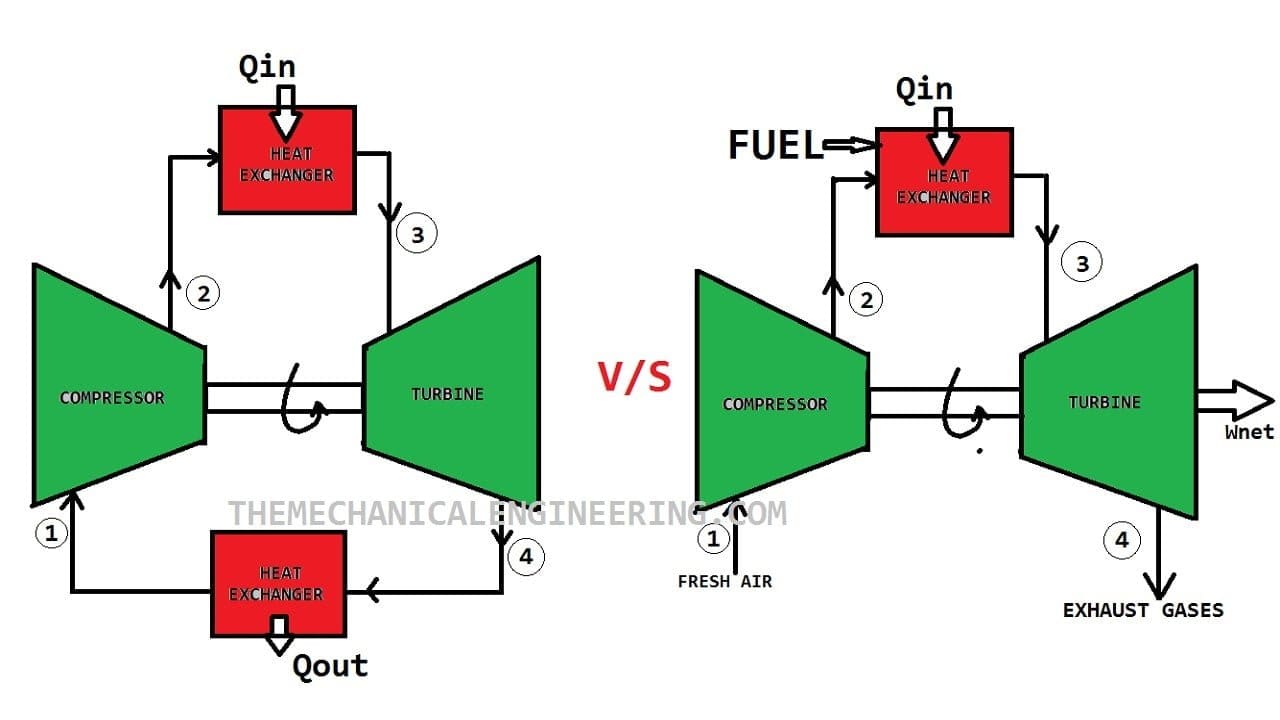
The main differences between the Closed cycle Gas turbines and Open cycle gas Turbines are, The working fluid can be used continuously in closed-cycle gas turbines and In the open cycle, the working fluid once used can not be used again and again.
Today we will study the difference between the closed cycle Gas turbine and open cycle gas Turbine and at the end of the article, you can download a PDF of the whole article.

Difference between the Closed cycle and Open cycle Gas Turbine:
| Sl No. | Closed Cycle Gas Turbine | Open Cycle Gas Turbine |
| 1. | The pressure is higher here. | Here the pressure is lower. |
| 2. | The output closed cycle gas turbine produce is more. | The output open cycle gas turbine produce is less. |
| 3. | The plant size is larger. | The plant size is not as larger as comparatively. |
| 4. | The working fluid can be used continuously. | But here the working fluid can not be used continuously. |
| 5. | Here the thermal efficiency is more. | Thermal efficiency is less. |
| 6. | This is a more costly comparatively open cycle gas turbine. | It is less costly. |
| 7. | Air filtration is not required here. | Here it is required. If not do then it may cause severe problems. |
| 8. | A large amount of water cooling is required. | here there is no requirement for water cooling because of the open cycle gas turbine. |
| 9. | Per KW the more mass installation is required. | Per KW the less mass installation is required. |
| 10. | A maintenance cost is more. | Less maintenance cost of this type of turbine |
| 11. | The closed-cycle gas turbine is best suited for the stationary installation and marine uses because the air from the turbine is cooled by the circulating water. | Open cycle gas turbine is best suited for the moving vehicle because the air can be directly discharged into the atmosphere. |
| 12. | Here the parts load efficiency is better. | Part-load efficiency is less comparatively. |
| 13. | The heat is transferred indirectly through a heat exchanger. | Open cycle gas turbine directs heat supply. The heat is generated directly in the combustion chamber. |
| 14. | The blade life is longer. | The blade life is shorter in open cycle gas turbine. |
This is all about differences between the closed cycle Gas turbines and open-cycle gas Turbines. Here you can check all the articles on Thermodynamics.
I have also written on Turbojet Engine you can check that too.



Discussion about this post