Cochran Boiler
Reference [External Links]:
- https://web.iit.edu/sites/web/files/departments/academic-affairs/academic-resource-center/pdfs/Thermodynamic_Properties.pdf
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/chemistry/thermodynamic-property
- https://nptel.ac.in/content/storage2/courses/112103016/module1/lec1/4.html
Conclusion:
Here we finally studied the Thermodynamic properties in detail. I have also written many articles on Thermodynamic subjects if you are interested then please do check out and share them with your friends.
And let me know your doubt bout this topic in the comment section. And If there are any improvements needed do let me know or any further recommendations in the comment section.




Discussion about this post